4-Chlorotoluene 4-Chlorotoluene
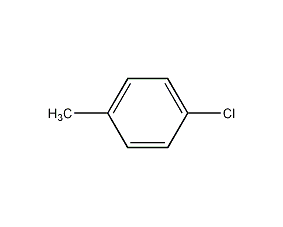
Structural formula
| Business number | 02TF |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C7H7Cl |
| Molecular weight | 126 |
| label |
4-Chlorotoluene, parachlorotoluene, 1-Chloro-4-toluene, 4-Chloro-1-methylbenzene, 4-Chloro-1-toluene, 4-Chlorotoluene, p-Chlorotoluene, 4-Chloro-1-methylbenzene, Aromatic halogen derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:106-43-4
MDL number:MFCD00000631
EINECS number:203-397-0
RTECS number:XS9010000
BRN number:1903635
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid with special smell. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): 7.5[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 162 [3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 1.07[4]
5. Relative vapor density (Air=1): 4.37[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 0.35 (20℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -3754[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 385.7[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 3.91[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 3.33[ 10]
11. Flash point (℃): 49; 60 (OC) [11]
12. Ignition temperature ( ℃): 595[12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 6.7[13]
14. Explosion Lower limit (%): 1.3[14]
15. Solubility: insoluble in water, soluble in ethanol, chloroform, acetic acid, miscible in ether. [15]
16. Viscosity (mPa·s, 10ºC): 1.0325
17. Heat of evaporation (KJ/kg, 160.38ºC): 306.22
18. Volume expansion coefficient (K-1, 30ºC): 0.00092
19. Refractive index at room temperature (n25 ): 1.515230
20. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 1.059630
21. Liquid phase Standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 199.4
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: Rat oral LD50: 2100mg/kg; rat LD50: 4mg/kg; mouse oral LD50: 1900mg/kg; mouse inhalation LC50: 34mg/m3/2H; mouse LD50: 4mg/kg; guinea pig LD50: 3750mg/kg;
2. Other multiple dose toxicity: rat oral TDLo: 182mg/kg/26W-I; large Intravenous TDLo in rats: 25200mg/kg/2W-I; Oral TDLo in rats: 72mg/kg/90D-I;
3. Acute toxicity[16]
LD50: 3600mg/kg (rat oral)
LC50: 34000mg/m3 (Inhaled by mice, 2h)
Ecological data
1. This substance may be harmful to the environment. It is recommended not to let it enter the environment.
2. Ecotoxicity[17] LC50: 5.2mg/L (48h) (medaka)
3. Biodegradability No data available
4. Non-biodegradability No data available
5. Bioconcentration[18] BCF: 21.9~76.5 (carp, contact concentration 0.3ppm, contact time 8 weeks) ;14~101.6 (carp, exposure concentration 0.03ppm, exposure time 8 weeks)
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 35.97
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 117.6
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 280.7
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 32.4
5. Polarizability: 14.26
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 0
7. Number of heavy atoms: 8
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 62.8
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Stability[19] Stability
2. Incompatible substances[20] Strong oxidizing agent
3. Polymerization Hazard[21] Does not polymerize
4. Decomposition products[22] Hydrogen chloride
Storage method
Storage Precautions[23] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 37°C. Keep container tightly sealed. should be kept away from oxidizer, do not store together. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
The preparation methods are as follows.
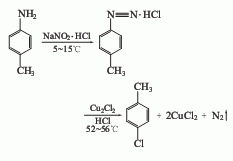
1. Diazotization method
Add industrial hydrochloric acid and p-methylaniline into the reaction kettle. The temperature in the kettle will drop to 0°C, so that p-methylaniline will generate hydrochloride. Stir and add methylaniline. Sodium nitrate solution is used to cause diazotization reaction. The temperature is maintained at 0-5°C for about 30 minutes. After the diazotization reaction is completed, add it to the stirring cuprous chloride solution and gradually warm it to room temperature. Stir at room temperature for 2.5 to 3 hours, and then heat to 60°C. The reactant gradually decomposes into nitrogen and p-chlorotoluene. Then it is distilled with water vapor. The mixture of p-chlorotoluene and water is collected, separated into layers, and the organic layer is washed with acid. Then wash with water, dry, and distill. The 158-162°C fraction is collected as p-chlorotoluene, with a yield of about 70% to 79%.
2. Direct chlorination method
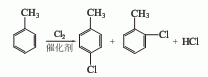
The toluene that has been dried and dehydrated with salt is measured in a metering tank and then enters the toluene chlorination reactor. The metered chlorine gas is introduced from the bottom of the reactor. Toluene and chlorine gas are chlorinated at a certain temperature using ferric chloride as a catalyst. , generating a chlorinated liquid of monochlorotoluene. The chlorinated liquid uses nitrogen to drive away the residual gas and hydrogen chloride, and then conducts crude evaporation to obtain a mixture of p-chlorotoluene and o-chlorotoluene. The p- and o-ratios vary with the catalyst and reaction conditions. However, the general pair and neighbor ratio is 55:45.
P-chlorotoluene and o-chlorotoluene can be separated by distillation method, molecular sieve adsorption method, combined distillation and crystallization method, etc. The combined method of distillation and crystallization consumes less energy, and the content of p-chlorotoluene and o-chlorotoluene obtained is high. If the falling film freezing crystallization method is used, the content of p-chlorotoluene can reach more than 99%.

Purpose
1. Used as an intermediate for dyes, medicines, and organic synthesis, such as intermediates for the synthesis of pyrimethamine and fenalol. It is also used as a solvent and a solvent for rubber and synthetic resins. Recently, it is widely used as raw material for manufacturing sulfur carbamate herbicides.
2. Used in organic synthesis, preparation of dye intermediates, and as solvent. [24]
