4-Chlorophenol 4-Chlorophenol
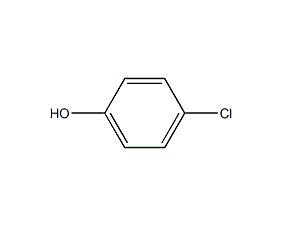
Structural formula
| Business number | 02TL |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H5ClO |
| Molecular weight | 128.56 |
| label |
4-Chloro-1-hydroxybenzene, 4-Hydroxychlorobenzene, p-hydroxychlorobenzene, p-chlorophenol, p-chlorophenol, 4-chlorophenol, 4-Chloro-1-hydroxybenzene, p-Chlorfenol, Parachlorophenol, Phenol, aromatic alcohols and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:106-48-9
MDL number:MFCD00002318
EINECS number:203-402-6
RTECS number:SK2800000
BRN number:507004
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Characteristics: white crystal with unpleasant odor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): 43~45[2]
3. Boiling point (℃) : 220[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 1.31[4]
5. Relative Vapor density (air=1): 4.43[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 0.13 (49.8℃)[6]
7. Critical pressure (MPa): 4.75~5.32[7]
8. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 2.39[8 ]
9. Flash point (℃): 121 (CC) [9]
10. Explosion limit (%): 8.8 [10]
11. Lower explosion limit (%): 1.7[11]
12. Solubility: slightly soluble In water, easily soluble in ethanol, ether, chloroform and benzene. [12]
13. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 1.200499.2
14. Refractive index at room temperature (n25): 1.536165
15. Refractive index at room temperature (n20): 1.541955
16. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 1.200499.2
17. Gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ ·mol-1): -145.8
18. Liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -181.3
19. Crystal phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -197.7
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[13]
LD50: 670mg/kg (rat oral); 1500mg/kg (rabbit dermal )
LC50: 11mg/m3 (rat inhalation)
2. Irritation [14]
Rabbit transdermal: 2mg (24h), severe stimulation.
Rabbit eye: 250μg (24h), severe irritation.
3. Mutagenicity[15]
Microbial mutagenicity: Salmonella Typhimurium Bacteria 200μg/dish. Cytogenetic analysis: Rat oral administration 81mg/kg
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[16]
LC50: 3.83mg/L (96h) (bluegill, static); 29mg /L (96h) (sugar shrimp); 9mg/L (24h) (goldfish)
LD50:4.06mg/L (96h) (Daphnia)
EC50: 4.79mg/L (96h) (green algae); 3.27mg/L (96h) (Skeletonema costatum)
2. Biodegradability No data yet
3. Non-biodegradability[17] In the air, when When the hydroxyl radical concentration is 5.00×105 pieces/cm3, the degradation half-life is 1.6d (theoretical).
4. Bioconcentration [18] BCF: 24 (carp, contact time 42 days); 10~15 (goldfish)
5. Other harmful effects [19] It can cause pollution to water bodies and soil, especially to molluscs, fish and mammals, causing serious harm.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 33.02
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 99.8
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 258.1
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 44.7
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 13.09
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: 2
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 20.2
7. Number of heavy atoms: 8
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 66.9
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. It is flammable when exposed to open flames and high heat, and decomposes to release toxic and corrosive fumes.
2. Stability[20] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[21] Strong oxidants, strong acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides
4. Polymerization hazards[22] No polymerization
5. Decomposition products[23] Hydrogen chloride
Storage method
Storage Precautions[24] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The packaging is sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
1. The direct chlorination method of phenol uses phenol as raw material and is divided into the following three methods according to the different chlorinating agents and solvents used:
(1) Sulfuryl chloride method to convert phenol into After heating and melting, lower the temperature to 40°C, slowly add sulfuryl chloride, it will take about 40-45 minutes to complete the addition, stir for another 4 hours, raise the temperature to 30-40°C and keep it for 4 hours, keep it at 40-45°C for 4 hours, and use alkali solution for the reaction tail gas Absorb, cool to room temperature after the reaction, wash with water, 10% sodium carbonate solution, and water in sequence, distill under reduced pressure, collect the 110-115°C (2.67kPa) fraction to obtain p-chlorophenol. This method has a high yield of p-chlorophenol, reaching 70%-75%. At the same time, 25-30% of the by-product o-chlorophenol is generated. Each ton of p-chlorophenol consumes about 1000kg of phenol and about 2000kg of sulfuryl chloride.
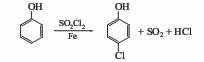
(2) Benzene solvent method Benzene is used as solvent and chlorine is used as chlorinating agent. This product is prepared by direct chlorination of phenol. (3) The solvent-free chlorination method uses iron, bromine, etc. as catalysts to pass chlorine gas into molten phenol and directly chlorine it to produce monochlorophenol. After washing, the reaction solution is distilled under reduced pressure to collect fractions with a p-chlorophenol content of ≥95%. The yield based on phenol (total ortho/para position) is ≥95%, the yield based on chlorine is 95%, the para/ortho position ratio is 3-4, and the product content is ≥98%. Raw material consumption quota: phenol 0.77t/t, chlorine 0.58t/t. The by-product hydrogen chloride is 0.28t/t.
2. Parachlorobenzene hydrolysis method uses paradichlorobenzene as raw material and water, alcohol or benzene as solvent.
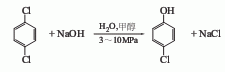
3. Chlorination by sodium phenolate A chlorinated liquid mixed with o-, p-chlorophenol and 2,4-dichlorophenol is obtained. Fractionate under reduced pressure, collect the high boiling fraction of 85-132℃ (2.0kPa), cool it to below 10℃, p-chlorophenol will precipitate, and it can be separated. The yield is about 25%.
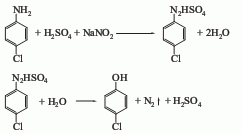
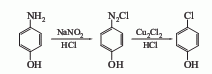
4. From p-aminophenol Derived from diazotization and cuprous chloride replacement. 5. Obtained from p-chloroaniline through diazotization, hydrolysis and elimination.

Purpose
1. Used in the synthesis of neutral brilliant green dye BL, pharmaceutical Clofibrin and pesticides, etc. It can also be used as a solvent for refined mineral oil.
2. Used as an intermediate in the synthesis of dyes and pharmaceuticals. [25]
