Diethylamine Diethylamine
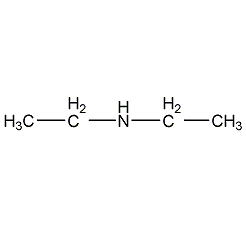
Structural formula
| Business number | 0303 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H11N |
| Molecular weight | 73.14 |
| label |
N-Ethylethylamine, Aminodiethane, Diethylamine, Aminodiethylamine, N-Ethylethanamine, Aliphatic carboxylic acids and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:109-89-7
MDL number:MFCD00009032
EINECS number:203-716-3
RTECS number:HZ8750000
BRN number:605268
PubChem number:24893300
Physical property data
1. Properties: water-white liquid with ammonia odor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -50[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 55.5[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.71[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 2.53[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 25.9 (20℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -3001.7[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 226.8[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 3.758[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.58 [10]
11. Flash point (℃): <-26 (CC); -15 (OC) [11]
12. Ignition temperature (℃): 312[12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 10.1[13]
14. Lower explosion limit (%): 1.7[14]
15. Solubility: soluble in water, soluble in ethanol, ether and most organic solvents. [15]
16. Refractive index (20ºC): 1.3864
17. Viscosity (mPa·s, 10.2ºC): 0.3878
18. Viscosity (mPa·s, 37.6ºC): 0.2732
19. Flash point (ºC): 312.2
20. Heat of vaporization (KJ/mol, b.p.): 29.20
21. Heat of formation (KJ/mol, 25ºC, liquid): -103.79
22. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol, 20ºC, liquid): 3044.43
23. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), constant pressure): 2.42
24. Electrical conductivity (S/m, -33.5ºC): 2.2×10-9
25.pKa (25ºC, water): 10.98
Toxicological data
1. Irritation: Rabbit transdermal: 500mg, slightly irritating.
2. Acute toxicity:
Oral LD50 in rats: 540mg/kg; Oral LC50 in mice: 500mg/kg; Dermal LD50 in rabbits: 820ul/kg; Mammals Inhalation LC50: 5000mg/m3; rat inhalation LC50: 4000ppm/4H; rabbit inhalation LCLo: 20000mg/m3/2H;
3. It has an irritating effect on the skin and mucous membranes, and liquid splashing into the eyes can cause serious Burns, corneal edema. Contaminated skin can cause blisters and necrosis. The olfactory threshold concentration is 0.897mg/m3. The maximum allowable concentration in the workplace is 74.5 mg/m3.
4. Acute toxicity[16]
LD50: 540mg/kg (rat Oral); 820mg/kg (rabbit transdermal)
LC50: 11960mg/m3, (rat inhalation, 4h)
5. Irritation[17] Rabbit eye: 50μg, severe irritation (open stimulation test)
6.src=”http://images.basechem.org/internal/day_100910/201009101559385927.gif” alt=”” />
5. Diethylaniline method.

6. Its preparation method is The mixed gas of ethanol, ammonia and hydrogen is preheated to a temperature of about 180°C. Under the action of a nickel-copper catalyst, it sequentially enters the first converter (temperature is about 200°C) and the second converter (temperature is about 80°C). The synthesis reaction is carried out, and the reaction product is subjected to crude distillation and rectification to obtain the finished product.
Refining method: often contains impurities such as ethylamine, triethylamine, and acetaldehyde. It can be refined by fractional distillation. The distillate was dehydrated with solid potassium hydroxide and then dried with sodium fluorenone for later use. Or heat and reflux in the presence of metallic sodium for 2 hours and then fractionate and refine. Diethylamine can also be converted into hydrochloride, and then recrystallized repeatedly with dry petroleum ether until the melting point reaches 223.5°C. Add potassium hydroxide to free diethylamine, then dry and distill it to obtain pure product.
7. Ethanol atmospheric pressure gas phase catalysis method. The reaction can obtain a mixture of monoethylamine, diethylamine, triethylamine, ethanol, etc., and then undergo crude distillation, rectification, and collect the diethylamine fraction. Can. Or ethyl chloride and ammonia (ammonia) react in a calcium hydroxide aqueous solution at a certain temperature and pressure, and finally undergo distillation and rectification.
Purpose
1. Used in the manufacture of medicines, pesticides, dyes, rubber vulcanization accelerators, textile auxiliaries, metal preservatives, emulsifiers, polymerization inhibitors, etc. It is also used as a refining solvent for waxes, an activator during emulsion polymerization of conjugated dienes, and as an antifreeze for engines.
2. Diethylamine is a solvent and chemical raw material intermediate, which can be used to prepare drugs such as procaine, chloroquine, nicosamide, colamin and sulfa, and can also be used to produce pesticides. , dyes, rubber vulcanization accelerators, mineral processing agents, textile auxiliaries, fungicides, corrosion inhibitors, polymerization inhibitors and antifreeze agents, etc.
3. Used in organic synthesis, dye and drug synthesis. Used as analytical reagents, such as chromogenic reagents for detecting thiobarbituric acid by thin layer chromatography. Also used as a preservative.
4. Used in organic synthesis and epoxy resin curing agent. [24]
