3-Buten-2-one 3-Buten-2-one
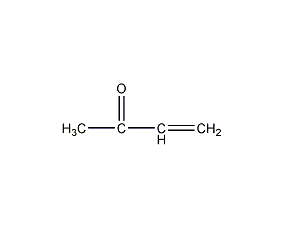

Structural formula
| Business number | 01NY |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H6O |
| Molecular weight | 70.09 |
| label |
butenone, Methyl Vinyl Ketone, 1-buten-3-one, Methyl vinyl ketone, 1-Buten-3-one, Methyl ethenyl ketone |
Numbering system
CAS number:78-94-4
MDL number:MFCD00008777
EINECS number:201-160-6
RTECS number:EM9800000
BRN number:506021
PubChem number:24856333
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless or yellow liquid with pungent odor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -7[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 81[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.86[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 2.41[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 11 (25℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -2383.4[7]
8. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.117[8 ]
9. Flash point (℃): -7 (CC); -1 (OC) [9]
10. Ignition temperature (℃): 491[10]
11. Explosion limit (%): 15.6[11]
12. Lower explosion limit (%): 2.1[12]
13. Solubility: soluble in water, soluble in organic solvents such as alcohols, slightly soluble in hydrocarbons. [13]
14. Specific optical rotation (º): [α]+29.78°
15. Temperature refractive index (n20 ): 1.4081
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity
Rat caliber LD50: 23100 ug/kg; rat inhalation LC50: 7 mg/m3/4H
Rat abdominal LD50: 15 mg/ kg
Mouse caliber LD50: 23300 ug/kg; mouse inhalation LC50: 8mg/m3/2H
Mouse abdominal LD50: 76 mg/kg
Pig caliber LD50: 15 mg/kg
Pig abdominal cavity LD50: 15 mg/kg
2. Other multiple dose toxicity data
Rat inhalation of TCLO: 3900 ppb/6H/9D-I
Rabbit inhalation TCLO: 7800 ppb/6H/9D-I
Pig inhalation TCLO: 7800 ppb/6H/9D-I
3. Teratogenicity
Salmonella: 250 umol/L
E. coli: 100 nmol/tube
4. Acute toxicity[14]
LD50: 30mg/kg (rat oral)
LC50: 7mg/m3(rat inhalation, 4h)
5. Irritation[15] Mouse transdermal: 1%, severe irritation.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[16] EC50: <10mg/L (green algae)
2. Biodegradability No data yet
3. Non-biodegradability[17] In the air, when the hydroxyl radical concentration is 5.00×105 pieces/cm3, the degradation half-life is 21h (theoretical).
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 20.33
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 86.7
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 185.3
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 20.8
5. Polarizability (10-24
sup>cm3): 8.06
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 0.5
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: 2
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 17.1
7. Number of heavy atoms: 5
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 54.7
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Form a binary azeotropic mixture with water. The azeotropic point is 75°C, and the azeotropic mixture contains 12% water. It is easily absorbed through the skin and causes systemic poisoning. Irritation to mucous membranes and respiratory tract. It is flammable and can easily cause combustion when exposed to open flames, high heat, or strong oxidants. At high temperatures in a fire, an exothermic polymerization reaction can occur, causing the container to rupture. Its vapor is heavier than air and can spread to a considerable distance from a lower place. It will cause backfire when exposed to an open flame.
2. Toxic, irritating to the mucous membranes of the eyes, nose and throat. Inhalation of vapors can cause wheezing, bronchitis and pulmonary edema. Skin contact will cause scarring and can be absorbed through the skin and cause poisoning. The oral LD50 for small rodents is 15 to 30 mg/kg.
3. Form a binary azeotrope with water, with an azeotropic point of 75ºC (101.3kpa) (containing 12% water).
4. Stability[18] Stable
5. Incompatible substances[19] Strong oxidants, acids
6. Conditions to avoid contact[20] Heating
7. Aggregation hazards[21] Aggregation
Storage method
Storage Precautions[22] Usually products contain polymerization inhibitors. Store in a cool, well-ventilated special warehouse, and implement the system of “two people to send and receive, and two people to keep”. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 37℃. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Acetyl ethanol is obtained by condensation of acetone and formaldehyde, and then dehydrated in the presence of oxalic acid to obtain methyl ketene. Mix the formaldehyde solution and acetone at a ratio of 1:30 into the pipeline reactor (temperature 51-53°C), control the flow rate, and maintain the reaction residence time for 3-4 minutes. Move the reaction solution to a reaction tank containing lemon-acetone and reflux for 10 minutes. Recover acetone, evaporate the water, add oxalic acid for dehydration, add a small amount of hydroquinone, and distill under normal pressure to obtain an azeotrope of methyl ketene and water. Salt out with refined salt, separate layers, add calcium chloride to the organic layer to dehydrate, hydrogenate until distillation, collect the 80-83°C fraction, which is methyl ketene, with a yield of 42%. In addition, sulfates of mercury, silver, copper, etc. can also be used as catalysts to obtain methyl ketene from vinyl acetylene through hydration.
Purpose
1. This product has strong reactivity and is used as a monomer for polymers to prepare anionic resins and film emulsifiers; it is also used as an alkylating agent and an intermediate for the synthesis of steroids and vitamin A, etc. .
2. As a monomer for polymerization, it can be used to manufacture ion exchange resins and drugs. [23]
