dibutyl sulfate
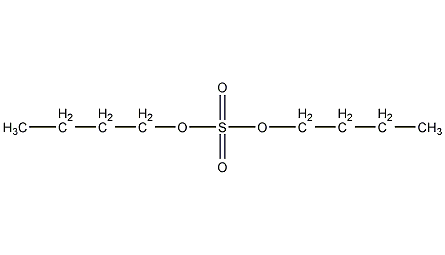

Structural formula
| Business number | 06RQ |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C8H18O4S |
| Molecular weight | 210.29 |
| label |
n-butyl sulfate, dibutyl sulfate, Butyl sulfate, Dibutyl sulfate, (CH3CH2CH2CH2O)2SO2 |
Numbering system
CAS number:625-22-9
MDL number:MFCD00059420
EINECS number:None
RTECS number:WS7700000
BRN number:1707498
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid.
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4℃): 1.06
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): Undetermined
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): Undetermined
6. Boiling point (ºC, 5.2kPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive index: 1.421
8. Flash point (ºC): Undetermined
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
p>
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V /V): Undetermined
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Insoluble in water.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: Rat (oral) TDLo: 12mg/kg
Rat (subcutaneous) TDLo: 9,500mg/kg
Since the LD50 of table salt is 3,000 mg /kg, the acute toxicity level of BPA is the same as that of table salt.
Ecological data
Do not allow large quantities of products that are slightly harmful to water to come into contact with groundwater, waterways or sewage systems. Do not discharge materials into the surrounding environment without government permission.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 51.38
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 194.3
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 472.9
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 35.0
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 20.37
�Calculate chemical data
1. Hydrophobic parameter calculation reference value (XlogP): 2.2
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 4
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 8
5. Topological molecular polar surface area (TPSA): 52.6
6. Number of heavy atoms: 13
7. Surface charge: 0
8. Complexity: 177
9. Number of isotope atoms: 0
10. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters : 0
11. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Determined number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
13. Uncertain chemical bond formation Number of structural centers: 0
14. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Keep away from oxides.
Storage method
Store in an airtight container in a cool, dry place. Store away from oxidizing agents.
Synthesis method
1. The reaction between dibutyl sulfite and sulfuryl chloride requires cooling at the beginning. The reaction device should have good reflux condensation equipment. After a large amount of sulfur dioxide is released, the temperature is then raised to 130-135°C to allow the sulfur dioxide to escape. The reaction product is distilled under reduced pressure to obtain dibutyl sulfate.
2. Preparation method:
In a stirrer, thermometer, dropping funnel, and reflux condenser (with a gas pipe connected to the top to the sulfur dioxide absorption device), add sulfite Take 625g (3.2mol) of n-butyl ester (2), cool it in a water bath, slowly add 217g (1.6mol) of sulfuryl chloride dropwise, and finish the addition in about 0.5h. After adding, slowly heat until the generated 1-chlorobutane refluxes (about 100~110℃). At this time, a large amount of sulfur dioxide escapes. Change to a distillation device for distillation, and slowly heat it to raise the internal temperature to 130-135°C until there is basically no sulfur dioxide or 1-chlorobutane steaming out. Cool to room temperature, add 100 mL of saturated sodium carbonate solution, stir thoroughly, separate the organic layer, dry with anhydrous calcium chloride, then add anhydrous sodium carbonate and leave it for 1 day. Distill under reduced pressure twice, collect the fraction at 109~111℃/0.53kPa, and obtain 250g of di-n-butyl sulfate ① (1), with a yield of 74%. Note: ① Refer to the above method and use di-n-propyl sulfite instead of di-n-butyl sulfite to prepare di-n-propyl sulfate (C6H14O4S), bp88~91℃/0.53kPa, yield 66~70%. [1]
Purpose
Organic intermediates.
