Phthalimide Phthalimide


Structural formula
| Business number | 01VQ |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C8H5NO2 |
| Molecular weight | 147.14 |
| label |
Phthalimide, Isoindole-1,3-dione, imine phthalate, Isoindole-1,3-dione, Benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid imide, Aromatic nitrogen-containing compounds and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:85-41-6
MDL number:MFCD00005881
EINECS number:201-603-3
RTECS number:TI3920000
BRN number:118522
PubChem number:24862742
Physical property data
1. Properties: White leaf-like crystals or crystalline powder.
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4℃): 1.367
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Uncertain
4. Melting point (ºC): 238
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 366
6. Boiling point (ºC, 5.2kPa): Uncertain
p>
7. Refractive index: Uncertain
8. Flash point (ºC): 165
9. Specific rotation (º): Uncertain
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Uncertain
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Uncertain
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa , 60ºC): Uncertain
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Uncertain
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Uncertain
15 . Critical pressure (KPa): Uncertain
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Uncertain
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V ): Uncertain
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Uncertain
19. Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, ether, benzene and chloroform, slightly soluble In ethanol, easily soluble in alkali solution, glacial acetic acid and pyridine.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity:
Rat abdominal cavity LD50: >500mg/kg;
Mouse abdominal cavity LD50: 5mg/kg; Mouse abdominal cavity LD50: 1175mg/kg;
2. Reproductive toxicity;
Mouse abdominal TDL0: 6200 ug/kgSEX/DURATION, malformation; Mouse abdominal TDL0: 100mg/kgSEX/DURATION, fetal death;
Ecological data
None yet
Molecular structure data
5. Molecular property data:
1. Molar refractive index: 37.42
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 107.5
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2 K): 291.0
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 53.6
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3 ): 14.83
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: 2
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 46.2
7. Number of heavy atoms: 11
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 190
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Emit toxic nitrogen oxide gas when heated. Can be poisonous if swallowed by mistake. Slightly irritating to skin.
2. Exist in smoke.
Storage method
This product is sealed and stored in a dry place.
Glass bottles and plastic bottles should be lined with padding or fiber barrels and metal barrels lined with plastic bags. Store in a cool and ventilated warehouse, away from fire and heat sources. Store and transport separately from food raw materials. Handle with care when transporting to prevent damage to the container.
Synthesis method
There are many methods for preparing phthalimide using phthalic anhydride as raw material. The ammonium carbonate method and urea method are actually used in industrial production.
1. Ammonium bicarbonate method: Mix phthalic anhydride and ammonium bicarbonate at a molar ratio of 1:1.2, crush it with a pulverizer and put it into the reaction kettle, heat it for about 4 hours to 200°C, and then heat it up to 280-300°C at a slightly faster speed. ℃. The melt is discharged until it crystallizes, cooled, solidified, and pulverized to obtain the finished product, with a yield of more than 95%. Each ton of phthalimide with a content of 95% requires 1030kg of phthalic anhydride and 660kg of 95% ammonium bicarbonate. 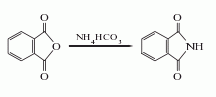 2. Urea method
2. Urea method 
Purpose
This product is an intermediate for many fine chemicals such as dyes, pesticides, medicines, and rubber additives. It is used for the production of phthalide, phthalonitrile, indigo, fungicides, and insecticide imines. Sulfur, phosphorus, etc.
