2-Methylbutane 2-Methylbutane
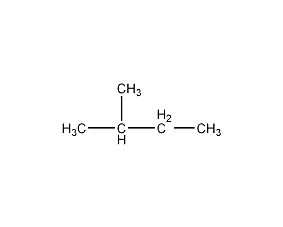
Structural formula
| Business number | 01NJ |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C5H12 |
| Molecular weight | 72.15 |
| label |
Ethyldimethylmethane, isopentane, 1,1,2-Trimethylethane, IsoPentane, Isoamyl hydride, 1,1,2-Trimethylethane, Industrial foaming agent |
Numbering system
CAS number:78-78-4
MDL number:MFCD00009338
EINECS number:201-142-8
RTECS number:EK4430000
BRN number:1730723
PubChem number:24856746
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless, transparent and volatile liquid with pleasant aromatic odor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -159.9[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 27.8[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.62[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 2.48[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 79.31 (21.1℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -3405.1[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 187.8[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 3.33[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 2.3 [10]
11. Flash point (℃): <-51 (CC) [11]
12. Ignition temperature (℃): 420[12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 7.6[13]
14. Lower explosion limit (%): 1.4[14]
15. Solubility: insoluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol, soluble in most organic solvents such as hydrocarbons and ether. [15]
16. Total combustion calorific value (KJ/mol): 3505.65
17. Minimum combustion calorific value (KJ/mol): 3241.38
18. Viscosity (20℃, liquid)/mPa·s: 0.299
19. Heat of evaporation (0ºC) (kJ/mol): 25.89
20. Heat of fusion (kJ/mol): 5.158
21. Aniline point (ºC): 70.7
22. Thermal conductivity (25º, liquid )/[W/(m·K)]: 105.51×10-3
23. Heat of formation (25º, liquid)/ / (kJ·mol): -179.40
24. Specific heat capacity (25º, constant pressure)/[kJ/(kg·K)]: 2.27
25. Critical density (g·cm-3
sup>): 0.236
26. Critical volume (cm3·mol-1): 306
27. Critical Compression factor: 0.270
28. Eccentricity factor: 0.228
29. Lennard-Jones parameter (A): 6.1037
30. Lennard-Jones parameter (K ): 250.23
31. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 13.858
32. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 8.280×109
33. van der Waals volume ( cm3·mol-1): 58.020
34. Gas-phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1 sup>): -3529.20
35. Gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -153.34
36. Gas phase standard Entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 343.74
37. Gas phase standard formation free energy (kJ·mol– 1): -13.5
38. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 118.87
39. Liquid phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -3503.97
40. Liquid phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -178.57
41. Liquid phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 260.54
42. Liquid phase standard formation free energy (kJ·mol-1): -14.14
43. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J· mol-1·K-1): 164.89
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[16] LC50: 280000mg/m3 (rat inhalation, 4h); 150000mg/m3(mouse inhalation, 2h)
2. Irritation No information available
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data available
2. Biodegradability No data available
3 .Non-biodegradability[17] In the air, when the concentration of hydroxyl radicals is 5.00×105/cm3 When, the degradation half-life is 4.2d (theoretical).
4. Other harmful effects [18] This substance is harmful to the environment, and special attention should be paid to the pollution of water bodies.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 25.17
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 111.4
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 228.4
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 17.6
5. Dielectric constant (F/m): 1.83
6. Polar Chemical rate (10-24cm3): 9.97
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 2.6
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 0
7. Number of heavy atoms: 5
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 14
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Chemically inactive. However, because there are hydrogen atoms on the tertiary carbon atom, it is more susceptible to oxidation than other similar compounds.
2. Stability[19] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[20] Strong oxidants, strong acids, strong bases, halogens
4. Polymerization hazards[21] No polymerization
Storage method
Storage Precautions[22] Stored in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 29℃. Keep container tightly sealed. should be kept away from oxidizer, do not store together. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. It is separated from petroleum cracking products or platinum reformed oil. The impurities contained in industrial grade 2-methylbutane are alkanes with similar boiling points, naphthenes, unsaturated hydrocarbons and moisture. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are removed by washing with concentrated sulfuric acid; water is removed with dehydrating agents such as anhydrous calcium chloride, phosphorus pentoxide or metallic sodium, or molecular sieves can be used for dehydration; finally, they are fractionated and refined, and the distillate is treated with a high-temperature activated silica gel adsorption column. Remove trace amounts of linear hydrocarbon impurities. Using pentane as raw material, 2-methylbutane can be obtained through liquid phase catalytic isomerization at 95°C.
2. Dehydrate tert-amyl alcohol to obtain a mixture of 2-methyl-1-butene, 2-methyl-2-butene and 3-methyl-1-butene, which is hydrogenated The crude isopentane is obtained by treatment, and then high-purity isopentane is obtained by distillation. Natural gas condensate can also be used as raw material, and C2, C3, C4 and n-pentane fractions can be removed through pressurized distillation to produce high-purity isopentane.
3. Use industrial product isopentane as raw material, wash it several times with concentrated sulfuric acid under strong stirring until the acid layer is colorless, let it stand to separate the acid layer, and then wash with water and 5% hydrogen in turn. Alkaline washing with sodium oxide, washing with water, leaving to separate the water layer, then adding anhydrous calcium chloride and drying. Aspirate the supernatant liquid and distill it. The distillate passes through a pre-activated silicon adsorption column to remove trace amounts of linear hydrocarbons to obtain pure product.
4.![]()
In the atmospheric hydrogenation reaction bottle (placed in an ice bath on a magnetic stirrer), add 100 mg of Adam’s platinum oxide, 2-methyl-2-butene (2) 9.8 ( 0.14 mol), replace the air with nitrogen, repeat twice, and then replace the nitrogen with hydrogen. Remove the cold bath, start the magnetic stirrer, and perform hydrogenation under normal pressure until approximately 3L of hydrogen is absorbed. Cool the reactant, transfer the liquid in the reaction bottle to a distilling bottle, distill (ice water is passed into the condenser, and the receiving bottle is placed in an ice bath), and the fraction at 30°C is collected to obtain 2-methylbutane ( 1) 7g, yield 70%. [24]
Purpose
1. When used as a solvent, it has the same function as pentane, hexane, heptane, etc., but its solubility is slightly worse than pentane. This product has a high octane number and can be used as fuel for automobiles and aircraft.
2. Used as solvent and gas chromatography reference liquid, and also used in organic synthesis.
3. Used in organic synthesis, and also used as solvent and foaming agent for polystyrene. [23]
��The same, but its solubility is slightly worse than that of pentane. This product has a high octane number and can be used as fuel for automobiles and aircraft.
2. Used as solvent and gas chromatography reference liquid, and also used in organic synthesis.
3. Used in organic synthesis, and also used as solvent and foaming agent for polystyrene. [23]
