Pyrrole Pyrrole
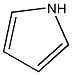

Structural formula
| Business number | 0309 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H5N |
| Molecular weight | 67.09 |
| label |
1H-pyrrole, azapentane, Azadiene pentacyclic, azole, pyrrole, azocene, 1-Aza-2,4-cyclopentadiene, Azole, Divinylenimine, Imidole, Solvent for polyester fiber spinning, metal preservatives, Epoxy resin hardener, Catalyst for olefin polymerization |
Numbering system
CAS number:109-97-7
MDL number:MFCD00005216
EINECS number:203-724-7
RTECS number:UX9275000
BRN number:1159
PubChem number:24901681
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid with special smell.
2. Boiling point (ºC, 101.3kPa): 130~131
3. Melting point (ºC): -24
4. Relative density (g/ mL, 20/4ºC): 0.9691
5. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): 2.31
6. Refractive index (20ºC): 1.5085
7. Viscosity (mPa·s, 20ºC): 1.352
8. Flash point (ºC, closed): 39
9. Heat of vaporization (KJ/mol, 25ºC): 45.21
10. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol): 7.91
11. Heat of formation (KJ/mol, 25ºC, liquid): 63.14
12. Heat of formation (KJ/mol, 25ºC, gas): 108.35
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol, constant volume): 2375.6
14. Specific heat capacity (KJ/ (kg·K), 295.13K, constant pressure): 1.89
15. Critical temperature (ºC): 366.5
16. Critical pressure (MPa): 5.67
17. Solubility (%, 25ºC, water): 8
18. Solubility: Miscible with alcohol, ether and other organic solvents. Can dissolve a variety of organic matter.
Toxicological data
Pyrroles are of low toxicity. Although the acute oral toxicity is not strong, it has cumulative toxicity. Injection into mammals causes urine discoloration. It has an inhibitory and anesthetic effect on the central nervous system. Skin contact should be avoided. Pyrrole can produce highly toxic gases when heated in the air, so please be careful when using it.
Ecological data
The substance�The environment may be hazardous and special attention should be paid to water bodies.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 20.68
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 67.7
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 166.8
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 36.7
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 8.20
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 15.8
7. Number of heavy atoms: 5
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 22.8
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Avoid contact with light and air. Do not put it together with acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, strong oxidants, and acids. Under the action of light and air, the color gradually turns brown, producing a resinous substance. Resinization also occurs in the presence of trace amounts of inorganic acids. Reacts violently with oxidizing agents. Avoid contact with oxidizing agents.
Chemical properties: Compared with pyridine, pyrrole is extremely weakly alkaline and does not form a stable salt in concentrated acid but polymerizes to produce a resinous substance. Pyrrole reacts with metal sodium, potassium, solid potassium hydroxide or sodium hydroxide to form sodium salt or potassium salt. The salt reacts with the alkyl halide to introduce an alkyl group, and with continued heating, rearrangement occurs to generate α-alkylpyrrole. Pyrrole easily undergoes halogenation reaction to generate tetrahalogenated pyrrole. For example, it reacts with sulfonate in alkaline medium to generate tetraiodopyrrole. Nitration, sulfonation and coupling reactions can occur at the α-position of pyrrole. Catalytic hydrogenation of pyrrole produces tetrahydropyrrole (pyrrolidine).
2.Toxicity: LD50 (mg/kg): Rat oral administration: 61. Health Hazards: Inhalation of vapor can cause anesthesia and cause a sustained increase in body temperature. Fire and explosion hazard: This product is flammable and irritating. Hazardous characteristics: Its vapor and air can form an explosive mixture, which can cause combustion and explosion when exposed to open flames or high heat. Can react with oxidizing agents. It decomposes at high temperatures and releases highly toxic nitrogen oxide gas. If the flow rate is too fast, it is easy to generate and accumulate static electricity. It is easy to self-polymerize, and the polymerization reaction accelerates rapidly as the temperature rises. Its vapor is heavier than air and can spread to a considerable distance from a lower place. It will ignite and backfire when encountering a fire source. In case of high heat, the internal pressure of the container will increase and there is a risk of cracking and explosion
Storage method
Stored in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 30℃. The packaging must be sealed and must not come into contact with air. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. It should not be stored in large quantities or for long periods of time. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. It is obtained through gas phase catalytic reaction using furan and ammonia as raw materials and γ-alumina as catalyst.
2. After co-thermal fractionation of bone oil and sulfuric acid, it is converted into its potassium salt (C4H4NK), washed with ether and treated with water, then dried and fractionated.
Produced by the pyrolysis of ammonium galactoseate in glycerin or mineral oil.
Refining method: Distill pyrrole in nitrogen flow. Or make a pure complex in an ammonia solution of nickel cyanide, and then carry out dry distillation.
Purpose
It is used as a standard material for chromatographic analysis, and also used in organic synthesis and pharmaceutical industry. Mainly used as solvent for polyester fiber spinning. It is also used as metal preservative, epoxy resin curing agent, catalyst in olefin polymerization and raw material in the pharmaceutical industry. Also used as photosensitizer.
