3-hydroxy-2-methyl-4-pyrone
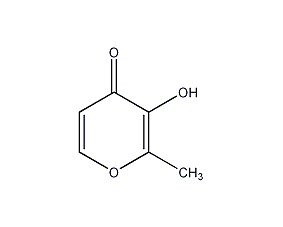

Structural formula
| Business number | 03A1 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H6O3 |
| Molecular weight | 126.11 |
| label |
Maltol, Laricidin; maltol; larchic acid; larchic acid; 2-methylpyroxaconic acid; flavonol; balazone; kaolin;, Flavor enhancer |
Numbering system
CAS number:118-71-8
MDL number:MFCD00006578
EINECS number:204-271-8
RTECS number:UQ1050000
BRN number:112169
PubChem number:24879746
Physical property data
1. Properties: White to slightly yellow needle-like crystals or crystalline powder.
2. Density (g/mL, 25℃): 1.046
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 160-164
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 205
6. Boiling point (ºC, kPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive index: 1.541
8. Flash point (ºC): Undetermined
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): 740
11. Vapor pressure (mmHg, 25ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, ºC ): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical Pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) distribution coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): 25
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Soluble in hot water, chloroform, ethanol, slightly soluble in benzene and ether, Insoluble in petroleum ether.
Toxicological data
1. Irritation: Rabbit transdermal: 500mg/24H Moderately irritating.
2, acute toxicity: chicken mouth LD50: 3720ug/kg
Guinea pigs LD50: 1410mg/kg
mouse passing LC50: 550mg/550mg/550mg/ kg
Rabbit oral LD50: 1620 mg/kg
Rabbit transdermal LD:>5000mg/kg
Ecological data
Slightly harmful to water.
Molecular structure data
5. Molecular property data:
1. Molar refractive index: 30.29
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 93.5
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 250.9
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 51.7
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 12.00
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 0.4
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: 5
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 46.5
7. Number of heavy atoms: 9
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 200
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Avoid contact with oxides.
Storage method
Store sealed in a cool, dry place. Make sure the workspace has good ventilation. Store away from oxidizing agents.
Synthesis method
1. There are three main methods of making maltol: 1. Extracting maltol from natural products. Maltol is present in the decomposition liquid of wheat and soybeans and in the roasted condensate of barley. It also exists in the bark of some fir trees and larch. middle. In 1986, the United States used extraction crystallization to extract maltol from wood vinegar. In 1970, the United States used chloroform to extract maltol from larch bark. In Japan, it is directly extracted from the leaves of cinnabar with chloroform or extracted from its steam distillate. Maltol can also be separated from wood tar obtained by the dry distillation of wood by vacuum distillation. 2. Semi-synthetic method (using kojic acid as raw material) The parent substance of kojic acid is glucose, which is equivalent to the dehydration product of 3-keto-glucose. Starch is fermented with Aspergillus flavus, and the kojic acid produced in the fermentation broth is converted into kojic acid, which is oxidized with air (or oxygen) under catalysis to form pyroconic acid, and then decarboxylated into pyroconic acid at 225°C. Pyrosconic acid is reacted with formaldehyde under alkaline conditions to form hydroxymaltol. Then use hydrochloric acid and zinc powder for reduction to obtain maltol. After distillation or sublimation, and recrystallization in chloroform, the finished product of maltol is obtained. To make kojic acid from kojic acid, kojic acid and benzyl chloride can also be etherified to form kojic acid benzyl ether, and then oxidized with manganese dioxide to form kojic acid ether, and then debenzylated to form kojic acid. 3. Use furfural as raw material to synthesize maltol.
2. Furfuryl alcohol method
Furfuryl alcohol is chlorinated with chlorine in a methanol aqueous solution to form 4-chloro-6-hydroxy-2[H]-pyran-3[6H]-one. Then it is heated and hydrolyzed to obtain pyrocosconic acid, which is condensed with formaldehyde under alkaline conditions to obtain hydroxymethyl pyrocosconic acid, which is reduced to maltol in hydrochloric acid with zinc powder. Semi-synthetic method
Using starch as raw material, kojic acid is produced through fermentation of Piriformis spp. Kojic acid and benzyl chloride are etherified in a sodium hydroxide-methanol solution to form kojic acid benzyl ether; then oxidized with manganese dioxide to form comannate benzyl ether, and debenzylated in the presence of hydrochloric acid to form comannic acid, and then decarboxylated to form Pyroconic acid is finally combined with formaldehyde and reduced to maltol with zinc powder.
Furfural method
Furfural reacts with methylmagnesium bromide to obtain methylfurfuryl alcohol, which is then oxidized in a methanol aqueous solution with chlorine gas at 0°C, and then heated to 100°C for hydrolysis to obtain maltol. This method has a wide source of raw materials, a short process route, mild conditions, simple equipment, less “three wastes”, and has good development prospects.
Kojic acid is produced by fermentation and then etherified with benzyl chloride to obtain kojic acid benzyl ether, which is catalyzed by manganese dioxide and hydrochloric acid to generate caustic acid, and then decarboxylated to obtain pyroconic acid. formed by methylation.
It is made by reacting azepine with pyroconic acid, and then methylating the 2-position.
Diethyl oxalate is condensed with acetone in the presence of sodium ethoxide, and then bromine is introduced into the chloroform solution to obtain γ-derivatives; it is then hydrolyzed by potassium hydroxide into astriconic acid, and then heated Decarboxylation gives pyroconic acid, which is treated with formaldehyde and piperidine and then reduced.
3.The kojic acid is oxidized with air (or oxygen) under the catalysis of palladium to form kojic acid, and then decarboxylated at high temperature to form pyroxaconic acid. It reacts with formaldehyde under alkaline conditions to form hydroxymaltol. Then use hydrochloric acid and zinc powder for reduction to obtain maltol. After distillation or sublimation, and recrystallization in chloroform, fine maltol is obtained.
Purpose
1. Mainly used to prepare strawberry, coffee, malt, nuts, vanilla and various fruit flavors. Used for bread, cakes have a freshly baked flavor.
2.This product has caramel aroma and strawberry aroma in dilute solution. Maltol is a derivative of γ pyrone, which is mainly used as food flavoring agent, daily necessities and tobacco flavoring, photosensitive materials, preservatives and skin care drugs. Adding a trace amount of maltol to food not only improves and thickens the aroma, but also prolongs the storage period of the food without mold. Used to prepare daily fragrance, it can also exert a good fragrance effect. Maltol is also an excellent substance for coating photosensitive film evenly to prevent spots and streaks.
3. Skin care cosmetics formulated with it have good effects on inhibiting the growth of melanin and whitening the skin. When used in the production of various foods, the general dosage is less than 100kg.kg-1. It has a significant effect on improving and enhancing the aroma of food. Plays a sweetening role in sweet foods. One part maltol can be used in place of four parts coumarin. Adding 5 to 200g of maltol per ton of feed can promote the rapid growth of piglets.
�Can extend the storage period of food without mold. Used to prepare daily fragrance, it can also exert a good fragrance effect. Maltol is also an excellent substance for coating photosensitive film evenly to prevent spots and streaks.
3. Skin care cosmetics formulated with it have good effects on inhibiting the growth of melanin and whitening the skin. When used in the production of various foods, the general dosage is less than 100kg.kg-1. It has a significant effect on improving and enhancing the aroma of food. Plays a sweetening role in sweet foods. One part maltol can be used in place of four parts coumarin. Adding 5 to 200g of maltol per ton of feed can promote the rapid growth of piglets.
