N-Methylaniline N-Methylaniline
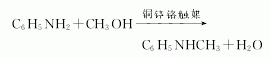
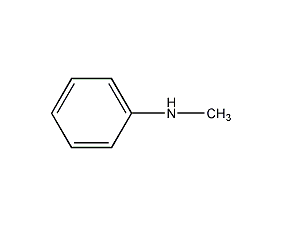
Structural formula
| Business number | 02JC |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C7H9N |
| Molecular weight | 107.16 |
| label |
Toluidine, Methylphenylamine, Methylphenylamine, Methylaniline, N-Methylbenzeneamine, Aromatic nitrogen-containing compounds and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:100-61-8
MDL number:MFCD00008283
EINECS number:202-870-9
RTECS number:BY4550000
BRN number:741982
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless to reddish brown oily liquid. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -57[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 196.2[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.99[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 3.70[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 0.13 (36.0℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -4069.2[7]
8. Critical pressure (MPa): 5.2[8]
9. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.66[9]
10. Flash point (℃): 78.89 [10]
11. Ignition temperature (℃): 511[11]
12. Explosion limit (%): 7.4 [12]
13. Lower explosion limit (%): 1.2[13]
14. Solubility: slightly soluble Soluble in water, soluble in ethanol, ether and chloroform. [14]
15. Viscosity (mPa·s, 15ºC): 2.568
16. Viscosity (mPa·s, 30ºC): 1.766
17. Heat of evaporation (KJ/kg, 193.6ºC): 423.6
18. Heat of formation (KJ/mol, liquid): 32.19
19. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol, constant volume): 4075.9
20. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 20~190ºC, constant pressure): 2.148
21. Conductivity ( S/m, 20ºC): <10-7
22. Thermal conductivity (W/(m·K), room temperature): 0.185057
23. Body expansion coefficient (K-1): 0.000815
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: cat intravenous LDL0: 24mg/kg; rabbit oral LDL0: 280mg/kg; rabbit intravenous LDL0: 24mg/kg; guinea pig oral LDL0: 1200mg/kg; guinea pig subcutaneous LDL0: 1200mg/ kg;
2. Other multi-dose toxicity: rats inhaled TCLo: 300μg/m3/24H/14W-C;
3. Can be absorbed through the skin and cause poisoning. Acute symptoms include nerve damage and hematuria. Chronic symptoms include deterioration of the bladder mucosa. Carcinogenic. TJ 36-1979 stipulates that the maximum allowable concentration in workshop air is 5 mg/m3. The oral LD50 in rats is about 280 mg/kg.
4. Acute toxicity No data yet
5. Irritation No data
6. Others[15] LDLo: 280mg/kg (rabbit oral)
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data available
2. Biodegradability No data available
3 .Non-biodegradable[16] In the air, when the concentration of hydroxyl radicals is 5.00×105/cm3, the degradation half-life is 8.8h (theoretical).
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 35.86
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 108.8
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 266.1
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 35.6
5. Polarizability: 14.21
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 12
7. Number of heavy atoms: 8
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 55.4
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Chemical properties: It is weakly alkaline and forms salts with acids. Easily reacts with alkylating agents to obtain N-alkyl derivatives. Reacts with nitrous acid to form nitrosamines. Gradually turns brown in the air.
2. It has roughly the same toxicity as aniline. The maximum allowable concentration in the air in the workplace is 5×10-6. Production equipment should be airtight. Operators should wear protective equipment.
3. Stability[17] Stable
4. Incompatible substances[18] Acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, strong oxidants
5. Conditions to avoid contact[19] Heating
6. Aggregation hazards[20] No aggregation
Storage method
Storage Precautions[21] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. There are several methods: mix aniline vapor and methyl ether, react with activated alumina catalyst at 230-295°C to prepare it. Aniline and methanol generate crude N-methylaniline under the action of lead-zinc-chromium catalyst. Then, methanol, water, aniline and N,N-dimethylaniline are removed by distillation to obtain N-methylaniline finished product. This reaction can also be carried out in the presence of phosphorus trichloride (aniline: methanol: phosphorus trichloride = 1: 0.9: 0.003 mol). In laboratory preparation, dimethyl sulfate can be used as the methylating agent. Add dimethyl sulfate dropwise to a mixture of less than 10% aniline and water, stir for 1 hour and then add 30% sodium hydroxide solution dropwise. Leave to stand and separate the upper organic phase, and extract the lower layer with benzene. The oil obtained after recovering benzene from the extract is combined with the organic phase. This is a mixture of aniline, N-methylaniline and N,N-dimethylaniline. Treat the mixture with sulfuric acid. The mixture is treated with sulfuric acid to form sulfate crystals from aniline and filtered out. N,N-dimethylaniline can be converted into N-methylaniline through the following reaction with acetic anhydride. The content of N-methylaniline in industrial products is ≥98%. Raw material consumption quota: aniline 1200kg/t, methanol 700kg/t.
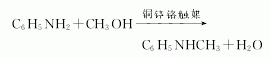
Refining method: using solid hydrogen oxidation The color can be removed by drying potassium and then fractionating it under reduced pressure. Since N-methylaniline is prepared by methylation of aniline, it often contains N,N-dimethylaniline and is difficult to separate by distillation. It can be acetylated, and the resulting acetyl derivative is recrystallized to a very small melting point range (m.p. 101~102°C), then hydrolyzed with hydrochloric acid, and distilled under reduced pressure.
2. The product N-methylaniline is purified by vacuum distillation.
Purpose
1. Used as intermediates, acid absorbers and solvents in organic synthesis. In the dye industry, it is used in cationic brilliant red 5GN, cationic pink FG, cationic pink B, reactive yellow-brown KGR, reactive yellow-brown KGR, and reactive brilliant blue. Production of X-BR, Reactive Orange K-2RL, Acid Blue BR, etc.
2. Used as raw materials for dyes, explosives, etc. and as metal preservatives. It is also used to increase the octane number of gasoline and as a solvent.
3. Used in organic synthesis and as solvent. [22]
