N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)ethylenediamine N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)ethylenediamine
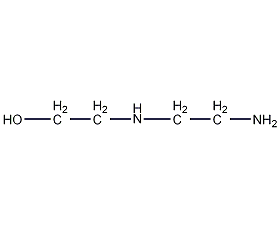
Structural formula
| Business number | 033F |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H12N2O |
| Molecular weight | 104.15 |
| label |
Hydroxyethylethylenediamine, AEEA, N-(β-hydroxyethyl)-ethylenediamine or N-(2-aminoethyl)ethanolamine, Hydroxyethyl-ethylenediamine, AEEA, N-(β-hydroxyethyl) – ethylenediamine or N-(2-aminoethyl) ethanol ammonia, Surfactant raw materials |
Numbering system
CAS number:111-41-1
MDL number:MFCD00008170
EINECS number:203-867-5
RTECS number:KJ6300000
BRN number:506012
PubChem number:24847789
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless viscous liquid with ammonia odor.
2. Density (g/mL, 20℃): 1.0304
3. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 243.7
4 Boiling point (ºC, 1.33kPa): 103.7
5. Refractive index: 1.4863
6. Flash point (ºC): 135
7. Solubility: soluble in water and Ethanol, slightly soluble in ether.
Toxicological data
1. Irritation: Rabbit percutaneous open irritation test: 445mg mild irritation; rabbit eye standard Drez eye dye test: 50mg severe irritation.
2. Acute toxicity: rat oral LD5O: 3gm/kg; rat transdermal LD5O: 2250mg/kg; rat intraperitoneal LD5O: 120mg/kg; rat subcutaneous LD5O: 2250mg/kg; rat intravenous LD5O: 417mg/kg; rat intramuscular LD5O: 2gm/kg; mouse oral LD5O: 3550mg/kg; rabbit oral LD5O: 2gm/kg; rabbit transdermal LD5O: 3560ul/kg; guinea pig oral LD5O: 1500mg/kg; guinea pig transdermal LD5O: 1800ul/kg.
3. Mutagenicity: Salmonella mutation: 2800ug/plate
4. The toxicity of this product is 6 to 7 times lower than that of ethylenediamine. Under the same conditions, this product The possibility of poisoning caused by vapor that volatilizes into space through the respiratory tract is 3,500 times less than that of ethylenediamine, and its irritation (to the skin, conjunctiva, etc.) is far less than that of ethylenediamine.
Ecological data
Slightly harmful to water bodies.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 29.24
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 104.5
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 265.0
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 41.2
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 11.59
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 3
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors.�: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 4
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 58.3
7. Number of heavy atoms: 7
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 32.9
10. Isotopes Number of atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine chemical bonds Number of stereocenters: 0
14. Number of stereocenters of uncertain chemical bonds: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Avoid contact with oxides, acids, and moisture.
It is hygroscopic, strongly alkaline, has an ammonia smell, and can absorb carbon dioxide and water in the air. Low toxicity. The toxicity is 6 to 7 times lower than that of ethylenediamine. Under the same conditions, the possibility of poisoning caused by the vapor evaporated into the space through the respiratory tract is 3500 times less than that of ethylenediamine. Its irritation (to the skin, conjunctiva) etc.) is much smaller than ethylenediamine.
Storage method
Save sealed in a cool, dry place. Ensure that the workspace has good ventilation facilities and explosion-proof facilities. Keep away from fire and water sources. Store away from oxidants and acidic substances. The storage period is 1 year.
Synthesis method
It is derived from the reaction of ethylenediamine and ethylene oxide. Process flow:(1) The boiling points of N-β-hydroxyethyldiamine and ethylenediamine are 244℃ and 110℃ respectively , whose boiling points differ greatly and have no azeotropic point, which is very conducive to separation operations. Judging from the existence of the above-mentioned series side reactions, back-mixing should be avoided in the process, so it is not suitable to use a CSTR reactor, and a gas-liquid contact tower distillation reactor is usually used. Ethylenediamine evaporates in the distillation, rises through the tower to condensation, and is collected in a temperature-regulating heat exchanger to adjust to the set temperature. It enters the reaction zone through the collecting hole. The ethylene oxide entering the reactor through the gas inlet is The gas distribution plate meets ethylenediamine in the reaction zone, and reacts instantly to generate N-β-hydroxyethylethylenediamine. The generated product N-β-hydroxyethylethylenediamine and unreacted ethylenediamine enter the vacuum distillation tower. After separation, the ethylenediamine is recycled, and the bottom of the tower is the product obtained. At a suitable temperature, ethylene oxide and ethylenediamine undergo an instantaneous gas-liquid addition reaction to form N-β-hydroxyethylethylenediamine. The generated N-β-hydroxyethylethylenediamine must be immediately reacted with ethylene oxide. Separation, otherwise by-products such as polyhydroxyethylethylenediamine will be further generated, so the gas-liquid two-phase contact time should be shortened as much as possible to reduce the possibility of side reactions. (2) Place 133g ethylenediamine and 10% water in a four-neck bottle, heat and vaporize, and enter the reaction zone through the packed column , after condensation in the condenser and condenser tube, it accumulates in the receiving bowl, and then drips from the small opening at the bottom of the bowl to the ethylene oxide outlet, where ethylenediamine and ethylene oxide undergo a rapid gas-liquid phase contact reaction to form The product enters the funnel and then flows into the four-neck bottle. The reaction end point is when very little ethylenediamine is evaporated (the function of the packed column is to separate the mixed vapor containing the product and raw materials, so that the product flows back to the four-neck bottle to prevent it from entering the reaction zone again to produce polyhydroxyethyl groups. side reactions). Post-processing: Place the reaction mixture in a vacuum distillation device, and collect 210g of the 136-139°C fraction under a pressure of 2133pa, with a yield of 91.44% and a purity greater than 99% (gas phase method). ![]()
Purpose
It is used as a room temperature rapid curing agent for epoxy resin. The reference dosage is 16-18 parts by mass, and the curing conditions are RT/10h or 80℃/3h. Suitable for adhesives, moisture-proof packaging materials for telecommunications equipment, acid-proof, alkali-proof and corrosion-resistant materials for cement tanks, etc. The service life is about 25 minutes at 20°C, the curing speed is about twice slower than that of ethylenediamine, and it has a plasticizing effect. This product is used as epoxy resin curing agent, the dosage is 16 to 18 parts. The epoxy resin cured product using this product has good mechanical strength and electrical insulation properties. This product is not volatile and has low toxicity, but has a short service life and is easy to absorb moisture. This product is also used in the production of dyes, pesticides, surfactants, flotation agents and corrosion inhibitors 1017.
