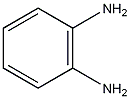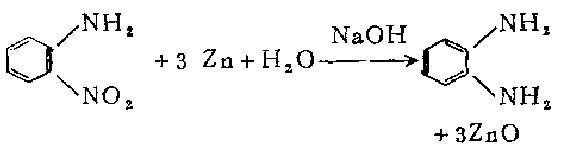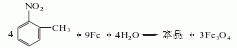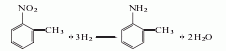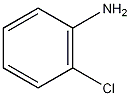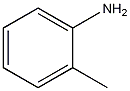
Structural formula
| Business number |
029A |
| Molecular formula |
C7H9N |
| Molecular weight |
107.15 |
| label |
2-methylaniline,
1-amino-2-toluene,
2-Methylaniline,
o-Aminotoluene,
2-Toluidine,
Aromatic nitrogen-containing compounds and their derivatives
|
Numbering system
CAS number:95-53-4
MDL number:MFCD00007730
EINECS number:202-429-0
RTECS number:XU2975000
BRN number:741981
PubChem number:24889242
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless or light yellow oily liquid [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -16.3 [2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 200.3[3]
4. Relative density (water=1): 1.008 [4]
5. Relative vapor density (air=1): 3.69[5]
6. Saturated vapor Pressure (kPa): 0.0346 (25℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -4054.3[7]
8. Critical pressure (MPa): 3.75[8]
9. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.32[9]
10. Flash point (℃): 85 (CC) [10]
11. Ignition temperature (℃): 481.67[11]
12. Explosion upper limit (%): 7.6[12]
13. Explosion lower limit (%): 1.5 [13]
14. Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, soluble in ethanol, ether and dilute acid. [14]
15. Viscosity (mPa·s, 15ºC): 5.195
16. Viscosity (mPa·s, 25ºC): 3.390
17. Heat of evaporation (KJ/kg, b.p.): 416.4
18. Heat of fusion (KJ/kg): 70.3
19. Heat of generation (KJ/ mol): -2.76
20. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol, constant pressure): 4060.9
21. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol, constant volume): 4035.2
22. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 15~64ºC, constant pressure): 2.05
23. Thermal conductivity (W/(m·K), liquid): 0.1845
24. Thermal conductivity (W/(m·K), 20ºC): 0.1586
25. Electrical conductivity (S/m, 25ºC): 3.792×10 -7
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: rat oral LD50: 940mg/kg; rabbit dermal LD50: 3250mg/kg.
2. The methemoglobin produced by o-toluidine has a strong effect on causing neurological disorders and can directly stimulate the bladder, causing severe cystitis, bladder bleeding and hematuria. This product can cause poisoning due to skin absorption, so contact with skin should be avoided. TJ 36-79 stipulates that the maximum allowable concentration in workshop air is 5 mg/m3.
3. Acute toxicity[15]
LD50: 670mg/kg (rat Oral); 3250ul (3250mg)/kg (rabbit transdermal)
LC50: 862ppm (rat inhalation, 4h)
4. Irritation[16]
Rabbit transdermal: 500mg (24h), mild stimulation.
Rabbit eye: 750μg (24h), severe irritation.
5. Mutagenicity[17] Microbial mutagenicity: Salmonella typhimuriumBacteria 40μg/dish. Micronucleus test: human lymphocytes 2mmol/L. Unprogrammed DNA synthesis: human HeLa cells 50μL/L. DNA inhibition: human HeLa cells 50μL/L. Sister chromatid exchange: human lymphocytes 200 μmol/L. Mammalian somatic mutations: human lymphocytes 450mg/L.
6. Carcinogenicity[18] IARC Carcinogenicity Comment: G2A, possible human carcinogen.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[19]
LC50: 100mg/L (96h) (fish)
EC50: 8mg/L (48h) (Daphnia)
IC50: 0.31~6.3mg/L (72h) (algae)
2 .Biodegradability[20]
Aerobic biodegradation (h): 24~168
Anaerobic biodegradation (h): 96~672
3. Non-biodegradability[21]
Photolysis maximum light absorption (nm): 234~284
Photolysis maximum light absorption wavelength range (nm): 62.4~3480
Photooxidation half-life in air (h): 0.394~3.94
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 35.31
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 107.9
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 270.7
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 39.5
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 13.99
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 26
7. Number of heavy atoms: 8
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 70.8
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Chemical properties: similar to aniline. Forms salt with acid. Diazotization reaction occurs with nitrous acid to generate diazo compounds. Reacts with alcohols, halogenated hydrocarbons, alkenes, etc. to generate N-alkyl compounds. Alkylation, halogenation, sulfonation, nitration, nitrosation and other reactions can occur on the aromatic nucleus, occurring in the ortho and para positions of the amino group. It is heated to 200°C with powdered sulfur to form a thiazole ring. When oxidized with chromic acid or manganese dioxide in dilute sulfuric acid, p-toluoquinone, 2,2′-dimethylazobenzene or o-nitrotoluene will be generated depending on the conditions. When reduced with lithium, 2-methylcyclohexylamine is obtained.
