Acetanilide Acetanilide
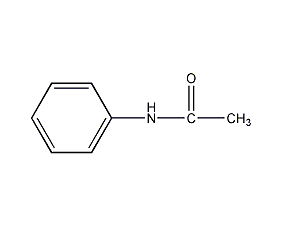
Structural formula
| Business number | 02PC |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C8H9NO |
| Molecular weight | 135.16 |
| label |
antipyretic ice, N-phenylacetamide, antifibulin, 4-acetamidobenzene, N-Phenylacetamide, Antifebrin, Acetamidobenzene, analytical identification reagents, Aromatic compounds and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:103-84-4
MDL number:MFCD00008674
EINECS number:203-150-7
RTECS number:AD7350000
BRN number:606468
PubChem number:24864694
Physical property data
1. Properties: White shiny flaky crystals or white crystalline powder. Odorless. Slight burnt smell.
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4℃): 1.219
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 113-115
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 304-305
6. Boiling point (ºC, 5.2kPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive index (n20D): 1.53
8. Flash point (ºC): 173
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol ): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Oil and water (polymer) Log value of the partition coefficient (alcohol/water): Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V ): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Slightly soluble in cold water, soluble in hot water, methanol, ethanol, ether, chloroform, acetone, glycerol and benzene, etc.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: Rat oral LD5O: 800mg/kg
Mouse oral LC5O: 1210mg/kg
Ecological data
This substance is slightly hazardous to water. Inhalation of this product is irritating to the upper respiratory tract. High dose intake can cause methemoglobinemia and bone marrow hyperplasia.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 40.52
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 122.5
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 311.0
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 41.5
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 16.06
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: 3
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 29.1
7. Number of heavy atoms: 10
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 116
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Avoid contact with oxides.
2. Entering the body through the respiratory and digestive systems can inhibit the central nervous system and cardiovascular system. Exposure to large amounts can cause dizziness and paleness. disease. Rat oral LD50: 800mg/kg. Production equipment should be airtight. Operators should wear protective equipment and avoid direct contact. Take a shower with warm water after get off work.
3. Toxic, irritating, and harmful when taken orally. Avoid inhaling the dust of this product when using it. Contact with eyes and skin.
4. Exist in mainstream smoke.
5. Rat oral administration LD50800g/kg
Storage method
1. Store in a cool, dry place and away from light.
2. Packed in inner plastic bags, outer sacks or canvas bags, with a net weight of 50kg per bag. Store in a cool, dry and ventilated place, protected from fire and moisture. It can be transported by car or train. Store and transport according to regulations on toxic chemicals.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from acetylation of aniline with acetic acid. Place aniline and glacial acetic acid (100% excess) in a jacketed glass-lined reactor and reflux for 6-14 hours until there is no free aniline. If dilute acetic acid is used, the reaction temperature is 150-160°C. After the reaction is completed, filter while it is hot to remove the residue. The filtrate is cooled, crystallized, centrifuged, filtered, washed with water and dried to obtain the product. Acetic anhydride can also be used as the acylating agent, and the reaction is carried out in a benzene solution with an excess of acetic anhydride of 150%. Operation Example 1 Arrange four reaction tanks in a trapezoid, with the highest reaction tank equipped with a fractionating column. Aniline is continuously added from the top of the fractionation column, the recovered acetic acid and aniline mixture is continuously added from the second reaction tank, and acetic acid is continuously added from the third reaction tank. Control different reaction temperatures (the third one is 160-170°C, the fourth one is 200-210°C), so that acetic acid and aniline undergo a gas-liquid relative flow reaction. The water generated by the reaction is evaporated from the top of the fractionation column, and the acetylate It flows into the fourth reaction tank, and then is pumped into the distillation tank. The unconverted aniline and acetic acid are evaporated under reduced pressure. The reaction product is cooled into flakes to obtain acetanilide. Weight ingredient ratio: aniline: acetic acid = 1: (0.65-0.70), yield 99.5%. Operation Example 2: First put aniline and 3/10 of the acetic acid (content above 60%) into the acylation pot, heat it, and slowly add 1/10 of the acetic acid, heat to boiling, collect the fractionated dilute acetic acid, and slowly Add 4/10 of concentrated acetic acid or glacial acetic acid to the pot and react for 7 hours. Add the remaining 2/10 amount of glacial acetic acid for the last time and perform reflux fractionation. When the concentration of fractionated acetic acid reaches more than 85%, perform vacuum distillation to evaporate the remaining acetic acid. Discharging, cooling and crushing are the finished products. Most of the acylation of anilide to produce acetanilide uses glacial acetic acid as the acylating agent. Raw material consumption quota: aniline (99%) 690kg/t, glacial acetic acid 500kg/t. Laboratory preparation can be carried out as follows: In a 500ml flask with a reflux condenser, add 20.5g (0.22mol) aniline, 21.5g (0.21mol) acetic anhydride, 21g (0.35mol) glacial acetic acid and 0.1g zinc powder. Mix well and slowly heat and boil for half an hour. Then pour the hot reactant into 500ml cold water in a thin stream, stir, and cool with ice. Filter and dry to obtain 26g of crude product. Melting point 113℃. Purified by recrystallization from ethanol and water, melting point is 114°C.
![]()
Purpose
1. It is a raw material and intermediate for sulfa drugs, rubber vulcanization accelerators, dyes and synthetic camphor.
2. Used as analytical reagents, standard samples for quantitative analysis of organic elements (C, H, N), determination of cerium, chromium, lead, nitrate, nitrite and hydrogen peroxide. Stabilizer, also used in the pharmaceutical industry.
3. Acetanilide is the raw material of sulfa drugs and can be used as an analgesic, antipyretic and preservative. Used to manufacture dye intermediates p-nitroacetanilide, p-nitroaniline and p-phenylenediamine. It was used extensively in the manufacture of acetylsulfanilylchloride during World War II. Acetanilide is also used in the preparation of thioacetamide. In industry, it can be used as a rubber vulcanization accelerator, a stabilizer for fiber fat coatings, a stabilizer for hydrogen peroxide, and for the synthesis of camphor.
4. This product is often used as a raw material for sulfonamide drugs, and is also used in dyes, rubber vulcanization accelerators and synthetic camphor.
Agents, and used in the synthesis of camphor, etc.
4. This product is often used as a raw material for sulfonamide drugs, and is also used in dyes, rubber vulcanization accelerators and synthetic camphor.
