Bisphenol A Bisphenol A

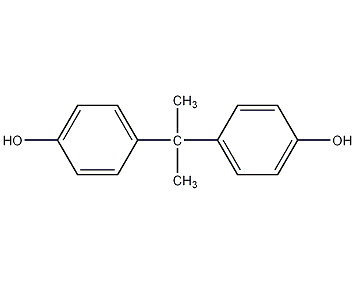
Structural formula
| Business number | 01QF |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C15H16O |
| Molecular weight | 228.29 |
| label |
4,4′-dihydroxydiphenylpropane, Diphenolpropane, 4,4′-dihydroxyphenyl-2,2-propane, 2,2′-bis-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propane, 4,4′- dihydroxy-diphenyl propane, Two phenyl propane, stabilizer, Phenol, aromatic alcohols and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:80-05-7
MDL number:MFCD00002366
EINECS number:201-245-8
RTECS number:SL6300000
BRN number:1107700
PubChem number:24848951
Physical property data
1. Properties: White needle crystals or flaky powder. Combustible. Slight phenol odor
2. Relative density (g/mL, 25/4℃): 1.195
3. Melting point (ºC): 155~158
4. Boiling point (ºC, 1.733KPa): 250~252
5. Flash point (ºC): 79.4
6. Solubility: soluble in methanol, ethanol, isopropyl Alcohol, butanol, acetic acid, acetone, diethyl ether, are insoluble in water.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: mouse LD50: 2,400 mg/kg; rat LD50: 3,250 mg/kg
Since the LD50 of table salt is 3,000 mg/kg, the acute toxicity of BPA is the same as that of table salt. .
2. Subacute toxicity
Mouse test: NOAEL: 2,000ppm (equivalent to 550 mg/kg/day). More than 5,000ppm has an impact on the kidneys.
Rat test: NOAEL: 3,000ppm (equivalent to 75 mg/kg/day). 9,000ppm increased liver relative weight and had no other effects.
3. Chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity
Mouse test: NOAEL: 1,000ppm (equivalent to 130 mg/kg/day). 5,000ppm or more inhibits weight gain. Not carcinogenic.
Rat test: no carcinogenicity. The safety factor is taken as 1000, not the usual 100.
4. Teratogenicity
Mouse test: 1,250 mg/kg/day, increased maternal and fetal mortality and inhibited weight gain. There is no effect on the mother or fetus below 1,000 mg/kg/day.
Rat test: maternal dosage above 160 mg/kg/day inhibits body weight gain. There is no effect on the fetus below 640 mg/kg/day.
5. Reproductive toxicity
Rat 1st generation reproductive toxicity test: NOAEL: 1,000ppm (equivalent to 50 mg/kg/day). There is no impact.
Mice 2nd generation reproductive toxicity test: The lowest dose was 2,500ppm (equivalent to 437 mg/kg/day), and abnormalities occurred. The weight of kidneys and liver increases, and the weight of male genitalia decreases. Because the dosage is too high, the NOAEL cannot be obtained.
Rat 3-generation reproductive toxicity test: NOAEL: 50 mg/kg/day.
6.Inhalation toxicity: NOAEL: 10mg/m3; above 50mg/m3 will cause mild inflammation of the nose, throat and bronchial mucosa.
7. Neurotoxicity: There were no abnormalities in tests conducted by the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare and the Ministry of the Environment of Japan.
8. Drug metabolism (absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion):
After BPA is put in, it is quickly absorbed by the digestive organs. It quickly combines with gluconic acid in the liver and enters the blood to participate in body circulation. More than 90% of BPA in blood exists in gluconic acid-conjugated form. It is highly water-soluble and is quickly excreted in urine. The half-life in the blood is 6 hours. 94% of the input BPA is discharged on the same day.
