Iodoacetic acid Iodoacetic acid
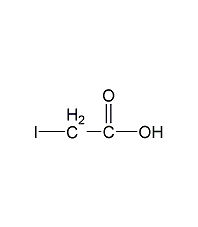
Structural formula
| Business number | 01DE |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C2H3IO2 |
| Molecular weight | 185.95 |
| label |
Iodoacetic acid, Enzymes·Proteins·Peptides |
Numbering system
CAS number:64-69-7
MDL number:MFCD00002685
EINECS number:200-590-1
RTECS number:AI3500000
BRN number:1739079
PubChem number:24896056
Physical property data
1. Character: colorless or white crystal[1]
2. Melting point (℃): 82~83[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): Decomposition[3]
4. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.850[4]
5. Solubility: soluble in water, hot petroleum ether, ethanol, insoluble in ether and chloroform. [5]
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[6]
LD50: 83mg/kg (rat oral); 75mg/kg (rat intraperitoneal ); 83mg/kg (orally in mice)
2. Irritation No data available
3. Subacute and chronic toxicity[7] Feed rats with feed containing this product at a dose of 50~70mg/(kg·d), and they will die within 10~40 days.
4. Mutagenicity [8] DNA inhibition: human Hela cells 500 μmol/L. Cytogenetic analysis: hamster fibroblasts 100 μg/L.
5. Teratogenicity [9] The lowest toxic dose of 158mg/kg was administered orally to male mice before mating, causing craniofacial (including nose and tongue) developmental malformations. Intraperitoneal administration of 40 mg/kg to female mice on the 8th day after pregnancy resulted in developmental malformations of the musculoskeletal system.
6. Carcinogenicity [10] Transdermal minimum toxic dose in mice (TDLo): 5800mg/kg (27 weeks), tumor-causing, Causes skin tumors and causes tumors at the application site.
7. Others[11] The lowest toxic dose in the abdominal cavity of mice (TDLo): 40g/kg (8 days of pregnancy), causing abnormal musculoskeletal development .
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data available
2. Biodegradability No data available
3 .Non-biodegradability[12] In the air, when the concentration of hydroxyl radicals is 5.00×105/cm3 When, the degradation half-life is 12d (theoretical).
4. Other harmful effects [13] This substance is harmful to the environment, and special attention should be paid to the pollution of water bodies.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 25.84
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 75.0
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 207.5
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 58.5
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 10.24
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 0.5
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 37.3
7. Number of heavy atoms: 5
8. Surface charge: 0
9 .Complexity: 42.9
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain atomic configuration Number of centers: 0
13. Determined number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
14. Uncertain number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
15. Covalent Number of key units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Stability[14] Stable
2. Incompatible substances[15] Strong oxidizing agent, strong reducing agent, strong alkali
3. Conditions to avoid contact[16] Heating
4. Polymerization hazard[17] No polymerization
5. Decomposition products[18] Hydrogen iodide
Storage method
Storage Precautions[19] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The packaging is sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, reducing agents, alkalis, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from the reaction of chloroacetic acid and sodium iodide. Mix chloroacetic acid, water (or acetone), and sodium iodide and react at 50°C for 1 hour. Filter and cool to 10°C with ice to precipitate crystals. Filter to obtain crude product and recrystallize with water to obtain finished product.
![]()
Purpose
1. Used as analytical reagents, dye preparation, organic synthesis and enzyme inhibitors.
2. Used for agricultural plant resource research, dye preparation, organic synthesis, etc. [20]
