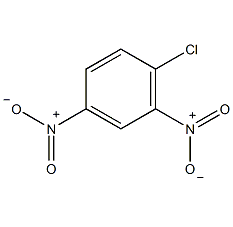
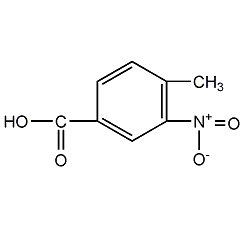
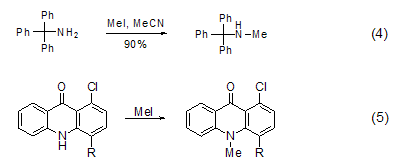
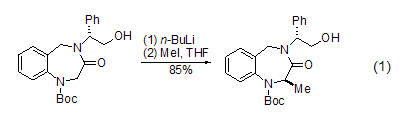2,4-dinitroaniline
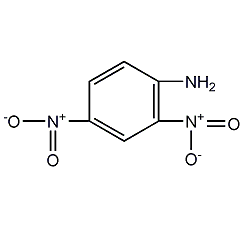
Structural formula
| Business number | 02BT |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H5N3O4 |
| Molecular weight | 183.12 |
| label |
Aromatic nitrogen-containing compounds and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:97-02-9
MDL number:MFCD00007151
EINECS number:202-553-5
RTECS number:BX9100000
BRN number:982999
PubChem number:24869580
Physical property data
1. Character: yellow needle crystal[1]
2. Melting point (℃): 180[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 333.6[3]
4. Relative density (water=1): 1.62[ 4]
5. Relative vapor density (air = 1): 6.31[5]
6. Octanol/water partition coefficient : 1.84[6]
7. Flash point (℃): 223.9 (CC) [7]
8. Solubility: Insoluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol, soluble in hot hydrochloric acid. [8]
Toxicological data
1. Skin/eye irritation:
Standard Dresser test: rabbit eye contact, 500mg/24HREACTION SEVERITY, moderate reaction;
2. Acute toxicity:
p>
Rat oral LD50: 285mg/kg; rat peritoneal cavity LDL0: 250mg/kg; mouse oral LD50: 370mg/kg; mouse peritoneal cavity LDL0: 400mg/kg; guinea pig oral LD50: 1050mg/kg;
3. Reproductive toxicity:
Inhalation of TCLo in rats 1-7 days after conception: 1100μg/m3/4HkgSEX/DURATION;
Pregnancy Rats 1-7 days inhaled TCLo: 17mg/m3/4HkgSEX/DURATION;
4. Mutagenicity:
Mutation microbial test: bacteria – Salmonella typhimurium, 10μg/ plate;
Mutation microorganism test: bacteria-Salmonella typhimurium, 2μg/plate;
Non-qualitative DNA comprehensive test: rat liver, 50μmol/L;
5. Acute toxicity[9] LD50: 285mg/kg (rat oral)
6. Irritation [10] Rabbit eye: 500mg (24h), mild irritation.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[11] LC50: 14.2mg/L (96h) (fathead minnow)
2. Biodegradability No data yet
3. Non-biodegradability[12] In the air, when the hydroxyl radical concentration is 5.00×105/cm3, the degradation half-life is 17.7h.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 43.58
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 115.3
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 344.0
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 79.0
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 17.27
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 1
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 5
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers:
6. Topological molecular polar surface area (TPSA): 112
7. Chongyuan��Number: 13
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 221
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. This product is highly toxic. Strongly irritating to skin and mucous membranes. It can be absorbed through the skin and cause poisoning, and is more toxic than nitroaniline. See m-nitroaniline.
2. Stability[13] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[14] Strong oxidants, strong acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides
4. Conditions to avoid contact [15] Heat
p>
5. Polymerization hazard[16] No polymerization
6. Decomposition products[17] sup> Nitrogen oxides, ammonia
Storage method
1. Storage precautions[18] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The packaging is sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
2. Packed in iron drums lined with plastic bags or cardboard drums, each drum is 40kg or 50kg. Keep dry during storage and transportation. Store and transport according to regulations on toxic and dangerous goods.
Synthesis method
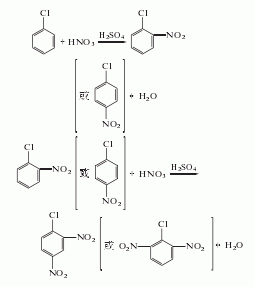
Mainly adopts ammonolysis method
It is obtained by pressurized ammonolysis of 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene. Add 15kg of open powder (sodium 1,2-dibutylnaphthalene-6-sulfonate), 300kg of 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene, and 1350L of ammonia water (containing 150kg of ammonia) into the ammonolysis reaction pot, heat, and wait for 1 hour Raise the temperature to 80℃ or so and stop heating. Control the reaction temperature to 108-110°C and the pressure to 0.35-0.4MPa. Release the pressure after 4 hours of heat preservation reaction. The released ammonia gas is absorbed and reused with water. The reaction solution is cooled to below 35°C and filtered, and the filter cake is washed with cold water until it is close to neutral to obtain the finished product. The yield is 90-95%.
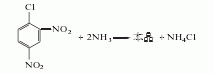
Purpose
1. Used in the manufacture of azo dyes and disperse dyes. It can also be used as a toner for printing inks and preservatives.
2. Used to prepare neutral dyes, sulfur dyes, azo dyes and disperse dyes, etc. Mainly used to prepare dyes such as sulfide deep blue 3R, dispersed red B, dispersed violet 2R, dispersed red violet P-R, dispersed deep blue HGL, permanent orange RN and so on. It is also used to prepare preservatives, pesticides, and toners for ink printing.
3. Used as azo dye intermediates, corrosion inhibitors, and analytical reagents. [19]
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44779extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/category/products/page/43extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/nt-cat-a-240-catalyst-cas1739-84-0-newtopchem/extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/catalyst-1028-polyurethane-catalyst-1028/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/pc-cat-t9-catalyst-nitro/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/1721extended-reading:https://www.cyclohexylamine.net/catalyst-25-s-catalyst-for-soles/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/heat-sensitive-metal-catalyst/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/n-3-dimethyl-amino-propyl-n-n-diisopropanolamine/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/lupragen-n201-catalyst-basf/