1H-Benzotriazole 1H-Benzotriazole
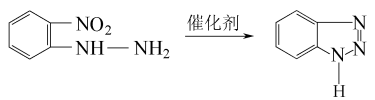
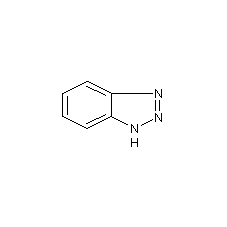
Structural formula
| Business number | 028N |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C7H5N3 |
| Molecular weight | 119.12 |
| label |
phenyltriazole, 1H-benzotriazole, Benztriazole, benzotriazepine, Indyne, benzotriazole, 1,2,-aminozophenylene, 1,2,3-triaza-1h-indene, 1,2,3-Benzotriazole, BTA, corrosion inhibitor, Heterocyclic compounds |
Numbering system
CAS number:95-14-7
MDL number:MFCD00005699
EINECS number:202-394-1
RTECS number:DM1225000
BRN number:112133
PubChem number:24847810
Physical property data
1. Properties: White to light brown needle-like crystals. Odorless. It oxidizes in the air and gradually turns red. Can explode when distilled in vacuum.
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4℃): Undetermined
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 98.5
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 204
6. Boiling point (ºC, 5.2kPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive index: Undetermined
8. Flash point (ºC): 170
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure ( kPa, 60ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/ V): Undetermined
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Soluble in ethanol, benzene, toluene, chloroform and dimethyl Formamide, slightly soluble in cold water. Insoluble in petroleum solvents.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: Rat oral LD50: 560mg/kg; Rat inhalation LD50: 1910mg/m3/24H; Rat skin contact LD50: >1mg/kg; Mouse oral LC: 615mg/kg; Mouse abdominal LC50: 400mg/kg; Mouse intravenous LC50: 238mg/kg; Rabbit skin contact LDLo: 450mg/kg; Guinea pig oral LD50: 500mg/kg;
2. Other multiple-dose toxicity: rat inhalation TDLo: 109mg/kg/26W-I;
3. Chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity
Rat Oral TDLo: 220mg/kg/78W-I; Mouse oral TDLo: 770mg/kg/78W-I;
4. Mutagenicity
Mutation of microorganism Salmonella typhimurium : 100μg/plate;
E. coli mutation: 33300μg/plate;
Rat embryonic morphological transformationAfter reacting for 3 hours, cool and use concentrated sulfuric acid to adjust the Pa value from 11.7 to 6 to obtain benzotriazole with a purity of 100% and a yield of 96.9%.
4.Benzimidazolone method Benzimidazolone and sodium nitrite aqueous solution react at 190℃ and high pressure for 75 minutes. After acidification, water washing and drying, the product was obtained with a yield of 85.3%.
5.O-nitrophenylhydrazine method o-Nitrophenylhydrazine is in a mixed aqueous solution of ammonia, isopropyl alcohol and hexylene glycol, React at 140°C and high pressure for 1.5 hours to generate 1-hydroxybenzotriazole (HBTA). Use copper-chromium trioxide as a catalyst, introduce hydrogen and nitrogen in a ratio of 92:8, and perform a deoxygenation and hydrogenation reaction at 160 to 170°C and high pressure for 1 hour. HBTA is deoxygenated and hydrogenated to generate BTA, and finally benzotriazole is recovered. The rate is 89%. The reaction formula is as follows:
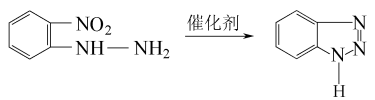
6.The o-nitrochlorobenzene method first directly synthesizes HBTA from o-nitrochlorobenzene and hydrazine hydrate, and then deoxygenates and hydrogenates Generate BTA, with the highest overall yield reaching 8.6%. The advantages of this method are high yield and few intermediate links. It is a promising and important method.
Purpose
1. When combined with ammonium hydroxide and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, it can selectively determine silver, copper, and zinc. Photographic anti-fogging agent. Photographic inhibitors. Organic Synthesis.
2.Benzotriazole has an anti-corrosion effect on metal materials such as copper, aluminum, cast iron, nickel, and zinc. It can be used with a variety of corrosion inhibitors, such as chromate, polyphosphate, molybdate, silicate, nitrite, ATMP, HRDP, EDTMP, etc., to improve the corrosion inhibition effectFruit. It has excellent corrosion inhibition effect in closed circulation cooling water system. It can be used in conjunction with a variety of scale inhibitors and bactericidal algaecides. Benzotriazole does not interfere with the corrosion inhibition of polyphosphate and has strong resistance to oxidation. However, when it exists at the same time as free chlorine, it loses its corrosion inhibition effect on copper, and after the disappearance of chlorine, its corrosion inhibition effect is restored. Its usage concentration is generally 1 to 2 mg/L, and its corrosion inhibition effect is very good in the pH range of 5.5 to 10, but when the pH value is low The corrosion inhibition effect is reduced in the medium.
3.Added into epoxy resin adhesive to prevent corrosion and blackening of copper and its alloys. The reference dosage is 0.2%~0.5%. For water-soluble adhesives, the adding amount is 0.005% to 0.1%. It is also widely used as anti-rust agent for copper, silver, zinc, aluminum, cast iron and other metals, water purifier, anti-fogging agent in the photographic industry, ultraviolet absorber, paint additive, preservative for synthetic detergents, anticoagulant, lubrication Oil additives, synthetic dye intermediates, polymer material stabilizers, plant growth regulators, anti-discoloration agents, gas phase corrosion inhibitors, antistatic and automotive antifreeze additives, etc.
4.Widely used for corrosion inhibition and rust prevention of copper and silver equipment. It can also be used for the preparation of photographic anti-fog, anti-fog, and gas-phase rust inhibitors.
5.Benzotriazole does not interfere with the corrosion inhibition effect of polyphosphate and has strong resistance to oxidation. . However, when it exists with free chlorine at the same time, it loses its corrosion inhibition effect on copper. After the chlorine disappears, its corrosion inhibition effect is restored. This is a property that MBT cannot have.
6.Used as metal rust and corrosion inhibitor, anti-tarnish agent for copper and silver, and photographic anti-fogging agent.
