Ethylene glycol monoacetate
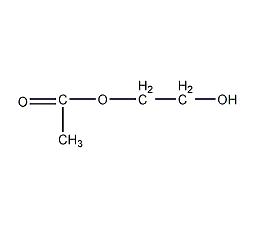

Structural formula
| Business number | 05LN |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H8O3 |
| Molecular weight | 104.10 |
| label |
2-hydroxyethyl acetate, Ethylene glycol monoacetate, 2-acetyl ethanol, 1,2-Ethanediol monoacetate, 2-Hydroxyethyl acetate, 2-Acetoxyethanol, paint remover, cellulose acetate solvent, Cosmetic fragrance solvent |
Numbering system
CAS number:542-59-6
MDL number:None
EINECS number:208-821-8
RTECS number:KW7175000
BRN number:1743114
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid with slight fruity aroma.
2. Density (g/cm3, 20/4℃): 1.109
3. Relative steam density (g/cm3 , air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): -61.7
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 180~190 p>
6. Boiling point (ºC, 66.70kPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive index (18ºC): 1.4175
8. Flash point (ºC, open): 101.7
9. Specific rotation (º): Not determined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Not determined
11. Vapor Pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 55.1ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Oil and water (octanol/water) distribution Log value of coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Soluble in water, alcohol, ether, aromatic hydrocarbons and other solvents, but insoluble in linear hydrocarbons. Can dissolve rosin, camphor, elemi, cellulose acetate, cellulose acetate-butyrate, nitrocellulose, ethyl cellulose, polymethyl methacrylate, polystyrene and polyvinyl acetate, etc.
Toxicological data
1. Skin/eye irritation data: Standard Draize test rabbit direct contact with eyes: 100mgREACTION SEVERITY: severe;
2. Acute toxicity: rat oral LD50: 8250mg/kg, behavior – lethargy ( Common depressive activity), gastrointestinal tract – other changes;
Rat dermal LD: >25 mL/kg, except lethal agentsNo detailed explanation beyond the dosage;
Mouse abdominal LD50: 1310 mg/kg, lung, chest or respiratory – acute lung water and other changes;
Guinea pig oral LD50: 3800 mg /kg, behavior – general anesthesia gastrointestinal, kidney, ureter, bladder – other changes;
3. Other multiple dose toxicity data: rat transdermal TDLo: 63 mL/kg/3W-I, blood – Changes in serum components (such as tea polyphenols, bilirubin, cholesterol), enzyme inhibition, induction or changes in blood or tissue levels of phosphatase and aminotransferase.
Ecological data
This substance may be harmful to the environment, and special attention should be paid to water bodies.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 23.89
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 95.5
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 232.7
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 35.2
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 9.47
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): -0.6
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
p>
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 3
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 46.5
7. Number of heavy atoms: 7
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 60
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Use and store according to specifications. It will not decompose and avoid contact with oxides. It is non-corrosive to metals, but it is not suitable to use copper containers because the acetic acid generated by hydrolysis is corrosive to copper. Its chemical properties are similar to ethylene glycol diacetate and is easily hydrolyzed in the presence of acid or alkali.
2. Exist in smoke.
Storage method
Stored in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Keep container tightly sealed. Should be stored separately from oxidizing agents. When handling, load and unload with care to prevent damage to packaging and containers.
Synthesis method
The direct esterification method of ethylene glycol and acetic acid is commonly used to synthesize ethylene glycol acetate. Toluene is generally used as the dehydrating agent and Lewis acid catalyst is used. Typical catalysts include iron-loaded molecular sieves, zinc chloride or ferric chloride.
Refining method: Continuous extraction with water-diisopropyl ether can remove ethylene glycol diacetate.
Purpose
Used as paint remover, cellulose acetate solvent and cosmetic fragrance solvent.
