Cinnamyl alcohol Cinnamyl alcohol
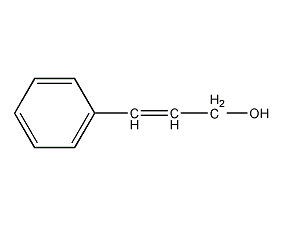

Structural formula
| Business number | 02Q9 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C9H10O |
| Molecular weight | 134.18 |
| label |
3-phenyl-2-propen-1-ol, phenylpropenol, Cinnamyl alcohol, cinnamon alcohol, beta-phenylpropenol, Cinnamyl alcohol, β-Phenylpropenol, 1-Phenyl-1-propen-3-ol, 2-Propen-1-ol,3-Fenyl-2-propen-1-ol, 3-phenyl-2-propen-1-o, 3-Phenyl-2-propenol, 3-phenyl-2-propen-1-ol, Cinnamon alcohol, γ-Phenylallyl alcohol, flavors and fragrances, alcohol solvent |
Numbering system
CAS number:104-54-1
MDL number:MFCD00002921
EINECS number:203-212-3
RTECS number:GE2200000
BRN number:1903999
PubChem number:24890289
Physical property data
1. Properties: The trans form is a white crystal, the cis form is a liquid, with a balsamic aroma, and a sweet floral and hyacinth aroma.
2. Density (g/mL, 25℃): 1.048
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): 4.6
4. Melting point (ºC): 33~35
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 258
6. Boiling point (ºC, kPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive index (n20D): 1.5819
8. Flash point (ºC): 126
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor Pressure (mmHg, 25ºC): <0.01
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
p>
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient Logarithmic value of p>
19. Solubility: Easily soluble in alcohol, ethanol and general organic solvents, soluble in water, glycerin and 2 times the volume of 60% ethanol.
Toxicological data
1. Skin/eye irritation: Standard Dresser test: rabbit skin contactContact, 500mg/24HREACTION SEVERITY, moderate reaction; 2. Acute toxicity: rat oral LD50: 2mg/kg; mouse oral LD50: 2675mg/kg; rabbit skin contact LD50: >5mg/kg; guinea pig oral LD50: 2675mg/kg; 3. Other multiple dose toxicity: rat oral TDLo: 6366mg/kg/17W-I; 4. Mutagenicity: DNA repair test: Bacillus subtilis, 10mg/disc;
Ecological data
None yet
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 43.67
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 127.9
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 326.9
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 42.6
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 17.31
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 20.2
7. Number of heavy atoms: 10
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 101
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 1
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Found in burley tobacco leaves.
2. Naturally found in styrax, certain aromatic resins, hyacinth flowers and a few essential oils.
Storage method
None yet
Synthesis method
1. Cinnamaldehyde reduction method
Add 0.01 part of aluminum chips to 1 part of benzyl alcohol by mass, heat to 60°C to react to release hydrogen, and increase the temperature to 180°C until the release of hydrogen stops. After cooling and filtering, the aluminum benzyl alcohol solution was added to the mixture of benzyl alcohol and cinnamaldehyde (mass 1:1). Heat to boiling under the conditions of 0.0027MPa, steam out the benzaldehyde generated by the reaction at 80°C and a reflux ratio of 3 to 4, and add benzyl alcohol at the same time. Stop feeding until 95% of the theoretical amount of benzaldehyde has been evaporated, and evaporate the remaining benzyl alcohol, and then evaporate the crude cinnamyl alcohol. After further distillation under reduced pressure, the 117°C (7kPa) fraction is collected, which is the product.
Styrax balsam saponification method
Cinnamyl alcohol occurs naturally in balsam of Peru, benzoin and styrax balsam in the form of cinnamyl cinnamate. Heat and saponify styrax balsam in 10% sodium hydroxide solution for 5 hours, then extract the hydrolyzate cinnamyl alcohol with diethyl ether, and finally purify it by distillation under reduced pressure to obtain the finished product.
2.It is obtained by heating and saponifying styrax balsam in sodium hydroxide solution, extracting and distilling under reduced pressure. Or it can be obtained by reducing cinnamic aldehyde with aluminum isopropenyl, aluminum butoxide or aluminum benzyl alcohol.
3. Tobacco: BU, 14.
Purpose
1. Widely used in the preparation of floral essences, cosmetic essences and soap essences, and also used as fixatives
2.Used In food flavor and daily chemical flavor formulas. Among edible flavors, it is mainly used to prepare fruit-based flavors such as strawberries, lemons, apricots, and peaches, and brandy flavors. The amount used in chewing gum is 720mg/kg; in baked goods, it is 33mg/kg span>; 17mg/kg in candies; 8.8mg/kg in soft drinks ; In cold drinks, 8.7mg/kg; in alcohol, 5.0mg/kg.
