n-Propyl acetate Propyl acetate
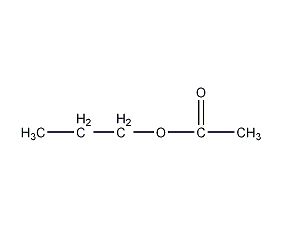

Structural formula
| Business number | 02ZA |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C5H10O2 |
| Molecular weight | 102.13 |
| label |
propyl acetate, Isopropyl acetate, n-Propyl ester, Propyl ethanoate, 1-Acetoxypropane, acetic acid, non-reactive diluent, Soothing and quick-drying agent, extraction solvent |
Numbering system
CAS number:109-60-4
MDL number:MFCD00009372
EINECS number:203-686-1
RTECS number:AJ3675000
BRN number:1740764
PubChem number:24865578
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless clear liquid with aromatic odor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -92.5[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 101.6[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.88[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 3.52[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 3.3 (20℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -2890.5[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 276.2[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 3.33[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.23~1.24[10]
11. Flash point (℃): 13 (CC) [11]
12. Ignition temperature (℃): 450[12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 8.0[13]
14. Lower explosion limit (%): 2[14]
15. Solubility: slightly soluble in water, soluble in alcohols, ketones, esters, oils and other organic substances Solvent. [15]
16. Viscosity (mPa·s, 20ºC): 0.585
17. Flash point (ºC, closed): 12.7
18. Flash point (ºC, open): 22.2
19. Fire point (ºC): 450
20. Heat of vaporization (KJ/mol, b.p.): 34.33
21. Heat of evaporation (KJ/kg, b.p.): 336.2
22. Heat of generation (KJ/mol): 472.3
23. Specific heat capacity (KJ /(kg·K), 20ºC, constant pressure): 1.92
24. Conductivity (S/m): 2.2×10-7
25. Volume expansion coefficient (K-1, 20ºC): 0.0012
26. Critical density (g·cm-3): 0.296
27. Critical volume (cm3·mol-1): 345
28. Critical compression factor: 0.254
29. Eccentricity factor: 0.394
30. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 18.005
31. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 9.140×109
32. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 63.000
33. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 196.6
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: Mouse oral LD50: 8300mg/kg; Rat oral LD50: 9370mg/kg; Rabbit oral LD50: 6640mg/kg; Rabbit dermal LD50: >20mg/kg
2. Effect on skin and eyes��Irritation: Rabbit skin: 500mg/24H, mild irritation. Rabbit eye: 500mg/24H, mild irritation.
3. It is slightly toxic. It has irritating and anesthetic effects on mucous membranes. Nausea, chest tightness, fatigue, etc. may occur after inhalation. The olfactory threshold concentration is 83.4mg/m3. TJ 36-79 stipulates that the maximum allowable concentration in workshop air is 300 mg/m3.
4. Acute toxicity [16]
LD50: 9370mg/kg (rat oral)
LC50: 8000ppm (rat inhalation, 4h)
5. Irritation [17] Rabbit transdermal: 500mg, mild Stimulation (open stimulation test)
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[18]
LC50: 60mg/L (96h) (fathead minnow)
IC50: 26~530mg/L (72h) (algae)
2. Biodegradability[19] MITI-I test, initial concentration 100mg/L, sludge concentration 30mg/L, 81% degradation after 14 days.
3. Non-biodegradability[20] In the air, when the hydroxyl radical concentration is 5.00×105 pcs/cm3, the degradation half-life is 5d (theoretical). At 25°C, when the pH value is 7, 8, and 9, the hydrolysis half-life is 3.3a, 119d, and 12d (theoretical) respectively.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 26.98
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 114.5
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 255.8
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 24.8
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 10.69
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 3
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 26.3
7. Number of heavy atoms: 7
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 59.1
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Chemical properties: It gradually hydrolyzes in the presence of water to produce acetic acid and propanol. The hydrolysis rate is 1/4 of that of ethyl acetate. When propyl acetate is heated to 450~470°C, in addition to propylene and acetic acid, there are also acetaldehyde, propionaldehyde, methanol, ethanol, ethane, ethylene and water. In the presence of a nickel catalyst, when heated to 375~425°C, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, methane, ethane, etc. are generated. Chlorine, bromine, hydrogen bromide and propyl acetate can react at low temperatures. When reacting with chlorine under light, 85% of monochloropropyl acetate is generated within 2 hours. Among them, 2/3 are 2-chloro substituents and 1/3 are 3-chloro substituents. In the presence of aluminum trichloride, propyl acetate is heated with benzene to produce propylbenzene, 4-propylacetophenone and cumene.
2. Stability[21] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[22] Strong oxidants, acids, alkalis
4. Polymerization hazard[23] No polymerization
Storage method
Storage Precautions[24] Stored in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 37°C. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, and alkalis, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from the esterification of acetic acid and propanol. In the glass-lined reaction pot, add propanol, acetic acid and sulfuric acid, heat to reflux for 10 hours, cool and neutralize with sodium methoxide to pH=7-8, dry with calcium chloride and carry out atmospheric fractionation, collect the 105-115°C fraction , which is the finished product.
2. Refining method: Propyl acetate often contains impurities such as water, acetic acid and propanol. During refining, the acid is neutralized with sodium chloride carbonate or a saturated sodium carbonate solution, washed with a saturated salt water solution, dried with a desiccant such as anhydrous sodium sulfate or magnesium sulfate, and then distilled.
3. Preparation method:
In a reaction bottle equipped with a reflux condenser, add 60g of glacial acetic acid (1.0mol) and 40g of 1-propanol (2) (0.67 mol), one grain of zeolite, 2 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid. Heat and reflux for 12 hours. After the reaction is completed, pour 250 mL of water and saturate it with sodium chloride. The upper organic layer was separated and washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate solution. Dry with anhydrous sodium sulfate, distill, and collect the fractions at 101 to 102°C to obtain 36 g of propyl acetate (1), with a yield of 53%. [26]
Purpose
1. This product is a softening and quick-drying agent, used for flexographic printing inks and gravure printing inks, especially for olefin reduction and polyamide film printing. Also used as nitrocellulose; solvent for chlorinated rubber and heat-reactive phenolic plastics. Propyl acetate has a slightly fruity aroma. It has a pear-like aroma after dilution. Natural products are found in bananas; tomatoes; raspberries, etc. my country’s GB2760-86 stipulates that edible spices are allowed to be used. It is mainly used to prepare pear and gooseberry flavors, and is also used as a solvent for fruit flavors. It is widely used as an extraction solvent for various organic and inorganic substances, as a solvent for coatings, nitrocellulose spray paints, varnishes and various resins, and in the manufacture of spices.
2. Used to make edible spices. It is also used as the volume of nitrocellulose, chlorinated rubber and heat-reactive phenolic plastics, as well as in paint making, plastics, organic synthesis, etc.
3. Used as flavoring agents, edible spices, nitrocellulose solvents and reagents, as well as in paint making, plastics, organic synthesis, etc. [25]
It is used as extraction solvent for various organic and inorganic substances, solvent for coatings, nitrocellulose spray paints, varnishes and various resins, and the manufacture of spices.
2. Used to make edible spices. It is also used as the volume of nitrocellulose, chlorinated rubber and heat-reactive phenolic plastics, as well as in paint making, plastics, organic synthesis, etc.
3. Used as flavoring agents, edible spices, nitrocellulose solvents and reagents, as well as in paint making, plastics, organic synthesis, etc. [25]
