Heptanoic acid Heptanoic Acid
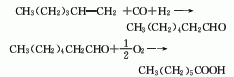
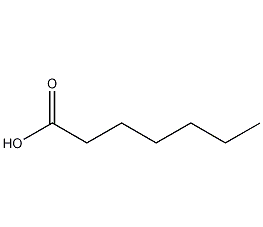
Structural formula
| Business number | 032T |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C7H14O2 |
| Molecular weight | 130.18 |
| label |
Grape flower acid, Toxic acid, n-heptanoic acid, 1-Hexanecarboxylic acid, Enanthic acid, Oenanthic acid, n-Heptanoic acid, food additives, flavor enhancer, Acid solvent |
Numbering system
CAS number:111-14-8
MDL number:MFCD00004426
EINECS number:203-838-7
RTECS number:MJ1575000
BRN number:1744723
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless oily liquid. It has a fat-like smell and a foul odor when impure.
2. Relative density (g/mL, 20/4℃): 0.9178
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): 4.5
4. Melting point (ºC): -7.5
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 223
6. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 0.9137
7. Refractive index (20ºC): 1.417
8. Flash point (ºC): >109
9. Refractive index at room temperature (n 25): 1.4210
10. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -4219.2
11. Gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -536.2
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 78ºC): 0.13
13. Critical temperature (ºC): 404.85
14. Critical pressure (MPa): 3.16
15. Critical density (g·cm-3) : 0.278
16. Critical volume (cm3·mol-1): 468
17. Critical compression factor: 0.262
18. Eccentricity factor: 0.717
19. Solubility: Soluble in ethanol, ether, dimethylformamide, dimethyl sulfoxide, slightly soluble in water.
20. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 21.949
21. van der Waals area ( cm2·mol-1): 1.193×1010
22. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 84.340
23. Liquid phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1 ): -4145.2
24. Liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -610.2
25. Liquid phase standard Hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 273.2
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: ratsOral LD50: 7000mg/kg; Mouse oral LD50: 6400mg/kg
Mouse intravenous LD50: 1200mg/kg
2. It is corrosive and can cause burns.
Ecological data
This substance is harmful to the environment, and special attention should be paid to the pollution of water bodies.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 36.04
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 138.7
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 332.4
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 32.9
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 14.28
Compute chemical data
1. Hydrophobic parameter calculation reference value (XlogP): 2.5
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 5
5. Number of tautomers:
6. Topological molecular polar surface area (TPSA): 37.3
7. Number of heavy atoms: 9
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 79
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters Number: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. It does not decompose under normal temperatures and pressures, and is prohibited from contact with oxidants, reducing agents, and alkalis. Corrosive.
2.The oral LD507000mg/kg for rats and the oral LD506400mg/kg for mice. This product is non-toxic.
3. Exist in flue-cured tobacco leaves, burley tobacco leaves, oriental tobacco leaves, and smoke.
4. Naturally found in beer, cheese, bread, mint, acacia, calamus, violet, and egg fruit.
Storage method
1. Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Protect from direct sunlight. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, reducing agents and alkalis, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
2.100kg aluminum drum. Store and transport according to “General Chemical Regulations”.
Synthesis method
1. First, heptaldehyde is obtained by carbonylation of heptene-1 and synthesis gas, and then heptanoic acid is obtained by air oxidation. First, 1-heptene synthesis gas (carbon monoxide + hydrogen), circulating gas and catalyst solution are sent into the carbonylation reactor, and the temperature is controlled to 94-150°C and the pressure is 1.30MPa; the reaction product is flashed under reduced pressure to separate the aldehyde Catalysts, catalysts and heavy components can be recycled. The aldehydes are then fed into the oxidation reactor and oxidized in air in a mixed transition metal catalyst system at a pressure below 0.69MPa. The aldehyde is almost completely converted, so there is no need for separation and recycling. After removing trace amounts of catalyst, the obtained product is sent to a double-column distillation system. Heavy components (which can be used as fuel) are removed in the first tower, and the top material is sent to the second tower to obtain the finished branched chain acid.
2. Heptanal is obtained by carbonylation of 1-hexene with synthesis gas (CO+H2), and then oxidized by air.
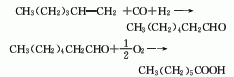
3. Tobacco: OR, 44 , 49; BU, 56; FC, BU, OR, 18; BU, OR, 26; FC, 40.
4. Preparation method:
In a reaction bottle equipped with a stirrer and thermometer, add 2.8L of water, slowly add 350mL of concentrated sulfuric acid, and cool to 15°C in an ice-water bath. Add 342g (3mol) of n-heptanal (2). Under vigorous stirring, add 340g (2.15mol) of potassium permanganate in batches, about 15g each time. Control the reaction solution to not exceed 20°C and finish the addition in about 2 hours. After the addition was completed, the reaction was continued to stir for 0.5 h. Pour in sulfur dioxide gas until it becomes clear (an appropriate amount of sodium bisulfite can also be added). Separate the oil and wash it once with water. Vacuum distillation. The water is removed from the previous fraction and then re-distilled. Collect the fractions at 159~161℃/13.3kPa to obtain 300g of n-heptanoic acid ① (1), with a yield of 77% and a purity of 95% to 97%. Note: ① Dissolve n-heptanoic acid with a purity of 95% in an appropriate amount of sodium hydroxide aqueous solution, and steam distill until there is no oil in the distillate. The residue is cooled and acidified with hydrochloric acid to separate n-heptanoic acid, and then distilled under reduced pressure to collect the fraction at 155-157°C/10.6KPa to obtain n-heptanoic acid with a purity close to 100% and a yield of 85%-90%. [1]
Purpose
1. Used in the production of enanthate products as raw materials for spices. Antifungal drugs. Chemical reagents, organic synthesis raw materials, solvents.
2. Commonly used in baked goods, candies, jams/gels.
