2-methylpyridine 2-Methylpyridine
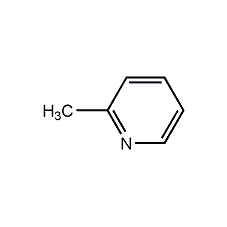

Structural formula
| Business number | 02YL |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H7N |
| Molecular weight | 93 |
| label |
2-Picolin, α-methylazobenzene, α-Methylpyridine, α-picolin, 2-picoline, α-Colloidin, α-Pyroline, α-Picoline, 2-Methylpyridine, 2-Picoline, α-Methylpyridine, 2-Methyl-Pyridine, Heterocyclic compounds |
Numbering system
CAS number:109-06-8
MDL number:MFCD00006332
EINECS number:203-643-7
RTECS number:TJ4900000
BRN number:104581
PubChem number:24887349
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid with special smell. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -70[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 128~129[3]
4. Relative density (water=1): 0.95[4]
5. Relative vapor density (air = 1): 3.2[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 1.2 (20℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -3414.7[7]
8. Critical pressure (MPa): 4.6[ 8]
9. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.11[9]
10. Flash point (℃): 39 ( OC)[10]
11. Ignition temperature (℃): 538[11]
12. Explosion upper limit (%): 8.6[12]
13. Lower explosion limit (%): 1.4[13]
14. Solubility: miscible with water and soluble in most organic solvents. [14]
15. Viscosity (mPa·s): 0.805
16. Flash point (ºC, closed): 27
17. Flash point (ºC, opening): 29
18. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol): 42.94
19. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol): 9.82
20. Heat of formation (KJ/mol, liquid): 58.99
21. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol, 25ºC): 3420
22. Specific heat capacity ( KJ/(kg·K), 25ºC, constant pressure): 1.70
23. Conductivity (S/m, 25ºC): 5.5×10-7
24. Volume expansion coefficient (K-1, 20ºC): 0.000992
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: Rat oral LD50: 790mg/kg; Rat inhalation LCLo: 4000ppm/4H; Rat intraperitoneal LD50: 200mg/kg; Mouse oral LD50: 674mg/kg; Mouse Inhalation LC50: 9mg/m3; Mouse abdominal LD50: 529mg/kg; Mouse skin contact LD50: 410μL/kg; Guinea pig oral LD50: 900mg/kg;
2. Other multiple dose toxicity: Rat oral TDLo: 1072mg/kg/9W-I; Rat oral TDLo: 1810μg/kg/26W-I;
3. Mutagenicity : Sex chromosome loss and non-disjunction test of yeast cells: 7400ppm.
4. It is of low toxicity.The toxicological effects are the same as those of pyridine. Contact between liquid and skin can cause skin degeneration within a few minutes.
5. Acute toxicity[15] LD50: 790mg/kg (rat oral); 529mg/kg (orally for mice); 410mg/kg (for rabbits through skin)
6. Irritation[16]
Rabbit transdermal: 470mg, mild stimulation (open stimulation test).
Rabbit eye: 750μg, severe irritation.
Ecological data
1. This substance is slightly harmful to water.
2. Ecotoxicity[17] LC50: 897mg/L (96h) (fathead minnow, dynamic)
3. Biodegradability No information available
4. Non-biodegradability[18] In the air, when the concentration of hydroxyl radicals is 5.00×105/cm3, the degradation half-life is 15d (theoretical).
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 29.16
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 98.9
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 239.0
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 34.0
5. Polarizability: 11.56
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 12.9
7. Number of heavy atoms: 7
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 52.1
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Chemical properties: 2-methylpyridine, like pyridine, can form salts with inorganic acids or organic acids, and can form addition compounds with inorganic salts, alkyl halides, etc. During hydrogenation, α-methylpiperidine or pyridine is obtained depending on the conditions. The 2-methyl methyl group in 2-methylpyridine is highly reactive and generates pyridine-2-carboxylic acid (picolinic acid, C5H4NCO2H) when oxidized. In the presence of a dehydrating agent, it condenses with benzaldehyde to form benzylidene derivatives. Reacts with paraformaldehyde at 200°C to generate 2-(β-hydroxyethyl)pyridine.
