2,2,4-Trimethylpentane
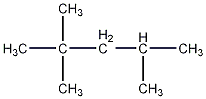

Structural formula
| Business number | 05KG |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C8H18 |
| Molecular weight | 114.23 |
| label |
2-methylheptane, Trimethylpentane, isooctane, 2,2,4-Trimethyl-pentan, Isobutyltrimethylethane, gasoline additives |
Numbering system
CAS number:540-84-1
MDL number:MFCD00008943
EINECS number:208-759-1
RTECS number:SA3320000
BRN number:1696876
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless, transparent liquid [1]
2. Melting point (ºC): -107.4[2]
3. Boiling point (ºC): 99.2[3]
4. Relative density (water=1): 0.69 (20ºC)[4]
5. Relative vapor density (air=1): 3.9[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 5.1 (20ºC)[6]
7. Critical pressure (MPa): 2.57[7]
8. Octanol /Water partition coefficient: 4.09[8]
9. Flash point (ºC): 4.5 (OC)[9]
10. Ignition temperature (ºC): 417[10]
11. Explosion upper limit (%): 6.0[11]
12. Lower explosion limit (%): 1.1[12]
13. Solubility: insoluble in water, miscible in heptane and acetone, soluble in Ether, benzene, toluene, xylene, chloroform, carbon disulfide, carbon tetrachloride, etc. [13]
14. Heat of evaporation (25℃, kJ/mol): 35.152
15. Heat of evaporation (b.p., kJ/mol): 31.024
16. Heat of fusion (kJ/mol): 9.219
17. Thermal conductivity [W/(m·K)]: 100.48×10–3
18. Heat of formation (liquid, kJ·mol): -250.20
19. Heat of formation (gas, kJ·mol): -208.59
20. Total combustion calorific value (25ºC, liquid, kJ/mol): 5468.98
21. Minimum combustion calorific value (25ºC, liquid, kJ/mol): 5068.58
22. Specific heat capacity (ideal liquid, 25ºC, constant pressure)/[kJ/(kg·K)]: 1.655
23. Specific heat capacity (liquid, 25°C, 101.3 kPa)/[kJ/(kg ·K)]: 2.09
24. Conductivity (25ºC) (S/m): <1.7×10–8
25. Critical Density (g·cm-3): 0.244
26. Critical volume (cm3·mol-1) : 468
27. Critical compression factor: 0.267
28. Eccentricity factor: 0.303
29. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3 )0.5: 14.051
30. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1) : 1.252×1010
31. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 88.690
32. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -5496.48
33. Gas phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ ·mol-1): -224.05
34. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 423.09
35. Gas phase standard formation free energy (kJ·mol-1): 14.2
36. Gas phase standard hot melt (J· mol-1·K-1): 188.41
37. Liquid phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -5461.33
38. Liquid phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -259.20
39. Liquid phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1) : 314.6
40. Liquid phase standard free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1): 11.06
41. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J· mol-1·K-1): 238.55
Toxicological data
1. Multiple dose toxicity data: rat oral TDLo: 10gm/kg/4W-I, kidney, ureter, bladder – changes (including acute renal failure, acute tubular necrosis), chronic data – death;
Rat oral TDLo: 8mL/kg/2W-I, kidney, ureter, bladder-changes in other components of urine;
Rat oral TDLo: 2100mg/ kg/21D-I, kidney, ureter, bladder – changes (including acute renal failure, acute tubular necrosis);
2. Mutagenicity data: non-programmed DNA synthesis TEST system: rat oral : 500mg/kg;
Non-programmed DNA synthesis TEST system: Mouse oral: 500mg/kg;
Mouse inhaled isooctane 20~30g/m3 , 2h, 40% died. When people are exposed to 1g/m3 of isooctane for 5 minutes, symptoms of respiratory tract and eye mucosa irritation will occur.
3. Acute toxicity [14] LC50: 80mg/m3 (mouse inhalation, 2h)
p>
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[15] LC50: 0.561mg/L (48h) (medaka)
2. Biology Degradability No data available
3. Non-biodegradability No data available
4. Bioaccumulation [16] BCF: 440~580 (carp, contact concentration 10mg/L, contact time 28d); 460~650 (carp, contact concentration 1mg/L, contact time 28d)
5. Other harmful effects[17] This substance is harmful to the environment. Special attention should be paid to the pollution of surface water, soil, atmosphere and drinking water.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 39.03
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 161.0
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 342.9
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 20.5
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 15.47
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 3.8
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 0
7. Number of heavy atoms: 8
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 54.9
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. It has no effect on 95% sulfuric acid. In a mixed acid of nitric acid and sulfuric acid, nitrification reaction occurs at 140°C. Since the tertiary carbon in the molecule contains hydrogen atoms, it is easier to oxidize than octane. Photochemical reactions can occur with halogens. Alkylation reaction with alkenes. It reacts with benzene under the catalysis of AlCl3-HCl to produce 1,4-di-tert-butylbenzene.
2. Stability[18] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[19] Strong oxidants, strong acids, strong bases, halogens
4. Polymerization hazards[20] No polymerization
Storage method
Storage Precautions[21] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 37°C and the container should be kept sealed. should be kept away from oxidizer, do not store together. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. It is obtained by refining petroleum and can also be produced by synthetic methods. Such as isobutane and isobutylene in the presence of anhydrous hydrogen fluoride derived from the reaction. Isooctane can also be produced by distillation and hydrogenation using the by-products of 264 antioxidant and isobutylene polymer as raw materials.
2. Refining method: separate olefins through a silica gel column, and then distill and refine.
3. Obtained from petroleum refining. Or it can be synthesized from isobutane and isobutylene in the presence of anhydrous hydrogen fluoride.
Purpose
1. Isooctane is a standard material for testing the antiknock performance of gasoline. The octane numbers of isooctane and heptane are specified as 100 and 0 respectively. If the anti-knock performance of a gasoline sample in a single-cylinder engine is equivalent to a certain isooctane-heptane mixture under specified test conditions, the octane number of the sample is equal to the volume of isooctane in the standard fuel. percentage. Gasoline with good anti-knock properties has a high octane number. Used as the standard fuel for determining the octane number of gasoline. It is also used as an additive for automobile gasoline and aviation gasoline. Used as a solvent during the polymerization of butadiene.
2. Used in organic synthesis, as a solvent and as a comparison sample for gas chromatography. It has good shock resistance when burned in the cylinder of an internal combustion engine and is an excellent engine fuel. It is a measure of automobileStandard fuel with ��octane number (shock resistance), mainly used as additives for gasoline, aviation gasoline, etc., and as non-polar inert solvents in organic synthesis.
3. Used in organic synthesis, as a solvent and as a comparison sample for gas chromatography. [22]
