1,6-Hexanediamine 1,6-Diaminohexane
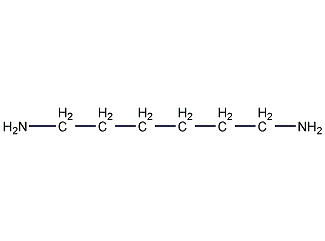
Structural formula
| Business number | 03HR |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H16N2 |
| Molecular weight | 116.21 |
| label |
1,6-diaminohexane, hexamethylenediamine, hexamethylenediamine, hexylmethylenediamine, hexanediamine, Hexanediamine, had methylene diamine, hexamethylene diamine, hexamethylene diamine, 1,6-diamino-hexane, 1,6-hexane diamine, Hardener, Rubber vulcanization accelerator |
Numbering system
CAS number:124-09-4
MDL number:MFCD00008243
EINECS number:204-679-6
RTECS number:MO1180000
BRN number:1098307
PubChem number:24885120
Physical property data
1. Characteristics: colorless flaky crystals with ammonia smell. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): 42~45[2]
3. Boiling point (℃) :205[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.85[4]
5. Relative Vapor density (air=1): 4.01[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 2.00 (90℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): -4440[7]
8. Critical pressure (MPa): 3.29[8 ]
9. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.35[9]
10. Flash point (℃): 71 (OC )[10]
11. Explosion upper limit (%): 6.3[11]
12. Explosion lower limit (%) ): 0.7[12]
13. Solubility: Easily soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol, benzene and ether. [13]
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[14] LD50: 750mg/kg (rat oral); 1110mg/kg (rabbit dermal )
2. Irritation No data available
3. Subacute and chronic toxicity[15] When rats were exposed to the drug at a concentration of 7 mg/m3 for 3 and a half months, histological changes were seen in the blood vessels of the lungs, liver, and kidneys. Repeated administration of hexamethylenediamine to guinea pigs caused anemia, weight loss, and microscopic examination of kidney and liver degeneration and mild myocardial degeneration.
4. Others[16] The lowest oral toxic dose in rats (TDLo): 3g/kg (pregnant 6 to 16 days of administration), causing embryotoxicity and abnormal development of the liver system. The lowest oral toxic dose in rats (TDLo): 1840mg/kg (administered on 6th to 16th day of pregnancy), causing abnormal development of the genitourinary system.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[17] LC50: 14mg/L (96h) (fish)
<strong�This process is similar to the hydrogenation of adiponitrile. Butadiene method (1) Cyanide chloride method: 1,3-butadiene and chlorine gas are chlorinated in a chlorination reactor at 200-250°C to generate 1,4-dichloro-2-butene (accounting for 66%) and 3,4-dichloro-1-butene (accounting for 33%). Dichlorobutene compound undergoes an isomerization reaction in the presence of calcium carbonate at 100-150°C with sodium hydroxide or ammonium as a catalyst at 50-100°C to generate 1,4-dicyano-1 -Butene. 1,4-dicyano-1-butene uses palladium as a catalyst and performs gas phase hydrogenation under normal pressure and 250°C to prepare ethanedinitrile. Ethylenediamine is obtained by catalytic hydrogenation of ethylene dinitrile.
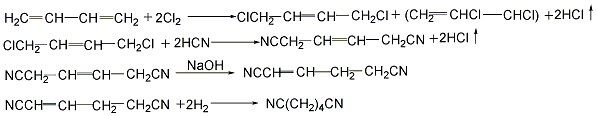
![]()
(2) Direct hydrocyanation method: 1,3-butanedi Enene reacts with hydrocyanic acid in a liquid phase in the presence of a catalyst, and the reaction temperature is controlled at 100°C to generate an isomer mixture of pentenenitrile. After the mixture is separated and the isomers are isomerized into linear pentenenitrile, it is then added with hydrocyanic acid to form oxalonitrile, which is then catalytically hydrogenated to obtain ethylenediamine.
Purpose
1. Most of this product is used to synthesize nylon 66 and 610 resins. It is also used to synthesize polyurethane resin, ion exchange resin and hexamethylene diisocyanate, and is used as a curing agent for urea-formaldehyde resin, epoxy resin, etc., organic Cross-linking agents, etc. are also used as stabilizers and bleaching agents in the textile and paper industries, corrosion inhibitors for aluminum alloys, and chloroprene rubber emulsifiers. Hexamethylenediamine and hydrochloric acid form a salt below 28°C to obtain 1,6-hexamethylenediamine hydrochloride (6055-52-3), which can be used to produce the fungicide chlorhexidine acetate. Hexamethylenediamine also has some applications in the production of adhesives, aviation coatings and rubber vulcanization accelerators.
2. This product is used as a curing agent for urea-formaldehyde resin and epoxy resin. The dosage is 15 parts. The curing condition is 25℃ for 1 day, which can improve the flexibility of the product. This product is used to prepare nylon 66, nylon 610, adhesives and coatings, etc. Also used as rubber vulcanization accelerator.
3. Used in organic synthesis, production of polymers (such as nylon 66), and also used as epoxy resin curing agent and chemical reagent. [26]