2. Stability[19] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[20] Acids, acid chlorides, strong oxidants, chloroform
4. Conditions to avoid contact[21] Heating
5. Hazards of aggregation[22] No aggregation
Storage method
Storage Precautions[23] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 37°C. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, etc., and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
Both pyridine and methylpyridine were previously recovered from coal coking by-products, which are distributed in coke oven gas, crude benzene and tar. Generally, the boiling point of the pyridine hydrate transferred from the coal gas to the ammonium sulfate mother liquor is very low, between 95-97°C. In the recovered crude light pyridine base, 2-methylpyridine contains about 15%, which can be further distilled. 2-methylpyridine can be cut. With the expansion of the uses of pyridine and methylpyridine, the synthetic production of pyridine and methylpyridine continues to develop. At present, about 95% of pyridine and pyridine compounds abroad are produced by synthetic methods. The main synthesis methods include acetaldehyde method, acetylene method, acrylonitrile method, etc. Acetaldehyde method The reaction of acetaldehyde, formaldehyde and ammonia, the main products are 2-methylpyridine, 3-methylpyridine and 4-methylpyridine. Acetylene method: Acetylene and ammonia react, and the main products are 2-methylpyridine and 4-methylpyridine. Ethylene method reacts ethylene and ammonia, and the main products are 2-methylpyridine and 2-methyl-5-ethylpyridine. The acrylonitrile method reacts acrylonitrile with excess acetone, and the main product is 2-methylpyridine. In addition, the reaction between acrolein and ammonia mainly produces 3-methylpyridine.
Refining method: Usually, the azeotropic mixture formed by 2-methylpyridine, benzene and water is used for azeotropic distillation and dehydration. Barium oxide, calcium oxide, calcium hydride, lithium aluminum hydride, metallic sodium or type 5A molecular sieve can also be used for dehydration. In addition to separation by fractional distillation, isomers and homologues can also be removed by azeotropic distillation with fatty acids, phenol or water. Pyridine is removed by treatment with perchloric acid. In addition, it can also be refined by forming an addition product with zinc chloride or mercury chloride. For example, add 90 mL of 2-methylpyridine to a mixture of 168 g of zinc chloride, 42 mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid, and 200 mL of absolute ethanol. The addition product was filtered off and recrystallized twice with absolute ethanol. When the melting point reaches 118.5~119.5℃, add excess sodium hydroxide aqueous solution, perform steam distillation, and add solid sodium hydroxide to the distillate for layering. Separate the upper layer, dry it with granular sodium hydroxide, add barium oxide and let it stand for several days before fractionating.
Purpose
1. Used for the preparation of 2-vinylpyridine, nitrogen fertilizer synergist (N-Serve), long-acting sulfonamides, anti-silicosis drugs, livestock anthelmintics, poultry drugs, organophosphorus antidotes, and local anesthetics , laxatives, film sensitizer additives, dye intermediates and rubber accelerators, etc. In addition to being used as a solvent, it is also used as a raw material for medicines, dyes, pesticides, synthetic resins and fertilizer synergists.
2. Used to prepare dyes, resins, pesticides, veterinary drugs, rubber accelerators, film photosensitizer additives, etc. In medicine, it is used to prepare drugs such as sikani, chlorpheniramine, pralidoxime, and acetylcysteine.
3. Used in the synthesis of chemicals such as medicines, dyes, rubber, etc., and also used as solvents and experimental reagents. [24]
Purpose
1. Used for the preparation of 2-vinylpyridine, nitrogen fertilizer synergist (N-Serve), long-acting sulfonamides, anti-silicosis drugs, livestock anthelmintics, poultry drugs, organophosphorus antidotes, and local anesthetics , laxatives, film sensitizer additives, dye intermediates and rubber accelerators, etc. In addition to being used as a solvent, it is also used as a raw material for medicines, dyes, pesticides, synthetic resins and fertilizer synergists.
2. Used to prepare dyes, resins, pesticides, veterinary drugs, rubber accelerators, film photosensitizer additives, etc. In medicine, it is used to prepare drugs such as sikani, chlorpheniramine, pralidoxime, and acetylcysteine.
3. Used in the synthesis of chemicals such as medicines, dyes, rubber, etc., and also used as solvents and experimental reagents. [24]
