Bis(2-chloroethyl)ether Bis(2-chloroethyl)ether
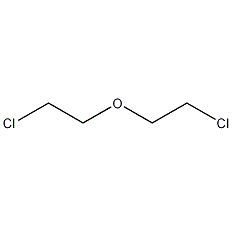
Structural formula
| Business number | 033J |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H8Cl2O |
| Molecular weight | 143.01 |
| label |
2,2′-Dichlorodiethyl ether, 2,2′-dichloroethyl ether, β,β’-dichlorodiethyl ether, 2,2′-Dichlorodiethyl ether, 1-Chloro-2-(2-chloroethoxy)ethane, soil pesticides, dry cleaning agent, Multifunctional solvent |
Numbering system
CAS number:111-44-4
MDL number:MFCD00000975
EINECS number:203-870-1
RTECS number:KN0875000
BRN number:605317
PubChem number:24892662
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless and transparent liquid with spicy and fruity flavor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -52[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 178.5[3]
4. Relative density (water=1): 1.22 (20℃)[4]
5. Relative vapor density (air = 1): 4.93[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 0.10 (20℃)[6]
7. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.29[7]
8. Flash point (℃): 55 (CC)[8]
9. Ignition temperature (℃): 368.89[9]
10. Solubility: insoluble in Water, miscible in ethanol, ether and most organic solvents. [10]
11. Refractive index (20ºC): 1.4568
12. Refractive index (25ºC): 1.4546
13 . Viscosity (mPa·s, 20ºC): 2.41
14. Viscosity (mPa·s, 25ºC): 2.14
15. Viscosity (mPa·s, 35ºC): 2.06
16. Flash point (ºC, open): 79
17. Flash point (ºC, closed): 55
18. Fire point (ºC): 369
19. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, b.p.): 42.26
20. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol): 8.67
21. Specific heat capacity (KJ / (kg·K), 30ºC, constant pressure): 1.55
22. Vapor pressure (kPa, 75ºC): 2.67
23. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): 0.21
24. Volume expansion coefficient (K-1, 10~30ºC): 0.00097
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[11]
LD50: 110mg/kg (rat oral); 140mg/kg (orally for mice)
2. Irritation[12] Rabbit transdermal: 500mg , mild stimulation (open stimulation test)
3. Mutagenicity[13] Microbial mutagenicity: Salmonella typhimurium 1ml/dish (2h)
4. Carcinogenicity[14] IARC carcinogenicity comments: G3, insufficient evidence of carcinogenicity to humans and animals.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[15]
EC50: 238mg/L (48h) (Daphnia, Static)
LC50: 600mg/L (96h) (Bluegill��Yang fish, static)
2. Biodegradability[16]
Aerobic aqueous biodegradation (h): 672~4320
Anaerobic aqueous biodegradation (h): 2688~17280
3. Non-biodegradability[17]
Photooxidation half-life in air (h): 9.65~96.5
First-order hydrolysis half-life (h): 1.93×105
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 32.02
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 123.6
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 290.5
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 29.3
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 12.69
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 4
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 9.2
7. Number of heavy atoms: 7
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 28.9
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Chemical properties are stable to heat. It reacts with sodium alkoxide to form ether. Reacts with amine compounds to form morpholine derivatives. Heating with sodium hydroxide generates 2-chloroethyl vinyl ether.
2. The vapor of this product is toxic. Pulmonary edema may occur after inhaling high-concentration vapor for several hours or days. The oral LD50 of mice is 105mg/kg, and the allowable concentration in the air is 15*10-6. It is easily absorbed by the skin and is highly toxic due to its strong irritation. When a person is briefly exposed to vapor with a concentration above 3.2g/m3, it will cause obvious irritation to the eyes and nasal cavity, and may cause unbearable feelings, including coughing, nausea and vomiting. Its vapors can slowly damage the lungs. The maximum allowable concentration in the workplace is 90 mg/m3.
3. Stability[18] Stable
4. Incompatible substances[19] Strong oxidants, strong acids, water, halogens, sulfur, sulfides
5. Conditions to avoid contact[20] Heat, humid air, light
6. Polymerization hazard[21] No polymerization
7. Decomposition Product[22] Chloride
Storage method
Storage Precautions[23] Store in a cool, dry and well-ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Avoid light. The packaging must be sealed and protected from moisture. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with leakage emergency response equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Refining method: wash with concentrated hydrochloric acid several times and then distill under reduced pressure.
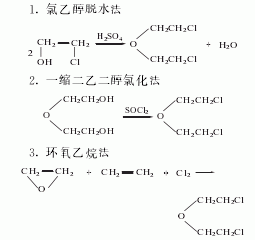
2. Preparation method:
p>
![]()
Installed with stirrer, thermometer, reflux Add 500g (4.71mol) of β, β′-dihydroxydiethyl ether (2) to the condenser (connected to an air tube to absorb hydrogen chloride and sulfur dioxide) and dropping funnel reaction flask, cool it to about 0°C in an ice-water bath, and slowly drip it Add 1200g of thionyl chloride, control the temperature of the reaction solution below 20°C, and complete the addition in about 5 hours. After addition, stir at room temperature for 3 hours and leave overnight. Slowly add 50 to 60 mL of pyridine, reflux for 3 hours, and evaporate excess thionyl chloride. After cooling, pour into ice water, let stand, separate the organic layer, wash with saturated sodium carbonate aqueous solution, dry with anhydrous calcium chloride, filter, distill under reduced pressure, collect the fractions at 55~65℃/1.0~1.2kPa to get β , β′-dichlorodiethyl ether (1) 538.4g, yield 80%. [25]
3. Preparation method:
![]()
In a reaction bottle equipped with a stirrer, thermometer, dropping funnel, and reflux condenser (install a gas conduit to the SO2 and HCl gas absorption bottle), add 500g of β, β’-dihydroxydiethyl ether (2) , cool to 0°C in an ice-salt bath, slowly add 1.2kg of thionyl chloride dropwise with stirring, control the temperature not to exceed 20°C, and complete the addition in about 4 hours. Then react at room temperature for 3 hours. Leave it overnight, add 5g of pyridine, and reflux for 3 hours. After cooling, slowly pour in ice water and stir thoroughly. Let sit to layer. The organic layer was separated and washed with saturated sodium carbonate solution until neutral. Dry the anhydrous calcium phosphate and distill under reduced pressure. Collect the fractions at 55~60℃/1.0~1.2kPa to obtain β,β’-dichlorodiethyl ether ① (1), with a yield of 80%. Note: ① It can also be prepared by heating and dehydrating chloroethanol in the presence of sulfuric acid. [26]
Purpose
1. Used as solvent, organic synthesis, gas chromatography stationary solution (maximum operating temperature 25°C, solvent is diethyl ether), separation and analysis of methylchlorosilane, and determination of iron. Used as a solvent for fats, oils, waxes, rubber, tar, asphalt, resins, ethyl cellulose, etc. It is also used as soil pesticide, dry cleaning agent and preparation of coatings.
2. Used as solvents, soil fumigation pesticides, and also used in organic synthesis and coatings. [24]
ether), separation and analysis of methylchlorosilane, and determination of iron. Used as a solvent for fats, oils, waxes, rubber, tar, asphalt, resins, ethyl cellulose, etc. It is also used as soil pesticide, dry cleaning agent and preparation of coatings.
2. Used as solvents, soil fumigation pesticides, and also used in organic synthesis and coatings. [24]
