Anisole Anisole
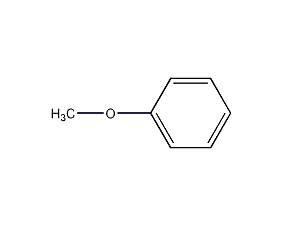

Structural formula
| Business number | 02JF |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C7H8O |
| Molecular weight | 108.14 |
| label |
Methoxybenzene, anisole, Methyl phenyl ether, phenyl methyl ether, Methoxybenzene, Methyl Phenyl ether, Phenyl methyl ether, essence, beer antioxidants, Ethylene polymer UV stabilizer, Ether solvent |
Numbering system
CAS number:100-66-3
MDL number:MFCD00008354
EINECS number:202-876-1
RTECS number:BZ8050000
BRN number:506892
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Characteristics: Colorless transparent liquid. Has a pleasant aromatic smell.
2. Density ( g/mL,25/4℃):0.9956
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL,Air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point ( ºC): –37.3
5. Boiling point ( ºC,Normal pressure):155.5
6. Boiling point ( ºC,5.2kPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive index: 1.51791
8. Flashpoint (ºC, open cup):51.6
9. Specific optical rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Not OK
11. Vapor pressure (kPa,25ºC): Undetermined
12. ):
7. Polarizability: 13.05
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 9.2
7. Number of heavy atoms: 8
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 55.4
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Chemical properties: When heated with alkali, the ether bond is easily broken. When heated to 130°C with hydrogen iodide, it decomposes to generate methyl iodide and phenol. When heated with aluminum trichloride and aluminum tribromide, it decomposes into halomethane and phenoxide. Heated to 380~400℃, it decomposes into phenol and ethylene. Dissolve anisole in cold concentrated sulfuric acid, and add aromatic sulfinic acid. A substitution reaction occurs at the para position of the aromatic ring to generate sulfoxide, which appears blue. This reaction can be used to test aromatic sulfinic acids (Smiles test).
2. Rats were injected subcutaneously with LD50: 4000mg/kg. Repeated contact with human skin can cause degreasing and dehydration of cell tissues and irritate the skin. The production workshop should have good ventilation and the equipment should be sealed. Operators wear protective equipment.
3. Stability[20] Stable
4. Incompatible substances[21] Strong oxidants, strong acids
5. Polymerization hazard[22] No polymerization
Storage method
This product should be sealed and stored in a cool, ventilated place away from light.
Synthesis method
It is prepared by reacting the methylating agent dimethyl sulfate with phenol in an alkaline solution. Mix phenol and sodium hydroxide solution in 10℃Slowly add dimethyl sulfate. Add to heat and heat to40℃reflux reaction18h, then let it stand to separate the oil layer, dry it with anhydrous calcium chloride and then reduce and distill it to obtain anisole.
It is obtained by reacting methyl chloride into liquid ammonia of sodium phenolate.
It is obtained by heating phenol and methanol.
It is derived from the reaction of phenol and dimethyl sulfate in the presence of sodium hydroxide.
Purpose
Solvent. Organic synthesis intermediates.
ONT-FAMILY: 宋体; mso-ascii-font-family: Verdana; mso-hansi-font-family: Verdana; mso-bidi-font-family: Tahoma; mso-bidi-font-size: 8.0pt”>, then Leave to stand to separate the oil layer, dry with anhydrous calcium chloride and then reduce and distill to obtain anisole.
It is obtained by reacting methyl chloride into liquid ammonia of sodium phenolate.
It is obtained by heating phenol and methanol.
It is derived from the reaction of phenol and dimethyl sulfate in the presence of sodium hydroxide.
Purpose
Solvent. Organic synthesis intermediates.
