Benzonitrile Benzonitrile
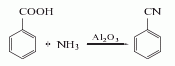
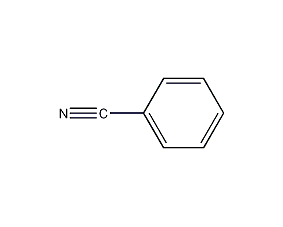
Structural formula
| Business number | 02J0 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C7H5N |
| Molecular weight | 103 |
| label |
phenyl cyanide, benzonitrile, Phenyl cyanide, Benzyl nitrile, Cyanobenzene, Aromatic nitrogen-containing compounds and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:100-47-0
MDL number:MFCD00001770
EINECS number:202-855-7
RTECS number:DI2450000
BRN number:506893
PubChem number:24857702
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless oily liquid with the smell of almonds. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -12.8[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 190.7[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 1.01[4]
5. Saturated steam Pressure (kPa): 0.13 (28.2℃)[5]
6. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -3617.8[6]
7. Critical temperature (℃): 426.2[7]
8. Critical pressure (MPa): 4.22[8]
9. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.56[9]
10. Flash point (℃): 71.7[10]
11. Ignition temperature (℃): 550[11]
12. Explosion upper limit (%): 8 [12]
13. Lower explosion limit (%): 1.3[13]
14. Solubility: slightly soluble in cold water, Soluble in hot water, easily soluble in ethanol and ether. [14]
15. Refractive index (20ºC): 1.5289
16. Viscosity (mPa·s, 15ºC): 1.447
17. Viscosity (mPa·s, 30ºC): 1.111
18. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, 25ºC): 55.52
19. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol) : 10.89
20. Heat of formation (KJ/mol, 25ºC): 163.29
21. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), constant pressure): 1.85
22. Conductivity (S/m): 5.0×10-8
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[15]
LD50: 700mg/kg (rat oral); 1250mg/kg (rabbit oral ); 1200mg/kg (rat transdermal); 971mg/kg (rabbit transdermal)
LC50: 6000mg/m3 (mouse inhalation)
2. Irritation No information available
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[16]
LC50: 78~135mg/L (96h) (fathead minnow); 78mg/L (96h) (Bluegill, soft water)
TLm: 75mg/L (7d) (Scenedesmus quadracoides); 3.4mg/L (8d) (Microcystis aeruginosa)
2. Biodegradability[17] Japanese MITI test, initial concentration 100mg/L, inoculated sludge concentration 30mg/L, degradation 63% after 2 weeks %.
3. Non-biodegradability[18] In the air, when the hydroxyl radical concentration is 5.00×105 pieces/cm3, the degradation half-life is 49 days (theoretical).
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 31.32
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 99.9
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 253.0
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 41.0
5. Polarizability: 12.41
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 23.8
7. Number of heavy atoms: 8
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 103
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Chemical properties: It has the general chemical properties of nitrile. Reduction with lithium aluminum hydride generates benzylamine. React with Grignard reagent, and the resulting product is then hydrolyzed to give the ketone. Benzonitrile hydrolyzes to form benzoic acid. Dissolve in fuming sulfuric acid or sulfuryl chloride to form three-molecule cyclized benzonitrile. It reacts with hydrogen sulfide to form thioamide. Heating with acetylene at 170~200℃ in the presence of potassium under pressure produces 2,4-diphenylpyrimidine. Heating with aluminum triazide produces 5-phenyltetrazole almost quantitatively.
2. Highly toxic, but less toxic than low-grade fatty nitriles. It can be absorbed through the skin and cause poisoning, causing symptoms such as spasm and nerve paralysis in animal tissues. Its vapor does not cause convulsions in experimental animals, but can cause depression and paralysis. Rats will not die if they inhale its saturated vapor for 4 hours. For small rodents, whether administered orally or intraperitoneally, the LD50 is 400 to 800 mg/kg. Mice were injected subcutaneously with LD180g/kg. The production workshop should be well ventilated, the equipment should be sealed, and operators should wear protective equipment.
3. Stability[19] Stable
4. Incompatible substances[20] Strong oxidants, strong reducing agents, strong acids, strong bases
5. Conditions to avoid contact [21] High fever
6. Hazards of aggregation[22] No aggregation
Storage method
1. Storage precautions[23] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, reducing agents, acids, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
2. Packed in iron drums, with a net weight of 100kg per drum. Store in a cool, dry place. Store and transport according to regulations on toxic chemicals.
Synthesis method
1. Nitrosation of phenol with sodium nitrite and sulfuric acid to produce p-nitrosophen, condensation with o-toluidine dissolved in sulfuric acid, and then reduction and sulfurization with sodium polysulfide with a certain sulfur reaction number , then passed through the gas for oxidation, and finally filtered, dried, crushed and standardized to obtain the product.
![]()
2. Use benzaldehyde and hydroxyl Aminosulfonic acid reacts to form hydroxylamine sulfonate, which is then converted into benzonitrile by the action of alkali.
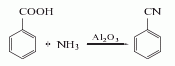
Refining method: often contains benzene and Impurities such as benzoic acid. During refining, the crude product is first distilled with water vapor, and the aqueous layer is separated from the distillate. The organic layer is washed with sodium carbonate aqueous solution, then dissolved in diethyl ether, washed with water, dried over calcium chloride, and the diethyl ether is evaporated and fractionated under reduced pressure. Benzonitrile with low impurity content can be dried with calcium sulfate or calcium hydride for several days, and then distilled 2 to 3 times in the presence of phosphorus pentoxide.
3. It can be obtained by ammonia oxidation of toluene or carbonization of ammonium benzoate.
Purpose
1. Used as an intermediate for medicines, dyes, pesticides, rubber chemicals, benzoic acid, etc. Also used as a solvent for vinyl resins. Used in the preparation of daily fragrance, as a modification to synergistically promote hair penetration. And improve the stability of fragrance.
2. Naturally found in roasted peanuts, hazelnuts, cocoa and dairy products. Used to prepare daily chemical fragrances and improve the stability of fragrances. Soap fragrance can be used up to 2%.
3. Used in rubber, resin, paint and synthetic intermediates. [24]
