Acrylonitrile Acrylonitrile
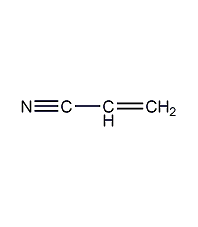
Structural formula
| Business number | 02UR |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C3H3N |
| Molecular weight | 53 |
| label |
vinyl cyanide, 2-Acrylonitrile, Ethylene cyanide, Cyanoethylene, cyanethylene, 2-Propenitrile, Vinyl cyanide, Acrylnitril, Acrylon, Acrylonitrile monomer, Carbacryl, synthetic raw materials |
Numbering system
CAS number:107-13-1
MDL number:MFCD00001927
EINECS number:203-466-5
RTECS number:AT5250000
BRN number:605310
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid with pungent odor. [1]
2. pH value: 6~7.5 (5% solution) [2]
3. Melting point (℃): -83.6[3]
4. Boiling point (℃): 77.3[4]
5. Relative density (water=1): 0.81[5]
6. Relative vapor density (air=1): 1.83[6]
7. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 11.07 (20℃)[7]
8. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -1761.5[8]
9. Critical temperature (℃): 246[9]
10. Critical pressure (MPa): 3.54 [10]
11. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.25[11]
12. Flash point (℃ ): -1 (CC) [12]
13. Ignition temperature (℃): 481[13]
14. Explosion upper limit (%): 17.0[14]
15. Explosion lower limit (%): 3.0[15]
16. Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, easily soluble in most organic solvents. [16]
17. Refractive index (20ºC): 1.3911
18. Viscosity (mPa·s, 25ºC): 0.34
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[17]
LD50: 78mg/kg (rat oral); 27mg/kg (mouse Oral); 148mg/kg (rat transdermal); 63mg/kg (rabbit transdermal)
LC50: 333ppm (rat inhalation, 4h)
2. Irritation[18]
Rabbit transdermal: 500mg, mild irritation.
Rabbit eye: 20mg, severe irritation.
3. Subacute and chronic toxicity[19] Rats, guinea pigs, rabbits and cats at 330mg/m3 Inhalation, 4 hours a day, 5 days a week, half of the animals died within 4 weeks; at a concentration of 220mg/m3, no obvious symptoms of poisoning appeared except for respiratory symptoms for 10 weeks.
4. Mutagenicity [20] Microbial mutagenicity: Salmonella typhimurium 25μl/dish. Mammalian somatic cell mutagenicity: human lymphocytes 25 mg/L.
Human inhalation of 0.8mg/m3 (146 weeks) causesNitriles have higher purity, but hydrocyanic acid is highly toxic and costly. 2. Acetylene method Acetylene and hydrocyanic acid react under the catalysis of cuprous chloride-potassium chloride-sodium chloride dilute hydrochloric acid solution at 80-90°C to obtain acrylonitrile. This method has a simple production process, good yield, and uses hydrogen Cyanic acid content can reach 97%. However, there are many side reactions, the product is difficult to refine, and the toxicity is high. The raw material acetylene is more expensive than propylene, so it lags behind the propylene ammoxidation method in technology and economy. Before 1960, this method was the main method for producing acrylonitrile in various countries around the world. 3. The propylene ammonia oxidation method uses propylene, ammonia, air and water as raw materials, and enters the ebullating bed or fixed bed reactor according to a certain proportion. Under the action of the phosphorus molybdenum bismuth or antimony iron catalyst with silica gel as the carrier , at a temperature of 400-500°C and normal pressure, acrylonitrile is generated. Then use dilute sulfuric acid to remove unreacted ammonia in the neutralization tower, and then absorb acrylonitrile and other gases with water in the absorption tower to form an aqueous solution. The acetonitrile is separated from the aqueous solution through the extraction tower, and the hydrocyanic acid is removed in the dehydrocyanic acid tower and dehydrated. , distillation to obtain acrylonitrile product, the single-pass yield can reach 75%, and the by-products are acetonitrile, hydrocyanic acid and ammonium sulfate. This method is currently the production method with the most industrial production value.
