Phenylurea Phenylurea
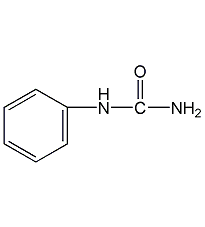

Structural formula
| Business number | 01D5 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C7H8N2O |
| Molecular weight | 136.15 |
| label |
Phenylcarbamide, Phenylcarbamide, N-Phenylurea, C6H5NHCONH2 |
Numbering system
CAS number:64-10-8
MDL number:MFCD00007944
EINECS number:200-576-5
RTECS number:YU0650000
BRN number:1934615
PubChem number:24898443
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless needle-like crystals
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4℃): 1.302
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL , air=1):>1
4. Melting point (ºC): 145-147 (decomposition)
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 238
6. Boiling point (ºC, 5.2kPa): Uncertain
7. Refractive index: Uncertain
8. Flash point (ºC): 238
9. Specific optical rotation (º): Uncertain
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Uncertain
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC) : Uncertain
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Uncertain
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Uncertain
14 . Critical temperature (ºC): Uncertain
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Uncertain
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Uncertain
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Uncertain
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): Uncertain
19 . Solubility: Soluble in hot water, hot alcohol, ether, ethyl acetate and acetic acid
Toxicological data
Acute toxicity: rat oral LD50: 2 mg/kg; mouse oral LD50: 1580 mg/kg; mouse abdominal LD50: 1060 mg/kg;
Ecological data
General remarks
Water hazard level 1 (German regulations) (self-assessment via list) This substance is extremely hazardous to water.
Do not allow undiluted or large amounts of product to come into contact with groundwater, waterways or sewage systems.
Do not discharge materials into the surrounding environment without government permission.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 39.42
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 109.6
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 300.2
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 56.1
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 15.63
Compute chemical data
1. Hydrophobic parameter calculation reference value (XlogP): 0.8
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 2
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: 3
6. Topological molecular polar surface area (TPSA): 55.1
7. Number of heavy atoms: 10
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 119
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. The number of uncertain stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
15. The number of covalent bonding units: 1
Properties and stability
None yet
Storage method
This product should be sealed and stored in a cool, dry place away from light.
Synthesis method
Derived from the reaction of aniline and urea. Put urea, hydrochloric acid and aniline into the reaction pot, heat and stir, reflux at 100-104°C for 1 hour, complete the reaction, add water, stir, cool, filter, wash the filter cake with water, and dry to obtain the finished product.
Purpose
Used in organic synthesis.
