3-Butenoic acid
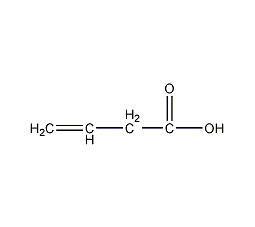

Structural formula
| Business number | 06RZ |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H6O2 |
| Molecular weight | 86.09 |
| label |
Butene-3-acid, vinyl acetic acid, Beta-butenoic acid, Vinylacetic Acid, β-Butenoic acid, Ethenylacetic acid, acidic solvent |
Numbering system
CAS number:625-38-7
MDL number:MFCD00002782
EINECS number:210-892-5
RTECS number:None
BRN number:1699159
PubChem number:24889969
Physical property data
1. Properties: gray-yellow liquid.
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4℃): 1.0091
3. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 1.011
4 . Melting point (ºC): -35
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 169
6. Refractive index at room temperature (n20): 1.4220
7. Refractive index (n20D): 1.423
8. Flash Point (ºC): 65
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol) : Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Oil and water (octanol /water) logarithmic value of the distribution coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V) : Undetermined
19. Solubility:.
Toxicological data
Ecological data
Do not allow large quantities of products that are slightly harmful to water to come into contact with groundwater, waterways or sewage systems. Do not discharge materials into the surrounding environment without government permission.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 21.87
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 84.2
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 202.0
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 33.0
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 8.67
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 0.5
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 37.3
7. Number of heavy atoms: 6
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity :65.9
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determined number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
14. Uncertain number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units :1
Properties and stability
1. Keep away from oxides, alkali and heat.
2. Exist in smoke.
Storage method
Store in an airtight container in a cool, dry place. The storage area must be locked and the keys must be given to the technical experts and their assistants. refrigeration. Store away from oxidants and strong alkali. heat proof. Storage temperature 4ºC
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from the hydrolysis of butene-3-nitrile. Heat butene-3-nitrile and concentrated hydrochloric acid together. After the reaction, a large amount of ammonium chloride precipitate is generated. The temperature rises quickly. After refluxing for 15 minutes, add water, separate the upper acid layer, distill under reduced pressure, and collect 70-72°C (1.2 kPa) fraction is obtained.
2.3-Butenenitrile (3): In a reaction bottle equipped with a stirrer, thermometer, and reflux condenser, add 293g of newly distilled allyl bromide (bp70~71°C) (2) (2.42 mol), 226 g of dry copper cyanide (2.52 mol), slowly heat allyl bromide to reflux, but do not stir. After the reaction progressed vigorously, the heat source was removed and cooled in an ice-water bath. After the reaction is stable, start stirring, heat and stir in a water bath for 1 hour. Change to a distillation device, heat the oil bath, and use a water pump to distill under reduced pressure. The collected crude product was re-distilled, and the fraction between 116 and 121°C was collected to obtain 140g of 3-butenenitrile (3) with a yield of 86%. Vinyl acetic acid (1): In a reaction bottle equipped with a stirrer, thermometer, and reflux condenser, add 134g (2mol) of 3-butenenitrile (3) and 200mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid, and heat slowly. After a few minutes, the reaction begins. Remove the heat source. If the reaction is severe, cool it in a water bath. Ammonium chloride solid is generated. When the reaction is stable, stir and reflux for 20 minutes. Add 200 mL of water, cool, and separate the upper organic layer. The aqueous layer was extracted with diethyl ether (100mL×3). The organic layers were combined and the ether was evaporated. Fractionate under reduced pressure and collect fraction A at 71°C/1.86kPa and fraction B at 72-74°C/1.86kPa. Fraction B weighs 100g and is vinyl acetic acid (1). The aqueous layer of Fraction A was separated, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and then fractionated again to obtain 15g of vinyl acetic acid (1). A total of 115g of product was obtained, with a yield of 66%. [1]
3. Preparation method:
In a reaction bottle equipped with a stirrer and a reflux condenser, Add 67g (80mL, 1.0mol) of 3-butenenitrile (2) and 100mL of concentrated acetic acid, and slowly heat over low heat. After 7 to 8 minutes, the reaction begins and a large amount of ammonium chloride white precipitate is generated. The temperature rises rapidly and refluxes. After 15 minutes, stop heating and add 100 mL of water. The organic layer was separated, and the aqueous layer was extracted with diethyl ether (100 mL × 2). Combine the organic layers, evaporate the solvent under normal pressure, and then distill under reduced pressure. After evaporating about 40g of the previous fraction, collect the fraction at 70~72°C/1.2kPa to obtain crude product (1) 50~53°C, with a yield of 52%~62 %. The crude product obtained can meet the requirements of most experiments. It contains a small amount of by-products that cannot be removed by distillation and can be purified by the following method. In a reaction bottle equipped with a stirrer, thermometer, and dropping funnel, add a solution of 24 g sodium hydroxide dissolved in 80 mL water, and add 45 g of the crude product of the above compound (1) dropwise at 8 to 15°C, and the reaction is completed in about 25 minutes. Extract with 50mL chloroform. After the aqueous layer was acidified with 300 mL of dilute sulfuric acid, it was immediately extracted with chloroform (100 mL × 3). Combine the chloroform extracts, evaporate the solvent under normal pressure, and then distill under reduced pressure to collect the 69-70°C/1.6kPa fraction to obtain 30-33g of pure product with a recovery rate of 75%-82%. [2]
Purpose
None yet