2. Stability[22] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[23] Strong oxidants, acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, chloroform
4. Conditions to avoid contact[24] Light, heat
5. Polymerization hazard[25] No polymerization
6. Decomposition products [26] Ammonia
Storage method
Storage Precautions[27] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The packaging must be sealed and must not come into contact with air. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
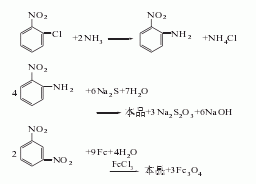
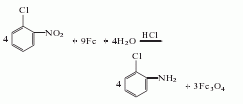
1. Obtained from the reduction of o-nitrotoluene. In the reduction reaction, iron powder can be used as the reducing agent, or o-toluidine can be obtained by hydrogenation reaction at 260-280°C in the presence of a copper catalyst. The content of industrial product o-toluidine (total amino content) is above 99%. The hydrogenation reduction method consumes 1,300kg of o-nitrotoluene and 940m3 of hydrogen per ton of product.
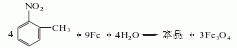
2. Its preparation method is: O-nitrotoluene is produced by catalytic hydrogenation and reduction. Due to different hydrogenation catalysts, the reaction conditions vary. For example, if a copper catalyst is used, the reaction temperature is 260°C, and a nickel catalyst can also be used.
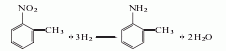
Refining method: different according to the manufacturing method , containing impurities such as m-toluidine, p-toluidine, and nitrotoluene. In particular, it contains a large amount of p-toluidine and a trace amount of moisture. The refining method is similar to that of aniline, but it is difficult to separate other toluidines by distillation. Therefore, the crude o-toluidine is first distilled twice, then dissolved in four times the volume of ether, and an equivalent amount of oxalic acid ether solution is added. The generated p-toluidine oxalate is removed by filtration, the ether is evaporated from the filtrate and the generated o-toluidine oxalate is filtered out. Recrystallize 5 times with water containing oxalic acid, and then treat with sodium carbonate solution. The free o-toluidine is dried with calcium chloride and distilled under reduced pressure three times to obtain the pure product.
3. Take o-nitrotoluene, reduce it with iron powder in dilute acid medium, and then separate. The crude o-toluidine obtained above is dissolved with acid to form a salt, and then precipitated with sodium hydroxide to obtain the pure product.
Purpose
1. Used to prepare azo dyesMaterials, triphenylmethane dyes, vulcanization accelerators and saccharin, etc. Also used as analytical reagents.
2. Used in organic synthesis as analytical reagents and dye intermediates.
3. Used for the preparation of sulfide blue, sulfide light yellow GC, sulfide yellow brown 5G, phenol AS-D, red base RL, big red base G, maroon base GBC, acidic pink 3B, reduction Pink R, basic fuchsin and basic pink T, etc. In the pharmaceutical industry, it is used in the preparation of o-cloxacillin, methaqualone, bisupin, rhodin, etc. It is used in the pesticide industry to synthesize pyrimidine. It is also used to synthesize vulcanization accelerators DT, BG, PR, etc.
4. Used as dye intermediate, used in organic synthesis and saccharin synthesis, etc. [28]
extended-reading:https://www.morpholine.org/pc-41/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/4-acetyl-morpholine/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/fascat4350-catalyst/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/niax-b-26-delayed-foaming-tertiary-amine-catalyst-momentive/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/KAOLIZER-12-MSDS.pdfextended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/category/products/page/21extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/Catalyst-1027-polyurethane-catalyst-1027-foaming-retarder-1027.pdfextended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/39966extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/lupragen-n600-trimer-catalyst-basf/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/dibutyl-tin-bis-1-thioglycerol/