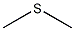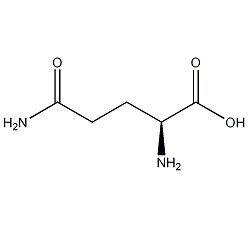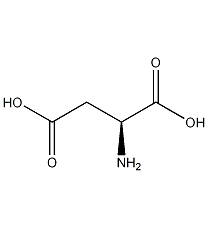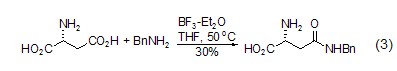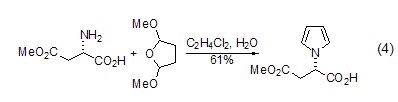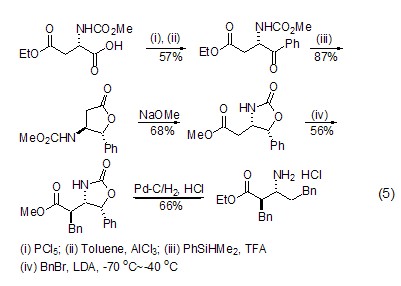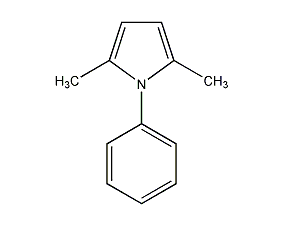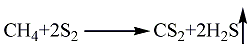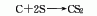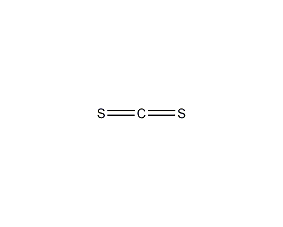
Structural formula
| Business number |
01J2 |
| Molecular formula |
CS2 |
| Molecular weight |
76.14 |
| label |
carbon disulfide,
Dithoicarbonic anhydride,
Carbon bisulfide,
Aliphatic sulfur compounds
|
Numbering system
CAS number:75-15-0
MDL number:MFCD00011321
EINECS number:200-843-6
RTECS number:FF6650000
BRN number:1098293
PubChem number:24860298
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless or light yellow transparent liquid with pungent odor and easy to evaporate. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -111.5[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 46.3[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 1.26[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 2.63[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 40 (20℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -1029.4[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 280[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 7.39[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.94 [10]
11. Flash point (℃): -30 (CC) [11]
12. Ignition temperature ( ℃): 90[12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 50.0[13]
14. Explosion Lower limit (%): 1.3[14]
15. Solubility: Insoluble in water, soluble in most organic solvents such as ethanol and ether. [15]
16. Refractive index (25ºC): 1.6241
17. Viscosity (mPa·s, 20ºC): 0.363
18. Ignition point (ºC): 100
19. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, 25ºC): 27.54
20. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol): 4.392
p>
21. Heat of formation (KJ/mol): 89.47
22. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 25ºC, constant pressure): 1.00
23 .Conductivity (S/m, 25ºC): 3.7×10-3
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[16] LD50: 3188mg/kg (rat oral)
2. Irritation No data yet
3. Subacute and chronic toxicity[17] Rabbit inhalation 1.28g/m3, 5 months, causing chronic poisoning; 0.5~0.6g/m3, 6.5 months, causing an increase in serum cholesterol.
4. Mutagenicity [18] Microbial mutagenicity: Salmonella typhimurium 100μg/dish. Sister chromatid exchange: human lymphocytes 10200μg/L
5. Teratogenicity [19] Inhalation is the lowest in rats 1 to 22 days after pregnancy Toxic dose (TCLo) 10mg/m3 (8h) can cause eye and ear development malformations. Rats inhaled the lowest toxic dose (TCLo) 100 mg/m3 (8 hours) from 1 to 21 days after pregnancy, causing developmental malformations of the craniofacial region (including nose and tongue).
6. Others[20] Minimum toxic concentration for male inhalation (TCLo): 40mg/m3 (91 weeks ), causing changes in sperm production. The lowest toxic concentration for inhalation in rats (TCLo): 100mg/m3 (8h) (administered from 1st to 21st day of pregnancy), �� Started with fetal death and abnormal craniofacial development.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[21] LC50: 162~135mg/L (24~96h) (mosquito fish)
2. Biodegradability No data yet
3. Non-biodegradability[22] In the air, when hydroxyl radicals When the concentration is 5.00×105 pieces/cm3, the degradation half-life is 5.5d (theoretical).
4. Bioaccumulation [23] BCF: <6.1 (carp, contact concentration 50μg/L) <60 (carp, contact concentration 5μg/L)
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 21.50
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 60.4
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 143.8
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 32.0
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 8.52
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 2.1
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 64.2
7. Number of heavy atoms: 3
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 18.3
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Extremely flammable and can easily burn and explode when exposed to heat, sparks, flames or oxidants. Decomposes when heated to produce toxic sulfide fumes. Reacts violently with aluminum, zinc, potassium, fluorine, chlorine, azide, etc., posing a risk of combustion and explosion. High-speed impact and friction can cause combustion and explosion due to static spark discharge.
