2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine
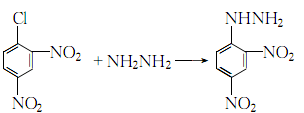
Structural formula
| Business number | 03AL |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H6N4O4 |
| Molecular weight | 198.14 |
| label |
2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine, solution, Dinitrophenylhydrazine, 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (0407 prohibited from air transport), dye |
Numbering system
CAS number:119-26-6
MDL number:MFCD00007578
EINECS number:None
RTECS number:MV3325000
BRN number:615586
PubChem number:24866416
Physical property data
1. Properties: red crystalline powder[1]
2. Melting point (℃): 196~200 (decomposition)[2]
3. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.47[3]
4. Solubility: slightly soluble in Water, ethanol, soluble in acid. [4]
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[5] LD50: 654mg/kg (rat oral); 450mg/kg (mouse intraperitoneal )
2. Irritation[6] Rabbit eye: 500mg (24h), mild irritation.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data available
2. Biodegradability No data available
3 .Non-biodegradability No information available
4. Other harmful effects[7] This substance It is harmful to the environment, and special attention should be paid to the pollution of water bodies.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 47.85
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 119.7
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 366.3
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 87.6
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 18.97
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 2
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 6
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 130
7. Number of heavy atoms: 14
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 235
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Reacts with aldehydes and ketones to produce red-yellow color. This product is flammable and toxic. Explosive when dry. Harmful if inhaled, swallowed or in contact with skin.
2. Irritating to eyes and skin. Sensitizing to skin. If this product is absorbed into the body, it can cause methemoglobinemia and cyanosis. Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The warehouse temperature should not exceed 30℃. Protect from direct sunlight. Keep container tightly sealed. for safetyIt is common to see that it is often moistened and passivated with no less than 25% water during storage and transportation.
3. Stability[8] Stable
4. Incompatible substances[9] Strong oxidizing agent
5. Conditions to avoid contact [10] Heat, vibration, impact
6. Polymerization hazard[11] No polymerization
7. Decomposition products[12] Nitrogen oxides
Storage method
Storage Precautions[13] For safety reasons, always moisten and passivate with no less than 25% water during storage. Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 35℃. The packaging is sealed. should be kept away from oxidizer, do not store together. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
1. Suspend hydrazine sulfate in hot water, add potassium acetate while stirring, boil the mixture for 5 minutes, cool to 70°C, and add ethanol. Filter out the solid, wash with ethanol, and the filtrate is hydrazine solution. Dissolve 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene in ethanol, add the above hydrazine solution, stir and reflux for 1 hour, filter after cooling, wash away unreacted raw materials with ethanol, wash with hot water, and dry to obtain 2,4- Dinitrophenylhydrazine (part of the product can be recovered by concentrating the filtrate), with a yield of 81-85%.
2. Suspend hydrazine sulfate in hot water, add potassium acetate, boil and cool, add ethanol, filter out the solid, wash with ethanol to obtain the filtrate. Add 2,4-dinitrophenyl ethanol to the above hydrazine solution, filter, wash, dry and concentrate the filtrate to obtain 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine.
3. Heat 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene to 70-80°C with industrial ethanol to dissolve, add activated carbon, heat to boiling with stirring, filter while hot, and then cool to 70-80°C. Slowly add 50% hydrazine hydrate to the filtrate at ℃, stirring while adding. When 1/5 is added, the reaction becomes intense and reflux begins. After adding hydrazine hydrate, keep it warm and reflux for 1.5 to 2 hours, and stir every 20 to 30 minutes:
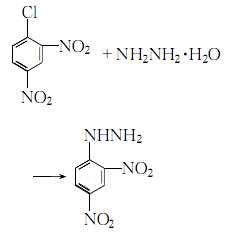
After the reaction is completed, let it cool to 50°C, filter the crystals obtained, soak them in ethanol, wash them with hot water, and dry them.
4. Add hot water to hydrazine sulfate, stir to form a suspension, then add anhydrous potassium acetate, heat and boil for 5 minutes. Cool to 70°C, add ethanol, filter out the solid and wash with ethanol to obtain a hydrazine solution for later use. Dissolve 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene in ethanol, add the reserved hydrazine solution dropwise while stirring, and reflux for 1 hour after the addition:
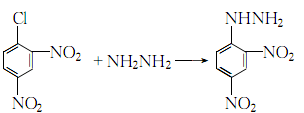
After the reaction is completed, the crystallization is cooled and the filtered crystals are washed with hot ethanol and hot water in sequence to obtain the finished product. The filtrate can be recycled: first concentrate, and the crystals obtained by cooling are recrystallized with n-butanol.
Purpose
1. Determination of aldehydes, ketones and synthetic camphor, determination of transaminase and liver function. Used as reagents for testing aldehydes and ketones and chromatographic analysis reagents.
2. Color reagent used for determination of aldehydes and ketones by thin layer chromatography. Used as UV derivatization reagent for aldehydes and ketones, used in organic synthesis and explosives manufacturing.
3. Used as a chromogenic reagent for the determination of aldehydes and ketones by photometry and as a chromogenic reagent for the determination of aldehydes and ketones by thin layer chromatography. Also used as UV derivatization reagent for aldehydes and ketones. Used in organic synthesis.
4. Used in the manufacture of explosives and also as chemical reagents. [14]