2. Its preparation method mainly uses the propylene ammoxidation method, using propylene, ammonia and oxygen in the air as raw materials, and reacting in the presence of a catalyst. The catalyst mainly contains phosphorus, molybdenum, and bismuth series. The molar ratio of the compound, propylene, ammonia and air is 1: (1~1.2): (1.8~2.3), the reaction temperature is 400~500°C, the reaction pressure is normal pressure, and the reactor is a fluidized bed. ![]()
The single-pass yield of acrylonitrile in this reaction is 60% to 75%.
3. The ethylene oxide method produces cyanoethanol by reacting ethylene oxide and hydrocyanic acid in the presence of water and trimethylamine; then, magnesium carbonate is used as a catalyst and dehydrated at 200~280℃ Produced acrylonitrile:
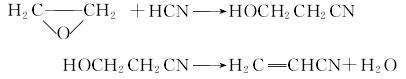
4. The acetylene method is obtained by the reaction between acetylene and hydrocyanic acid. The reaction is under normal pressure and at a temperature of 80 to 90°C. Cuprous chloride and ammonium chloride are used as catalysts. The characteristic of this method is that the production process is simple, but there are many types of by-products that are difficult to separate. The main reaction formula is as follows:
![]()
5. The propylene ammoxidation method uses propylene, ammonia oxygen and oxygen in the air as raw materials. The main by-products are hydrocyanic acid, acetonitrile, acrolein, CO2 and CO. The main reaction is as follows:![]()
The raw material gas is propylene: ammonia: air The ratio of =1.0:1.15:10.5 (mol) enters the fluidized bed reactor from the bottom, with a reaction temperature of 440°C and a pressure of 63.74kPa. The heat of reaction is recycled with soft water to generate high-pressure steam. After the reaction gas is cooled, washed, absorbed, and distilled, a high-purity product is obtained. This method is currently the main production method at home and abroad.
Purpose
1. Acrylonitrile is an important monomer for synthetic fibers, synthetic rubber and synthetic resin. Polyacrylonitrile fiber (acrylic fiber) made from acrylonitrile has properties very similar to wool, so it is also called (synthetic wool). Nitrile rubber can be obtained by copolymerizing acrylonitrile and butadiene, which has good oil resistance, cold resistance, abrasion resistance, and electrical insulation properties, and its performance is relatively stable under the action of most chemical solvents, sunlight and heat. ABS resin is produced by copolymerizing acrylonitrile with butadiene and styrene, which has the advantages of light weight, cold resistance, and good impact resistance. Acrylamide, acrylic acid and its esters can be produced by hydrolysis of acrylonitrile. They are important organic chemical raw materials. Acrylonitrile can also be electrolytically hydrogenated and coupled to produce adiponitrile. Hydrogenation of adiponitrile can also produce hexamethylenediamine, which is the raw material of nylon 66. It can be used to manufacture water-repellent agents and adhesives, etc., and is also used in other organic synthesis and pharmaceutical industries, and as grain fumigants. In addition, this product is also an aprotic polar solvent. It is used as a standard material for chromatographic analysis, and is also used in the manufacture of rubber, plastics, organic synthesis and pesticides. Acrylonitrile is an intermediate of the fungicides bromoclofenil and propamocarb, the insecticides chlorpyrifos, chlorpyrifos, and fenitrocarb. It can also prepare methyl permethrin to produce pyrethroids, which are also insecticides. Nitrile-containing intermediate.
2. It is an important organic synthetic monomer, mainly used in the production of polyacrylonitrile fiber (acrylic fiber), and also used in the manufacture of nitrile rubber and nitrile latex, ABS resin, acrylamide, acrylic acid, ethylene glycol Important products include dinitrile, succinonitrile, methineglutaronitrile, bromodioic acid, etc. It is also a raw material for manufacturing medicines, dyes, pesticides, food additives, antioxidants, and surfactants. As a hard monomer, it is used in the manufacture of acrylic emulsion adhesives.
3. Chromatographic analysis reference material, rubber synthesis. Plastic synthesis, organic synthesis of surfactants and antioxidants, and production of pesticides.
4. Used in the manufacture of polyacrylonitrile, nitrile rubber, dyes, synthetic resins, medicines, etc. [34]
