Benzaldehyde Benzaldehyde


Structural formula
| Business number | 02JZ |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C7H6O |
| Molecular weight | 106.12 |
| label |
Benzoin aldehyde, Benzaldehyde, artificial bitter almond oil, Benzoic aldehyde, Benzoyl hydride Artificial essential oil of almond, Aromatic aldehydes, ketones and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:100-52-7
MDL number:MFCD00003299
EINECS number:202-860-4
RTECS number:CU4375000
BRN number:471223
PubChem number:24866203
Physical property data
1. Properties: The pure product is a colorless liquid, and the industrial product is a colorless to light yellow liquid with a bitter almond smell.
2. Boiling point (ºC, 101.3kPa): 179
3. Melting point (ºC): -26
4. Density (g/mL, 20ºC ): 1.0458
5. Density (g/mL, 25ºC): 1.0415
6. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): 3.66
7. Refractive index (n20ºC): 1.5463
8. Refractive index (n25ºC): 1.5427
9. Viscosity (mPa·s,0ºC): 2.292
10. Viscosity (mPa·s, 20ºC): 1.53
11. Viscosity (mPa·s, 25ºC): 1.395
12. Flash point (ºC, open cup ): 73.9
13. Flash point (ºC, closed cup): 62
14. Fire point (ºC): 192
15. Lower explosion limit (% , V/V): 1.4
16. Vapor pressure (kPa, 26ºC): 0.13
17. Solubility: slightly soluble in water, solubility in water at 20°C is 0.3% , miscible with ethanol, ether, benzene, chloroform, etc.
18. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 1.0447
19. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 1.0408
20. Critical Temperature (ºC): 421.85
21. Critical pressure (MPa): 4.7
22. Eccentricity factor: 0.305
23. Solubility parameter (J· cm-3)0.5: 21.610
24. van der Waals area (cm2·mol– 1): 7.700×109
25. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 60.980
26. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -3575
27. Gas phase standard claim Heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -36.7
28. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 336.01
29. Gas phase standard free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1): -22.6
30. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 111.7
31. Liquid phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ ·mol-1): -3525.0
32. Liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -87.0
33. Liquid phase standard entropy (J·mol-1</sDistillation, benzaldehyde is evaporated with water, and the product is obtained by layering and distillation. 5.Chlorination of toluene can produce α, α ′-dichlorotoluene, which can then be hydrolyzed to obtain benzaldehyde: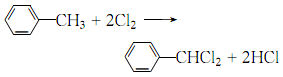
 Then extract with ether, evaporate the ether and then add sodium bisulfite to refine. To prepare chromatographically pure benzaldehyde, nitrogen can be used as the carrier gas, and the crude product is injected on a preparative gas chromatograph equipped with a SE30/white silanized diatomite carrier stationary phase column, and the main peak components are collected after separation, and then put into glass Just seal the ampoule. 5. Tobacco: BU, 56; OR, 57; BU, 14; FC, 9, 18; BU, OR, 18; FC, BU, OR, 40. 6. Preparation method:
Then extract with ether, evaporate the ether and then add sodium bisulfite to refine. To prepare chromatographically pure benzaldehyde, nitrogen can be used as the carrier gas, and the crude product is injected on a preparative gas chromatograph equipped with a SE30/white silanized diatomite carrier stationary phase column, and the main peak components are collected after separation, and then put into glass Just seal the ampoule. 5. Tobacco: BU, 56; OR, 57; BU, 14; FC, 9, 18; BU, OR, 18; FC, BU, OR, 40. 6. Preparation method:  in a reaction bottle equipped with a magnetic stirrer, reflux condenser, and thermometer , add 22.5 mL (25 mmol) of a THF solution of 2,3-dimethyl-2-butylborane, and cool to -20°C (CCl4 plus dry ice). Under vigorous stirring, slowly add a solution of 5 mmol benzoic acid (2) dissolved in 2.5 mL THF and cooled to -20°C into the reaction bottle. After 10 minutes, heat to reflux. Samples were taken and analyzed at different times to react the produced aldehyde with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine to generate the corresponding hydrazone, and the aldehyde yield was calculated based on the amount of hydrazone. The yield was 70% at 12h; 82% at 24h; and remained unchanged at 36h. [1]
in a reaction bottle equipped with a magnetic stirrer, reflux condenser, and thermometer , add 22.5 mL (25 mmol) of a THF solution of 2,3-dimethyl-2-butylborane, and cool to -20°C (CCl4 plus dry ice). Under vigorous stirring, slowly add a solution of 5 mmol benzoic acid (2) dissolved in 2.5 mL THF and cooled to -20°C into the reaction bottle. After 10 minutes, heat to reflux. Samples were taken and analyzed at different times to react the produced aldehyde with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine to generate the corresponding hydrazone, and the aldehyde yield was calculated based on the amount of hydrazone. The yield was 70% at 12h; 82% at 24h; and remained unchanged at 36h. [1]
7. Preparation method:
In a weighed reaction bottle equipped with a reflux condenser (calcium chloride drying tube on the top) and ventilation tube, add dry toluene ( 2) 46g (0.5mol), heated to boiling. Dry chlorine gas was slowly introduced under light until the mass increased by 39g and the boiling temperature reached 187°C to obtain crude a,a-dichlorotoluene (3). Transfer compound (3) to a 1.5L reaction bottle, add 500mL water and 150g calcium carbonate, and reflux for 4 hours. At the same time, carbon dioxide gas is introduced to prevent the oxidation of the generated benzaldehyde. After the reaction is completed, steam distillation is performed until no oil is distilled ①. The distillate was extracted three times with diethyl ether, and the diethyl ether layers were combined. After distilling off the ether, crude benzaldehyde is obtained. Slowly add saturated sodium bisulfite solution in batches to the crude benzaldehyde, shaking thoroughly after each addition. When there is crystalline precipitate and no smell of benzaldehyde, filter it with suction. The filter cake was washed with diethyl ether. Add the crystals to excess sodium carbonate solution and shake thoroughly to free the benzaldehyde. Extract with ether three times. The ether layers were combined, washed with sodium carbonate solution, water, and dried over calcium chloride. After distilling off the ether, perform fractional distillation and collect the fractions at 178-180°C to obtain 36g of benzaldehyde (1) with a yield of 70% (calculated as toluene). Note: ① The reaction solution contains benzoic acid. Filter the hot solution, acidify it with hydrochloric acid, and cool it to obtain flaky benzoic acid, mp121°C. [2]
Purpose
1. Mainly used for organic synthesis, solvents, determination of ozone and methylene next to the carbonyl group, determination of phenols and alkaloids, etc.
2. To enhance or enhance the aroma or taste of consumer products including food, chewing gum, pharmaceutical products, toothpaste and tobacco. Intermediates for manufacturing dyes, raw materials for pesticides, medicines, spices and seasonings, as well as auxiliaries for polyamide fiber dyeing, additives for electroplating solutions, etc.
3. It is an important chemical raw material used to prepare lauric aldehyde, lauric acid, phenylacetaldehyde and benzyl benzoate, etc.
4. Also used in daily chemical flavors and tobacco flavors.
