Methyl iodide Iodomethane
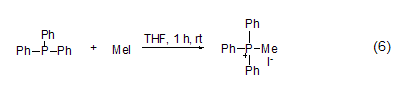
Structural formula
| Business number | 01HL |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | CH3I |
| Molecular weight | 141.94 |
| label |
Methyl iodide, Monoiodomethane, Methyl iodide, methylation reagents, Extinguishing agent, Halogenated hydrocarbon solvents |
Numbering system
CAS number:74-88-4
MDL number:MFCD00001073
EINECS number:200-819-5
RTECS number:PA9450000
BRN number:969135
PubChem number:24857202
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless and transparent liquid with a special odor. Turns brown when exposed to light. [12]
2. Melting point (℃): -66.5[13]
3. Boiling point (℃): 42.5[14]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 2.3[15]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 4.89[16]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 50 (20℃)[17]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -813.8[18]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 254.8[19]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 7.36[20]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.51~1.69[21]
11. Solubility: slightly soluble in water, soluble in ethanol and ether. [22]
12. Refractive index at room temperature (n25): 1.5270
13. Eccentricity factor: 0.193
14. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 20.172
15. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 4.600×109
16. van der Waals volume (cm3 ·mol-1): 32.850
17. Gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): 14.7
18. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 253.81
19. Gas phase standard Free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1): 16.4
20. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K -1): 44.08
21. Liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -12.3
22. Liquid phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 162.8
23. Liquid phase standard free energy of formation (kJ ·mol-1): 16.5
24. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1):82.91
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[23]
LD50: 100~200mg/kg (rat oral)
LC50: 1300mg/m3 (rat inhalation, 4h)
2. Irritation[24] Human Transdermal: 1g (30min), mild irritation.
3. Mutagenicity [25] Microbial mutagenicity: Salmonella typhimurium 2μl/dish; Escherichia coli 20μmol/L. Mammalian somatic cell mutagenicity: mouse lymphocytes 15mg/L (2h). DNA damage: E. coli 1μmol/L.
4. Carcinogenicity [26] IARC Carcinogenicity Comment: G3, insufficient evidence of carcinogenicity to humans and animals.
Ecological data
<ester. Phenolic hydroxyl groups can often also be methylated under such conditions[3], while fatty alcohol methylation usually occurs in aprotic polar solvents using stronger bases (Formula 2) [4].

S -Methylation Methyl iodide can methylate sulfides such as thiols [5] to obtain sulfides and sulfonium salts. For example, the reaction between thioamide and methyl iodide in THF can methylate thio to form thioether (formula 3)[6].

N -Methylation Methylation of ammonia and primary amines with methyl iodide is generally not a good method because further methylation will occur, but for secondary and tertiary amines Methylation is a better method and can be used to prepare tertiary amines and quaternary ammonium salts[7]. In acetonitrile solvent, tritylamine is methylated with methyl iodide to obtain the product with higher yield (Formula 4)[8]. The nitrogen atoms in the heterocyclic ring can also be methylated with methyl iodide (Formula 5)[9,10].
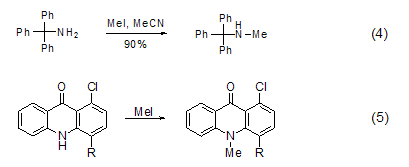
P -Methylation The reaction between three-coordinated phosphorus and methyl iodide can generate salt (formula 6) [11]. Usually, this reaction occurs in polar solvents such as acetonitrile, Perform in DMF or THF.
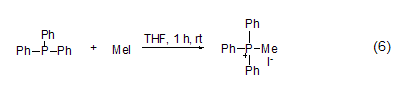
3. Used in medicine, organic Synthesis, testing of pyridine, microscopy, etc. [35]
