4-Chloroaniline p-Chloroaniline
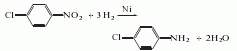
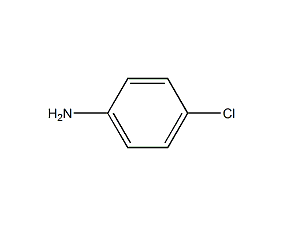
Structural formula
| Business number | 02TK |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H6ClN |
| Molecular weight | 127 |
| label |
Para-aminochlorobenzene, 4-Chloroaniline, p-chloroaniline, 4-Aminochlorobenzene, 4-Amino-1-chlorobenzene, 4-Aminochlorobenzene, Aromatic nitrogen-containing compounds and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:106-47-8
MDL number:MFCD00007835
EINECS number:203-401-0
RTECS number:BX0700000
BRN number:471359
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: white crystal or light yellow solid. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): 72.5[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 232 [3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 1.17[4]
5. Relative vapor density (Air=1): 4.4[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 0.0036 (26℃)[6]
7. Critical pressure (MPa): 4.45[7]
8. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.83[8]
9. Flash point (℃): 120[9]
10. Ignition temperature (℃): 685[10]
11. Explosion upper limit (%): 8.8[11]
12. Explosion lower limit (%): 2.2[ 12]
13. Solubility: soluble in hot water, soluble in most organic solvents such as ethanol, ether, acetone and so on. [13]
14. Refractive index (85ºC): 1.5546
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[14]
LD50: 310mg/kg (rat oral); 360mg/kg (rabbit dermal )
2. Irritation [15]
Rabbit transdermal: 500mg (24h), mild irritation.
Rabbit eye: 250μg (24h), severe irritation.
3. Mutagenicity [16] Microbial mutagenicity test: Salmonella typhimurium 100μg/dish. Unprogrammed DNA synthesis: rat liver 5mg/L.
4. Carcinogenicity [17] IARC Carcinogenicity Comment: G2B, suspected carcinogen in humans.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[18]
LC50: 2.4mg/L (96h) (bluegill sunfish); 9.7~11.5 mg/L (96h) (rainbow trout); 12mg/L (96h) (fathead minnow); 23mg/L (96h) (canal catfish)
2. Biodegradability[19]
GSF biodegradation test, 28% degradation in 5 days;
Improved OECD screening test, 10% and 18% degradation in 28 days
p>
3. Non-biodegradability[20] In the air, when the concentration of hydroxyl radicals is 5.00×105/ When cm3, the degradation half-life is 9h (theoretical).
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 35.38
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 103.6
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 268.9
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 45.3
5. Dielectric constant:
p>
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 14.02
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 26
7. Number of heavy atoms: 8
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 66.9
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. It has toxic effects on the human blood system and nervous system. Poisoning can cause symptoms such as liver swelling, liver pain, and memory loss. Production equipment should be airtight and well ventilated. Operators should wear protective equipment.
2. Stability[21] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[22] Acids, acid anhydrides, acid chlorides, chloroform, strong oxidants
4. Conditions to avoid contact[23] Heating
5. Polymerization hazard[24] No polymerization
6. Decomposition products[25 ] Hydrogen chloride
Storage method
1. Storage precautions[26] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The packaging is sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
2. Packed in iron drums, with a net weight of 200kg per drum. Store in a cool, ventilated place, moisture-proof and fire-proof. Store and transport according to regulations on toxic and dangerous goods.
Synthesis method
The preparation method is to reduce p-nitrochlorobenzene to obtain p-chloroaniline. There are several methods such as iron powder reduction, hydrogenation reduction and zinc powder reduction.
Iron powder reduction method:
Mix p-chloronitrobenzene, water and iron filings and heat to 95°C. After p-chloronitrobenzene is completely dissolved, add concentrated hydrochloric acid dropwise. Adjust the dropping speed so that the temperature Keep it at 25°C. After the dropwise addition, continue the reaction for 25 hours, cool, add excess sodium hydroxide to make the solution alkaline, and distill the oil layer to obtain the product.
![]()
Hydrogenation reduction Method:
Mix p-chloronitrobenzene and ethanol at a mass ratio of 1:1.5, add Raney nickel (made from 100 mesh nickel-aluminum binary alloy) as a catalyst, and heat it at a temperature of 50 to 70°C and a pressure of Under the conditions of 2.94 ~ 3.43 MPa and medium pH = 5 ~ 6, hydrogen gas is passed through the reaction for 2 hours. The obtained crude product is distilled out of ethanol and part of water under normal pressure, and then distilled under reduced pressure to obtain the finished product.
In addition, there is also the reduction of p-chloronitrobenzene and zinc powder in acetic acid medium, which can obtain p-chloroaniline in a higher yield, but the price of zinc powder is higher.
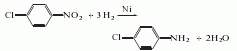
Purpose
1. Dye intermediates. Used in the preparation of azo dyes and naphthol AS-LB. It is also an intermediate in the manufacture of chlordiazepoxide, phenadine tincture and other drugs and pesticides. Also used as a coupler for color film films.
2. Used as dye intermediates, pharmaceuticals, and agricultural chemicals. [27]