2. Chemical properties: Stable to acids, and does not interact with concentrated sulfuric acid and concentrated nitric acid at room temperature. But it is unstable to alkali and reacts with potassium hydroxide to generate potassium thiosulfate and potassium carbonate. It reacts with sodium alcohol to form xanthate; it gradually oxidizes in the air, becoming yellow and smelly. It decomposes under the influence of sunlight; at low temperatures, it reacts with water to form crystals with the structure of 2CS2·H2O. It reacts with chlorine under appropriate conditions to produce carbon tetrachloride and sulfur chloride.
3. The high-concentration vapor of this product has an anesthetic effect. The concentration is 0.1% to 0.3%. Inhalation can cause death in 1 hour. Even if it is lower than the lethal dose, it will leave sequelae. Long-term inhalation (3 months) 160 When ×10-6 or more, neuritis will occur after 1 to 2 years. The maximum allowable concentration in the workplace is 60mg/m3. This product is toxic and irritating. Closed operation, local exhaust. Operators must undergo special training and strictly abide by operating procedures. It is recommended that operators wear self-priming filter gas masks (half masks), chemical safety glasses, anti-static overalls, and rubber oil-resistant gloves. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Smoking is strictly prohibited in the workplace. Use explosion-proof ventilation systems and equipment. Prevent vapors from leaking into the workplace air. Avoid contact with oxidants, amines, and alkali metals. The flow rate should be controlled during filling, and a grounding device should be installed to prevent the accumulation of static electricity. Equipped with corresponding varieties and quantities of fire-fighting equipment and leakage emergency treatment equipment. Empty containers may be harmful residues.
4. Due to its low boiling point, strong volatility and high toxicity, it is easily dispersed in the air during production and use, causing serious pollution and harm to the environment and human body. Carbon disulfide is a poison that damages nerves and blood vessels. When people are exposed to high concentrations of carbon disulfide, it has a paralyzing effect. If it lasts for a long time, the respiratory center may be paralyzed, resulting in loss of consciousness and death. At high concentrations, it can also be absorbed by human skin.
5. This product is a gas anesthetic. Its vapor has a strong irritating effect on the skin and eyes, and can easily cause dermatitis and burns. Acute poisoning begins to cause delirium, and later anesthesia, loss of consciousness, and even death from respiratory failure. Long-term inhalation of its vapor can cause symptoms such as weak stomach, insomnia, fatigue, loss of appetite, headache, dizziness, abnormal sensation, drop in blood pressure, trembling, stiffness of hands and feet, slow movement, salivation, sweating, memory loss and other symptoms. Mainly damages the nervous and cardiovascular systems. When the vapor concentration is 12440 mg/m3, death will occur in 30 to 60 minutes. TJ 36-79 stipulates that the maximum allowable concentration in workshop air is 10 mg/m3.
6. Stability[24] Stable
7. Incompatible substances[25] Strong oxidizing agent, aluminum
8. Conditions to avoid contact[26] Heating
9. Polymerization hazard[27] No polymerization
10. Decomposition products[28] Hydrogen chloride
Storage method
1. Storage precautions[29] It is easily volatile at room temperature, so the surface of the container can be covered with water. Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 29°C. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, amines, alkali metals, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with leakage emergency treatment equipmentequipment and suitable containment materials.
2. This product is packed in glass bottles and metal barrels (aluminum barrels, iron barrels, storage tanks) and protected by wooden boxes, and must be stored in In a warehouse constructed of non-combustible materials and with ground ventilation facilities, keep away from fire sources and avoid sunlight. In summer, cooling measures should be taken to keep storage below 17°C. There should be no electrical equipment or heating facilities near the warehouse, and lightning or static electricity must be prevented from igniting fires. The liquid level of the storage tank should be sealed with inert gas. Store and transport according to regulations for flammable materials.
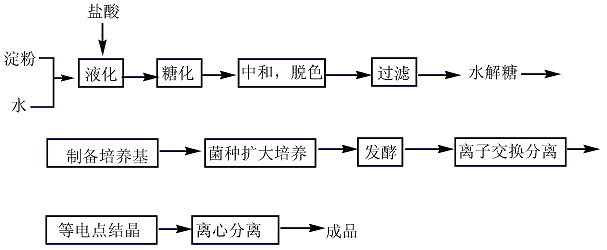
Synthesis method
1. Methane sulfur method: solid sulfur is heated and melted into liquid, and then purified with activated clay. Natural gas purification treatment uses light diesel to adsorb fractions above C2 and separate pure methane gas. After the natural gas and sulfur vapor are heated, they can be fully mixed and heated to 650°C, and then sent to the reactor for reaction. The pressurized partial condensation method is used to separate carbon disulfide and hydrogen sulfide, and carbon disulfide is obtained after distillation. The reaction formula is as follows:
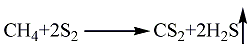
2. Charcoal sulfur method : According to different heating methods, it can be divided into two categories: external heating iron steamer method and internal heating electric furnace method. Generally, the three-phase electric furnace method is used. In the electric furnace method, charcoal is directly roasted at 800°C to remove moisture and organic matter and then added to the electric furnace intermittently. Molten sulfur is continuously added to the electric furnace to react with the red charcoal at about 1000°C. The generated carbon disulfide is desulfurized and condensed to obtain a crude product, which is then refined. Distillation and condensation to obtain carbon disulfide finished product. The reaction formula is as follows:
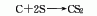
3. Commercially available Carbon disulfide is synthesized by heating charcoal and sulfur to 850 to 950°C. As a reagent, it can meet general requirements, but when the required purity is high, the following methods need to be used to remove the impurities contained in it. These impurities are hydrogen sulfide, sulfurous acid, sulfuric acid, organic sulfides, water and sulfur. Add 100 to 200 g of mercury and an appropriate amount of phosphorus pentoxide to 500 mL of commercially available carbon disulfide, shake for about 1 hour, filter, fractionate the filtrate away from light, discard the high and low fractions, and collect the middle fraction. The collected fractions are remixed with mercury and phosphorus pentoxide, shaken, and fractionated. Repeat this operation until the content of harmful impurities reaches the standard.
