Chlorophyll A
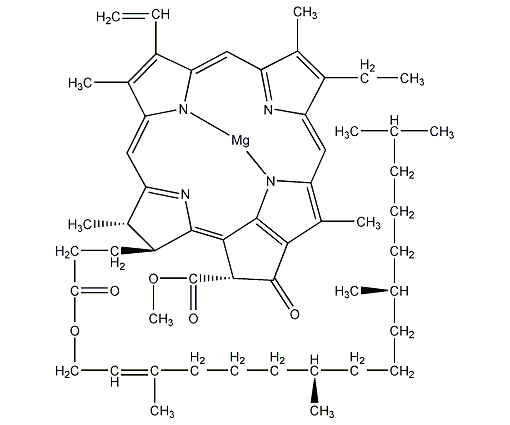

Structural formula
| Business number | 051Q |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C55H72MgN4O5 |
| Molecular weight | 893.49 |
| label |
None yet |
Numbering system
CAS number:479-61-8
MDL number:MFCD00079050
EINECS number:207-536-6
RTECS number:FW6420000
BRN number:3586237
PubChem number:24892839
Physical property data
1. Character:Waxy solid
2. Density (g/ m3,25/4℃): Undetermined
3. Relative vapor density (g/cm3,AIR=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC):34-36
5. Boiling point (ºC,Normal pressure):170
6. Boiling point (ºC,5.2kPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive Index: Undetermined
8. Flash Point (ºC):230
9. Specific optical rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa,25ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa,60ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Oil and water (octanol/Log value of water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion limit (%,V/V): Undetermined
18. Lower explosion limit (%,V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: insoluble in water
Toxicological data
None
Ecological data
Generally not hazardous to water, do not discharge material into the surrounding environment without government permission.
Molecular structure data
None
Compute chemical data
1. Hydrophobic parameters Calculate the reference value (XlogP):0
2. Hydrogen Bonding Number of donors: 9
3. Hydrogen Bonding Number of receptors: 22
4. Rotatable Number of chemical bonds: 3
5. Interchange Number of isomers:
6. Topological molecules Polar surface area (TPSA):96.4
7. Heavy Atom Quantity: 65
8. Surface charge :0
9. Complexity :2130
10. Isotope atomic number:0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters:3
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters:2
13. Determine the number of stereocenters of chemical bonds:1
14. Uncertain number of chemical bond stereocenters:0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 2
Properties and stability
Use and store according to specifications, no decomposition will occur, and avoid contact with oxides
Storage method
Seal and store at 2-8°C in a ventilated and dry place to avoid contact with other oxides.
Synthesis method
Most of them use plants (such as spinach, etc.) or dried silkworm sand as raw materials to extract chlorophyll. For example, the following method can be used to extract chlorophyll from silkworm sand. Organic solvent extraction: Take clean silkworm sand, mix it into a slurry with more than 70% industrial ethanol, filter out the dark green solution, and then dry it. Another operation is to mix 45 parts of petroleum ether, 15 parts of methanol, and 4 parts of benzene, mix with clean silkworm sand to make a slurry, filter, and wash the filtrate 4 times with water. Add a small amount of sodium sulfate to the organic extract to remove residual moisture, filter, and recover the solvent from the filtrate to obtain chlorophyll. Physical separation: Mix 0.4mol/L dilute sucrose solution and 0.06mol/L potassium phosphate dilute solution (pH 6-7) at a ratio of 1:1 to form a buffer medium. Add about 1L of buffer medium for every 2kg of silkworm sand, mix evenly, filter out the green suspension with multi-layer emery cloth, put it into a low-temperature centrifuge and centrifuge for 5-10 minutes, wash the precipitate with water, and centrifuge again to get the chlorophyll precipitate. Chlorophyll is treated with oxalic acid to obtain magnesium-free pheophytin, and then magnesium is introduced and converted back into chlorophyll. Removal of phytol and magnesium with strong acid results in pheophorbide, and phytol can also be reintroduced. Hydrolysis removes phytol and methanol to obtain chlorophyllin. Most of them use plants (such as spinach, etc.) or dried silkworm sand as raw materials to extract chlorophyll. For example, the following method can be used to extract chlorophyll from silkworm sand. Organic solvent extraction: Take clean silkworm sand, mix it into a slurry with more than 70% industrial ethanol, filter out the dark green solution, and then dry it. Another operation is to mix 45 parts of petroleum ether, 15 parts of methanol, and 4 parts of benzene, mix with clean silkworm sand to make a slurry, filter, and wash the filtrate 4 times with water. Add a small amount of sodium sulfate to the organic extract to remove residual moisture, filter, and recover the solvent from the filtrate to obtain chlorophyll. Physical separation: Mix 0.4mol/L dilute sucrose solution and 0.06mol/L potassium phosphate dilute solution (pH 6-7) at a ratio of 1:1 to form a buffer medium. Add about 1L of buffer medium for every 2kg of silkworm sand, mix evenly, filter out the green suspension with multi-layer emery cloth, put it into a low-temperature centrifuge and centrifuge for 5-10 minutes, wash the precipitate with water, and centrifuge again to get the chlorophyll precipitate. Chlorophyll is treated with oxalic acid to obtain magnesium-free pheophytin, and then magnesium is introduced and converted back into chlorophyll. Removal of phytol and magnesium with strong acid results in pheophorbide, and phytol can also be reintroduced. Hydrolysis removes phytol and methanol to obtain chlorophyllin.
Purpose
Edible green coloring. Used in pastries, beverages, liqueurs, etc. In fact, the leaves or dried powder of the plant are often used directly. For example, tea powder, mugwort, spinach, chlorella, etc. Added to gum to eliminate bad breath. Chlorophyll is used to color soaps, mineral oils, waxes and essential oils. Derivatives of chlorophyll or chlorophyllin, such as copper chlorophyll [11006-34-1], sodium iron chlorophyllate, sodium copper chlorophyllin, are used as colorants and deodorants in food, candy, beverages, toothpaste, etc. Chlorophyllin derivatives can be used together with the fungicides benzalkonium chloride, halocarban, etc. to formulate smelly cosmetics.