Ecological data
Seriously harmful to water and changing water quality.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 68.16
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 199.5
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 519.7
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 46.0
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 27.02
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 3.3
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 2
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: 3
6. Topological molecular polar surface area (TPSA): 40.5
7. Number of heavy atoms: 17
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 209
10. Number of isotope atoms : 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the chemical bond configuration Number of centers: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. White crystalline powder with phenol smell.
2. Soluble in acetic acid, acetone, methanol, ethanol, isopropanol, butanol, ether, benzene and alkaline solutions, slightly soluble in carbon tetrachloride, and hardly soluble in water. Weakly acidic. The ortho position of the hydroxyl group is very active and is easily nitrated, halogenated, sulfided, hydrocarbonated, etc. Low toxicity.
Storage method
This product should be sealed and stored in a cool, dry place, waterproof and explosion-proof.
Synthesis method
Obtained from the condensation of phenol and acetone in acidic medium. When sulfuric acid is used as the catalyst, the acid concentration is 72.5-76.3%, and the reaction temperature is about 40°C. The reaction is carried out in a stirred tank, which can be produced by batch method or a continuous production device can be arranged. The product is neutralized and separated to obtain crude bisphenol A, which is refined by xylene-water extraction to obtain the finished product. The sulfuric acid method requires less equipment and has a simple process, but the product quality is poor, raw material consumption is high, and there are more “three wastes”. It is only suitable for small and medium-sized intermittent production. In order to obtain high-quality polymer-grade bisphenol A, a commonly used industrial production method is to use hydrogen chloride gas as a catalyst. Mix acetone and phenol, and use dry hydrogen chloride as a catalyst to react under normal pressure. The reaction is carried out at 50-60°C for 8-9 hours, and the gas phase hydrogen chloride concentration is maintained above 96%. In addition to bisphenol A, the reaction also generates some isomers, trihydroxy or monohydroxy by-products. These small amounts of impurities do not affect the resin used to make the epoxy. But when used to make polycarbonate, it must be refined. The Hooke process uses distillation and extraction crystallization under pressure to refine bisphenol A, which reduces product costs. Raw material consumption quota: phenol 940kg/t, acetone 320kg/t, sulfuric acid (98%) 500kg/t.

Hydrogen chloride method: Bisphenol A is produced by reacting phenol and acetone in the presence of hydrogen chloride. This law is widely used in the United States, Japan and other countries. A typical process is the Hooker method. Excess phenol and acetone (ratio greater than 8:1) are added to the reactor together with the circulating material saturated with hydrochloric acid, and the reaction is stirred at 50-60°C for 8-9 hours under normal pressure. Then the reaction product is sent to the hydrogen chloride desorption tower, and the hydrogen chloride recovery system is steamed from the top of the tower through stripping, and the hydrogen chloride is separated and recycled back to the reactor. The organic phase mainly contains phenol, which can be recycled back to the hydrogen chloride desorption tower. The reaction mixture after removing the acid is discharged from the hydrogen chloride desorption tower into the phenol recovery tower. After excess phenol is separated from the top of the tower, it is recycled into the reactor. The crude product from the tower still is sent to the isomer separation tower, where ortho and para isomers are separated under vacuum and recycled back to the reactor. The kettle liquid enters the bisphenol A distillation tower, and the tar-like substance is distilled and separated under vacuum. The bisphenol A steamed off the top of the tower is refined by extraction with solvent toluene and recrystallization. After separation and crystallization, the mother liquor is distilled to recover the solvent.
Purpose
Bisphenol A is a widely used product and is widely used in the production of epoxy resin, polycarbonate, polyester resin, polyphenylene ether resin, and polysulfone resin. It can also be used as polyvinyl chloride stabilizer, plastic antioxidant, ultraviolet absorber, agricultural fungicide, rubber antioxidant, etc. It can also be used as an antioxidant and plasticizer in paints and inks.
In the ink industry, it is mainly used to manufacture rosin-modified phenolic resin in ink binders.
��Resin.