Refining method: Impurities contained include sulfur, sulfide and water. There are several refining methods: ① Distill 3 times with a glass still. ② Dry with calcium chloride and then fractionate multiple times. ③ Shake with mercury to remove sulfide, then dry and fractionate with phosphorus pentoxide. ④ Add 5g of crushed potassium permanganate to 1L of carbon disulfide and shake it thoroughly until the hydrogen sulfide is completely removed and then place it. After separation, add a small amount of mercury and shake it to remove the sulfur until the interface does not turn black further. Finally, add 5g of mercury sulfate to each 1L of carbon disulfide and shake to eliminate the odor. After separation, it is dried with calcium chloride and fractionated.
4. Use industrial carbon disulfide as raw material, add anhydrous copper sulfate (25-37.5g copper sulfate is required for each carbon disulfide), stir thoroughly until the black powder disappears and there is no unpleasant smell, immediately Filter to remove insoluble impurities, then add anhydrous copper sulfate to the filtrate, distill, and collect the fractions according to product specifications, which is the pure product.
Purpose
1. Used in the manufacture of viscose fiber, cellophane, xanthate, thiocyanate and carbon tetrachloride. Xanthate produced from carbon disulfide is used as an ore flotation agent in the metallurgical industry. Used in the production of agricultural pesticides. When vulcanized in the rubber industry, it can be used as a solvent for sulfur chloride. Use it to make anti-corrosion agents for equipment and pipelines in ammonia treatment systems. It is also a solvent used for testing primary amines, secondary amines and α-amino acids, measuring refractive index, and chromatographic analysis. It is also used to extract oil from linseed, olive fruit, animal bones, leather and wool. Used as an accelerator in aviation. It is also used as a solvent for grease, wax, paint, camphor, resin, rubber, sulfur, phosphorus, iodine, etc., as a degreaser for wool, as an agricultural pesticide, as a soil disinfectant, as a stain remover for clothes, etc. In analysis, it is used for the determination of primary amines, secondary amines and α-amino acids and as a solvent for infrared spectroscopy.
2. Carbon disulfide is widely used in metallurgy, pesticides, rubber, viscose fiber and other industrial fields. It has good penetrability and is generally used as a mixture with non-combustible ingredients when fumigating grain. Fumigation of dry seeds with carbon disulfide does not reduce seed viability. For grains such as wheat, barley, corn, rice, etc., fumigation at 250g/m3 for 24 hours will not affect germination. Gaseous carbon disulfide will seriously damage or kill growing plants or seedlings. Water-diluted carbon disulfide emulsion treats the soil around the roots of evergreen trees and deciduous seedlings, and can effectively control a variety of underground pests. Due to the flammable and explosive properties of carbon disulfide, this agent is used less and less in modern fumigations.
3. Mainly used as raw material for manufacturing viscose fiber and cellophane. Xanthate produced from carbon disulfide is used as an ore flotation agent in the metallurgical industry. Used in the production of agricultural pesticides. When vulcanized in the rubber industry, it can be used as a solvent for sulfur chloride. It is also a solvent used for testing primary amines, secondary amines and α-amino acids, measuring refractive index, and chromatographic analysis. It is also used to extract oil from linseed, olive fruit, animal bones, leather and wool. Used as aerospace accelerator.
4. Used as analytical reagents, solvents, viscose fibersVJ wool degreaser. Also used for refractive index determination.
5. Used in the manufacture of rayon, pesticides, accelerator M, accelerator D, and also used as solvents. [30]
extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/33-7.jpgextended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/1867extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/-BL-13-Niax-catalyst-A-133-Niax-A-133.pdfextended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44762extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44402extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/catalyst-9727/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/bis3-dimethylaminopropyl-N-CAS-33329-35-0-Tris3-dimethylaminopropylamine.pdfextended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/cas-23850-94-4-butyltin-tris2-ethylhexanoate/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44536extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/aeea/