3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate n-Propyl 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate
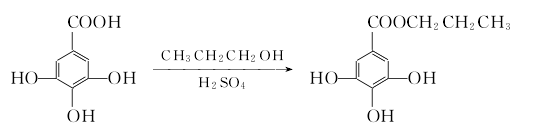
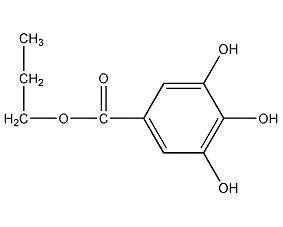
Structural formula
| Business number | 03E2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C10H12O5 |
| Molecular weight | 212.20 |
| label |
propyl gallate, 3,4,5-Trihydroxybenzoic acid n-propyl ester, Propyl benzoate, Propyl-3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate, Propyl gallate, Ranitidine Impurity B, Propyl gallate, propyl gallate, 3,4,5 – 3-hydroxy benzoic acid n-propyl, times the acid ester, propyl -3,4,5 – 3-hydroxy benzoic acid ester, gallic acid ester, Ranitidine impurity B, propylgallate, Antioxidants, Feed additives, food additives |
Numbering system
CAS number:121-79-9
MDL number:MFCD00002196
EINECS number:204-498-2
RTECS number:LW8400000
BRN number:1877976
PubChem number:24898394
Physical property data
1. Properties: White to light brown crystalline powder or milky white needle-like crystals, odorless and slightly bitter.
2. Melting point (℃): 150
3. Water solubility (g/100mL, 25 ºC): 0.35
4. Solubility: easily soluble Insoluble in ethanol, acetone and ether, insoluble in chloroform, fat and water.
Toxicological data
Low toxicity, median lethal dose (rat, oral) LD50: 3800mg/kg. Irritating.
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 52.93
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 155.6
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 436.7
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 62.0
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24 cm3):
7. Polarizability: 20.98
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 3
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 5
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 4
5. Number of tautomers: 14
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 87
7. Number of heavy atoms: 15
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 206
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12.��Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Uncertain number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. The color becomes darker when iron and iron salts are present. Solubility at 25°C: 0.35g/100ml in water, 103g/100g in ethanol, and 83g/100g in ether. The solubility in cottonseed oil is 1.23g/100g at 30℃, and the solubility in lard at 45℃ is 1.14g/100g. Low toxicity. Decomposes above 150℃. Light can promote its decomposition. It is relatively stable in heat, easily soluble in ethanol, ether, acetone, and insoluble in chloroform, aliphatic hydrocarbons and water. It is relatively stable to heat and is helpful for decomposition when exposed to light. It turns purple or dark green when exposed to copper and iron ions, and is hygroscopic.
Storage method
Stored sealed in a cool, dry place away from light.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from the esterification of gallic acid and propanol. Add gallic acid, propanol, benzene, sulfuric acid and p-toluenesulfonic acid to the glass-lined reaction pot, heat and dehydrate, recover benzene, and leave for 2 hours. Pour into water and leave for 24 hours. The crude product is obtained by filtration. The crude product is dissolved in ethanol and filtered. The filtrate is added to water to crystallize, filtered and dried to obtain the finished product. 1. Preparation of gallic acid
Gallnut contains 50% to 70% tannin , Gallic acid can be obtained by enzymatic or hydrolysis of tannins.
(1) Fermentation method Crush the air-dried gallnuts to 0.5-1.0cm, sieve out the insect powder, and extract with 4 times the water at 40-60°C for 18 hours; use the reverse cycle method to extract a total of 4 times , so that the final extract liquid reaches a relative density of 1.058; the extract liquid is decolorized with 5% activated carbon at 50-60°C for 4 hours with thermal insulation and stirring; filter while hot, and wash the filter residue 4 times with water. Combine the filtrate and washing liquid, concentrate under reduced pressure at 60°C to obtain a 30% to 35% tannin solution; cool it to room temperature, add Aspergillus niger seeds with 2% of the total liquid volume, and ferment at about 30°C for 8 to 9d, wash the precipitate with clean water to obtain crude gallic acid, and then recrystallize to obtain the finished product.
(2) Hydrolysis method Add 280kg 95% sulfuric acid to 1670kg 20% tannin solution, stir and hydrolyze at 105°C for 6 hours, or add 150kg 95% sulfuric acid to 1670kg 20% tannin solution, and stir at 133 The reaction was stirred for 2 hours at ~135°C and 0.18~0.20MPa. Cool the reactant to 10°C: precipitate crystals and separate the crude product; then dissolve it in water at 70-80°C, add activated carbon with 5% of the total liquid volume, keep stirring for 10 minutes, and filter while hot; cool the filtrate to room temperature and let it stand 12h, crystallize and separate to obtain the first decolorized fine product; recrystallize it once with the same method to obtain the second decolorized fine product, and obtain 200kg of finished product after drying.
2. Synthesis of PG
In a flask with a water separation device, add 0.1 mol gallic acid, 0.3 mol propanol, 20 mL benzene or 60-80°C petroleum ether and 0.01-0.04 mol p-toluenesulfonic acid , heat and reflux until no obvious water comes out; put the reaction mixture (light purple-red) under normal pressure and then evaporate the excess propanol and water-carrying agent under reduced pressure; with constant stirring, pour the remainder into cold water while it is hot After suction filtration, it was washed with dilute alkali solution and water until neutral, then decolorized, recrystallized with water, and dried at 80°C to obtain white needle-shaped crystals with a melting point of 147~148°C, with a yield of 87.2%~89.5%.
Using 70% perchloric acid instead of p-toluenesulfonic acid, the yield is 88.1% to 88.6%.
Purpose
1. This product is a food and feed additive. It is used as an oxidizing agent for grease, lard, etc. It has strong antioxidant effect, but has the disadvantage of coloring. The dosage is less than 0.1g/kg. When used as a feed antioxidant, the maximum dosage is 100ppm. Can also be used in cosmetics. The oral LD50 in rats is 3.8g/kg.
2.PG is also an oil-soluble antioxidant that is allowed to be used in my country and widely used abroad. The antioxidant capacity of PG on lard is stronger than that of BHA or BHT. When mixed with BHA and BHT, synergists are added to achieve the strongest antioxidant effect. However, the antioxidant effect of pasta products is not as strong as BHA and BHT. Our country stipulates that it can be used in edible oils and fats, fried foods, biscuits, instant noodles, quick-cooked rice, canned nuts, dried fish products and cured meat products, with a maximum usage of 0.1g/kg.
3.Oil-soluble antioxidant. The antioxidant capacity of PG on lard is stronger than that of BHA or BHT. When mixed with BHA or BHT, synergists are added to achieve the strongest antioxidant effect. Our country stipulates that it can be used in edible fats and oils, fried foods, biscuits, instant noodles, quick-cooked rice, canned nuts, dried fish products and cured meat products, with a maximum usage of 0.1g/ kg.
4.Used as an antioxidant for nitrile-phenolic and other adhesives. It can also be used as a food antioxidant and preservative in oils, baked goods, dried fish, biscuits, instant noodles, canned food, jams, preserves, dairy products, bread, ham, juice, etc. The maximum dosage in terms of fat shall not exceed 0.1g/kg. When used together with BHA or BHT, the total amount of BHA or BHT shall not exceed 0.1g/kg, and the total amount of PG shall not exceed 0.05g/kg.
