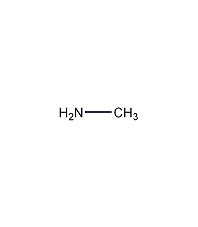
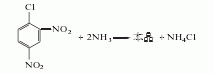Glycine
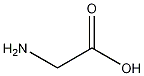
Structural formula
| Business number | 017L |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C2H5NO2 |
| Molecular weight | 75.07 |
| label |
Glycine, ethylamine, Glycine (glycine), aminoacetic acid, Aminoacetic acid, Glycocoll, Gly, Aminoethanoic acid |
Numbering system
CAS number:56-40-6
MDL number:MFCD00008131
EINECS number:200-272-2
RTECS number:MB7600000
BRN number:635782
PubChem number:24865701
Physical property data
1. Properties: White monoclinic or hexagonal crystals, or white crystalline powder. Odorless, with a special sweet taste.
2. Density (g/mL, 20/4ºC): 1.1607
3. Melting point (ºC): 290
4. Refractive index: 1.5370
5. Vapor pressure (kPa,,20ºC): 5×10-6kPa
6. Solubility (%, 0ºC, water): 14.18
7. Solubility (%, 25ºC, water): 24.99
8. Solubility (%, 50ºC, water): 39.10
9. Solubility (%, 75ºC, water): 54.39
10. Solubility (%, 100ºC, water): 67.17
11. Solubility: soluble in water, slightly soluble in pyridine, solubility in water: 25g/100ml at 25℃ ; 39.1g/100ml at 50℃; 54.4g/100ml at 75℃; 67.2g/100ml at 100℃. It is extremely difficult to dissolve in ethanol and dissolves about 0.06g in 100g of absolute ethanol. Almost insoluble in acetone and ether. Insoluble in organic solvents. Reacts with hydrochloric acid to form hydrochloric acid compounds.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: rat oral LD50: 7930mg/kg; rat subcutaneous LD50: 5200mg/kg;
rat intravenous LD50: 2600mg/kg; mouse oral LC50: 4920mg/kg;
Mouse abdominal cavity LC50: 4450mg/kg; mice LC50: 5060mg/kg;
Mouse venous LC50: 2370mg/kg; >2. Other multiple dose toxicity: rat subcutaneous TDLo: 45mg/kg/30D-I
3. Mutagenicity: SisterChromatid exchangeTEST system: human lymphocytes: 100mg/L
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 16.41
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol) 59.8
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K) : 162.5
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 54.4
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 6.50
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 2
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 63.3
7. Number of heavy atoms: 5
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 42.9
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Glycine is an amino acid with the simplest structure among the amino acid series and is non-essential to the human body. It has both acidic and alkaline functional groups in the molecule. It is a strong electrolyte in aqueous solution and has greater solubility in highly polar solvents. It is basically insoluble in non-polar solvents and has a high boiling point and melting point. Glycine can take on different molecular forms by adjusting the acidity and alkalinity of the aqueous solution. Reacts with hydrochloric acid to form hydrochloride. Non-toxic and non-corrosive.
2.This product is non-toxic and non-corrosive.
3. Exist in tobacco leaves and smoke.
Storage method
1. Packed in plastic bags with polypropylene woven bags, sacks or barrels, each bag is 25kg. Store in a cool, ventilated and dry place. Store and transport according to general chemical regulations
Synthesis method
1. Chloroacetic acidification method chloroacetic acid 95% 1600
Liquid ammonia industrial grade 880
Methenamine 98% 350
Ethanol 95% 1100

2. Strecker method formaldehyde 70 % 114
Sodium cyanide 70% 930
Ammonium chloride 70% 1020
Barium hydroxide 80% 1430
Sulfuric acid 90 % 725
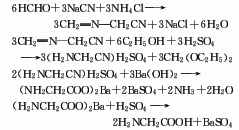
3.Mix ammonia and ammonium carbonate and heat them on a water bath. Prepare a chloroacetic acid aqueous solution and add it dropwise to the above mixed solution. After the mixture is heated and kept warm, it is cooled and crystallized to obtain a crude product. Dissolve the crude product in boiling water, add methanol, and obtain pure glycine after crystallization. The response is as follows:

