1,3-Dichlorotetrafluoroacetone 1,3-Dichlorotetrafluoroacetone
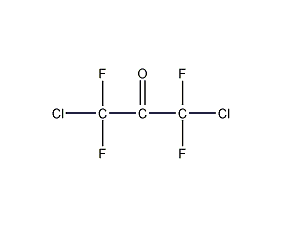

Structural formula
| Business number | 03KS |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C3Cl2F4O |
| Molecular weight | 198.93 |
| label |
dioxin, Dichlorotetrafluoroacetone, sym-Dichlorotetrafluoroacetone hydrates, Perchlorofiuoroacetone, (CClF2)2CO, Multifunctional solvents, aliphatic compounds |
Numbering system
CAS number:127-21-9
MDL number:None
EINECS number:None
RTECS number:None
BRN number:None
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless liquid, highly hygroscopic.
2. Boiling point (ºC, 101.3kPa): 45.2
3. Boiling point (ºC, +2.5H2O): 106
4. Relative density (g /mL, 25/4ºC): 1.52
5. Melting point (ºC, +2.5H2O): -8
6. Melting point (ºC, +10H2O, unstable): 24
7. Refractive index (20ºC): 1.3290
8. Heat of evaporation (KJ/kg, 25ºC): 101.2
9. Solubility: natural Excellent solvent for polymer compounds.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: Rat oral LD50: 61mg/kg; Rat inhalation LC50: 4800mg/m3
Mouse inhalation LC50: 4500mg/m3; Mouse intravenous injection LD50: 180mg/kg
Rabbit skin LD50: 91mg/kg
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 26.26
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 119.8
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 261.6
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 22.7
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 10.41
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 2.7
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 5
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 17.1
7. Number of heavy atoms: 10
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 141
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Chemical properties: Symmetry – Dichlorotetrafluoroacetone, like hexafluoroacetone, reacts with water exothermically. Generate various hydrates. It decomposes into carbon monoxide and chlorodifluoroacetic acid under the action of alkali.
Storage method
None
Synthesis method
Hydrates of symmetric-dichlorotetrafluoroacetone such as (CClF2)2CO·2.5H2O are stable liquids that can be distilled and are an excellent solvent. However, (CClF2)2CO·10H2O is an unstable liquid and decomposes into stable hydrates and water during distillation.
Purpose
Hydrate is an excellent solvent for synthetic and natural polymer compounds such as acetal resin, polyamide, polyacrylonitrile, polyvinyl alcohol, and polyester.
