Dibutyltin dilaurate Di-n-butyltin dilaurate
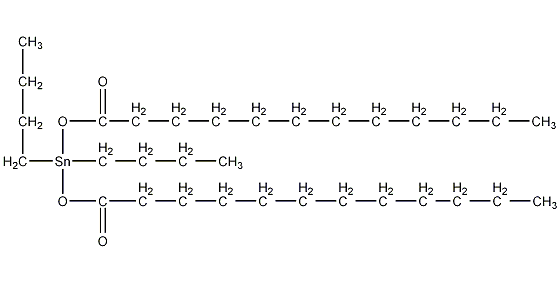
Structural formula
| Business number | 01LX |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C32H64O4Sn |
| Molecular weight | 631.56 |
| label |
Dibutyltin dilaurate, Di-n-butyltin dilaurate, dibutyltin laurate, Dibutylbis(1-oxododecanoxy)tin, Di-n-Butyldilauryltin, Di-n-Butyltin dilaurate, Dibutylbis(lauroyloxy)tin, Dibutyltin didodecanoate, Dibutyltin dilaurate, Dibutyltin(iv) dilaurate, Dibutyltin laurate, (CH3CH2CH2CH2)2Sn[OCO(CH2)10CH3]2, Heat stabilizers, lubricants, catalyst, Curing agent for silicone rubber |
Numbering system
CAS number:77-58-7
MDL number:MFCD00008963
EINECS number:201-039-8
RTECS number:WH7000000
BRN number:4156980
PubChem number:24857520
Physical property data
1. Properties: light yellow transparent oily liquid
2. Density (g/mL, 20℃): 1.066
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, Air=1): 21.8
4. Melting point (ºC): 22~24
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): Undetermined
6. Boiling point (ºC, 10mmHg): >204
7. Refractive index: 1.468~1.470 (25℃)
8. Flash point (ºC): 235
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): 235
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 20ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 160ºC): 0.027
13. Heat of combustion ( KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. The logarithmic value of the oil-water (octanol/water) distribution coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Insoluble in water, methanol, soluble in ether, acetone, benzene, carbon tetrachloride, petroleum ether, ester, soluble in…There are industrial plasticizers and most common organic solvents such as ethyl acetate, chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, benzene, ethane, petroleum ether, etc., which are insoluble in water, but are hydrolyzed after emulsification.
Toxicological data
1. Skin/Eye Irritation
Standard Draize test: rabbit, skin contact: 500mg, severity of reaction: severe.
Standard Draize test: Rabbit, eye contact: 100mg/24H, severity of reaction: moderate.
2. Acute toxicity: mus oral LD50: 2100mg/kg;
Ecological data
This substance is harmful to the environment and it is recommended not to let it enter the environment.
Slightly hazardous to water, avoid contact of undiluted or large quantities of product with groundwater, waterways or sewage systems.
Severely harmful to fish and organic matter.
Molecular structure data
None yet
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 2.8
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 4
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 30
5. Topological molecular polar surface area (TPSA): 52.6
6. Number of heavy atoms: 37
7. Surface charge: 0
8. Complexity: 477
9. Number of isotope atoms: 0
10. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters : 0
11. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Determined number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
13. Uncertain chemical bond positions Number of structural centers: 0
14. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Reacts with strong oxidants and alkalis. It is hydrolyzed after emulsification.
This product is toxic. The maximum allowable concentration in the air is 0.1mg/m3.
Storage method
Packed in tinplate barrels, it is a poisonous product and the dangerous goods number is 61857. Store in a cool, dry and ventilated place. Protect from heat, moisture, sun and organic solvents.
Synthesis method
(1) Preparation of di-n-butyltin diiodide It is prepared from iodine, red phosphorus, butanol, tin powder, magnesium powder, hydrochloric acid and solid alkali. For specific operation methods, see the preparation method of dibutyltin monobutyl maleate.
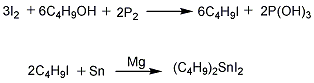
(2) Preparation of finished product Add 1 mol of lauric acid (industrial product) to the reaction kettle, raise the temperature to 60°C with stirring, and slowly add 2.1mol caustic soda is prepared into a 20% solution. After adding the alkali solution, stir for 0.5 to 1 hour, raise the temperature to 80 to 90°C, add 1 mol of di-n-butyltin diiodide, maintain 80 to 90°C, and react for 1.5 to 2 hours. After leaving for 15 to 30 minutes, sodium iodide will precipitate out as a solid, which will be recovered by filtration and then refined. The material from which sodium iodide is separated is distilled under reduced pressure, cooled and filtered to obtain the finished product.

Purpose
It can be used as a heat stabilizer for polyvinyl chloride plastics. It has excellent lubricity, weather resistance and transparency, and is resistant to sulfide pollution. It has good compatibility with plasticizers, has no adverse effects on heat sealability and printability, and has better kneading and dispersion in plastics than solid stabilizers. It can be used as the main stabilizer for soft transparent products or semi-soft products, and can be used as a lubricant in hard products. This product can also be used as a curing agent for silicone rubber at room temperature, a stabilizer for synthetic fibers and a catalyst for the synthesis of polyurethane materials. Stabilizers, etc. Compared with other organotins, this product has greater initial coloration, which may cause yellowing and discoloration of the product.