4.Using formaldehyde, hydrocyanic acid and ammonia as raw materials, aminoacetonitrile is first synthesized and then decomposed to generate glycine. Or it can be obtained by reacting ammonia water, ammonium bicarbonate and chloroacetic acid as raw materials through decolorization, crystallization, washing, recrystallization and drying.
5.Add 2.2L ammonia water to 2.1kg urotropine while stirring under cooling to fully dissolve it, and then Add dropwise 13.3kg of 75% chloroacetic acid solution and 20kg of 28% ammonia water. Control the reaction temperature to 50-60°C, the reaction solution pH = 7-8, incubate it at 72-78°C for 3 hours, suck off the supernatant, and dry the crystallized crude product, then refine and dry it with 75% ethanol, which is the finished product. . The process reaction formula is:

6. Tobacco: BU, 21; Synthesis: It can be made by the reaction of monochloroacetic acid and ammonium hydroxide, or it can be obtained by hydrolysis and refining of gelatin.
Purpose
(1) Food grade glycine: 1. Used as flavoring and sweetener, used in alcoholic beverages in combination with DL-alanine, citric acid, etc.; used as sour taste correction when synthesizing sake and refined feed. Agents and buffers; used as additives when pickling pickles, sweet sauce, soy sauce, vinegar and fruit juice to improve the flavor and taste of food, maintain the original taste, provide a source of sweetness, etc.; 2. Used as an additive for surimi products, peanut butter, etc. Preservative, it can inhibit the reproduction of Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli; 3. Utilize its own amino and carboxyl groups to buffer the taste of salt and vinegar; 4. Used as a food attractant (attractant) in feed additives; 5. Formulas for food brewing, meat processing and refreshing drinks, and debitter agent for sodium saccharin; 6. Used as a stabilizer for cream, cheese, margarine, instant noodles, wheat flour and lard; 7. Used as a stabilizer in food processing Vitamin C for stabilization; 8. 10% of MSG is glycine; 9. It can be used as a preservative and plays an important preservative role.
(2) Pharmaceutical grade glycine: 1. Used as a drug for medical microbiology and biochemical amino acid metabolism research; 2. Used as a chlortetracycline buffer and anti-Patient’s disease drug L-dopavitamin Raw materials for the synthesis of amino acids such as B6 and threonine; 3. Used as ammoniaAcid nutritional infusion; 4. Used as raw materials for cephalosporins; intermediates for thiamphenicol; intermediates for the synthesis of imidazole acetic acid, etc.; 5. Used as raw materials for cosmetics.
(3) Feed grade glycine: It is mainly used as an additive and attractant to increase amino acids in feeds for poultry, livestock and poultry, especially pets. Used as a hydrolyzed protein additive and as a synergist for hydrolyzed protein.
(4) Industrial grade glycine: used as a pesticide intermediate, such as the main raw material of the herbicide glyphosate; electroplating solution additive; PH regulator.
(5)Nutritional additives. Mainly used in feed for poultry, livestock and poultry.
(6) Used in pharmaceuticals, organic synthesis, and as biochemical reagents.
(7)It is used as a food additive to stabilize vitamin C in the processing of meat products, refreshing drinks, etc. Use alone or in combination with sodium glutamate, alanine, citric acid, etc. Also used as ph regulator. In medicine, it is used as a synthetic raw material for amino acid preparations (infusion), the anti-Parkinson’s disease drug L-Dopa (L-Dopa), etc. Used as auxiliary additive in cosmetics.
(8)Glycine is used in electroless nickel plating solutions or as electroplating additives.
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/40234extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/202extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/40057extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/pc-5-hard-foam-catalyst/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/fascat4350-catalyst-fascat-4350/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/spraying-composite-amine-catalyst-nt-cat-pt1003-pt1003/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/40534extended-reading:https://www.morpholine.org/category/morpholine/page/5400/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/39958extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44827