Diethanolamine Diethanolamine
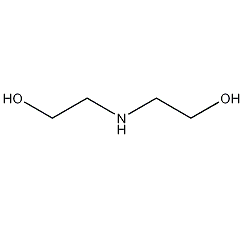

Structural formula
| Business number | 033G |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H11NO2 |
| Molecular weight | 105 |
| label |
2,2′-dihydroxydiethylamine, 2,2′-Iminodiethanol, 2,2′-Iminodiethanol, Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)amine, Dihydroxydiethylamine, Diethanolamine, 2,2′-Dihydroxydiethylamine, Aminodiethanol, 2,2′-Iminodiethanol, 2-(2-hydroxyethylamino)ethanol, DEA |
Numbering system
CAS number:111-42-2
MDL number:MFCD00002843
EINECS number:203-868-0
RTECS number:KL2975000
BRN number:605315
PubChem number:24894233
Physical property data
1. Character: colorless viscous liquid or crystal[1]
2. pH value: 11.0 (1% solution)[2]
3. Melting point (℃): 28[3]
4. Boiling point (℃): 269 ( Decomposition)[4]
5. Relative density (water = 1): 1.092[5]
6. Relative Vapor density (air=1): 3.65[6]
7. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 0.67 (138℃)[7]
8. Octanol/water partition coefficient: -1.43[8]
9. Flash point (℃): 137 (CC); 134 ( OC)[9]
10. Ignition temperature (℃): 662.2[10]
11. Explosion upper limit (%): 13.4[11]
12. Lower explosion limit (%): 1.8[12]
13. Solubility: Easily soluble in water and ethanol, insoluble in ether and benzene. [13]
Toxicological data
1. Irritation: Rabbit transdermal: 500mg/24H Slightly irritating. Rabbit eye: 750ug/24H severe irritation.
2. Acute toxicity:
Guinea pig oral LD50: 2000mg/kg; mouse oral LC50: 3300mg/kg; rat oral LD50: 1820mg/kg; rabbit oral Oral LD50: 2200mg/kg; intraperitoneal injection of mice LC50: 2300mg/kg.
3. Acute toxicity[14]
LD50: 1820mg/kg (rat Oral); 1220mg/kg (rabbit transdermal)
4. Irritation[15]
Rabbit transdermal: 500mg (24h), mild stimulation.
Rabbit eye: 5500mg, severe irritation.
5. Subacute and chronic toxicity[16] Rat oral administration: 170 mg/kg, 90 days, some animals Death, damage to certain organs.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[17]
LC50: 800mg/L (24h) (goldfish, pH Value is 9.6); >5000mg/L (24h) (goldfish, pH value is 7); 1800mg/L (24h) (bluegill sunfish); 100mg/L (96h) (fathead minnow)
EC50: 5000mg/L (5min) (photobacteria, Microtox test)
2. Biodegradability[18]
Aerobic biodegradation (h): 14.4~168
Anaerobic biodegradation (h): 57.6~672
3. Non-biodegradability[19]
Half-life of photooxidation in air (h): 0.72~7.2
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 27.24
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 98.3
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 252.7
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 43.5
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 10.80
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 3
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 4
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 52.5
7. Number of heavy atoms: 7
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 28.9
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Chemical properties: It has the chemical properties of secondary amines and alcohols. It reacts with acids to form ammonium salts, and is heated with higher fatty acids to form amides and esters. Heated with fatty acids to above 110°C to obtain amides. Reacts with aldehydes in the presence of potassium carbonate to form tertiary amines. Diethanolamine hydrochloride is heated at 220°C for a long time and dehydrated to form morpholine. Oxidation with sodium hypochlorite produces glycol aldehyde and 2-aminoethanol. Oxidation with periodic acid produces acetaldehyde and ammonia.
2. Stability[20] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[21] Acids, strong oxidants, copper, zinc
4. Conditions to avoid contact [22] Heat
p>
5. Hazards of aggregation[23] No aggregation
Storage method
Storage Precautions[24] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The packaging is sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, etc., and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Diethanolamine is obtained from the reaction of ethylene oxide and ammonia, and monoethanolamine and triethanolamine are also obtained. Send ethylene oxide and ammonia water into the reactor, perform a condensation reaction at a reaction temperature of 30-40°C and a reaction pressure of 70.9-304kPa to generate a mixed solution of mono-, di- and triethanolamine, which is dehydrated and concentrated at 90-120°C. Finally, it is sent to three vacuum distillation towers for vacuum distillation, and fractions are intercepted according to different boiling points to obtain monoethanolamine with a purity of 99%; diethanolamine and triethanolamine finished products. During the reaction process, if the proportion of ethylene oxide is increased, the proportion of di-triethanolamine generated will increase, which can increase the yield of di-triethanolamine.
Refining method: Industrial products contain less than 2% ethanolamine and triethanolamine and less than 1.5% moisture. During refining, vacuum distillation is performed first, and then ethanolamine is removed by steam distillation. Triethanolamine can be removed by adding sodium hydroxide to its aqueous solution to precipitate the alkali metal salt. Finally, vacuum distillation and purification are carried out. Be careful to prevent absorption of carbon dioxide during operation.
Purpose
1. Mainly used as acid gas absorbers such as CO2, H2S and SO2, nonionic surfactants, emulsifiers, polishes, industrial gas purifiers, and lubricants. Iminodiethanol, also known as diethanolamine, is an intermediate of the herbicide glyphosate. It is used as a gas purifier and as a raw material for synthetic drugs and organic synthesis.
2. Used as a thickener and foam improver in shampoos and light detergents, and as a softener in the production of synthetic fibers and leather. Diethanolamine reacts with 70% sulfuric acid to produce morpholine (1,4-oxazacyclohexane) through dehydration and cyclization. Morpholine and diethanolamine are both intermediates in organic synthesis. For example, they can be used to produce certain optical bleaching agents in the textile industry. Morpholine fatty acid salts can be used as preservatives. Morpholine can also be used to produce the central nervous system depressant drug Falco. fixed or used as a solvent. Diethanolamine is used in analytical chemistry as a reagent and gas chromatography stationary solution to selectively retain and separate alcohols, glycols, amines, pyridines, quinolines, piperazines, thiols, thioethers, and water.
3. Diethanolamine is an important corrosion inhibitor and can be used as a corrosion inhibitor in boiler water treatment, automobile engine coolant, drilling and cutting oil, and other types of lubricating oils. Also used in natural gas as an absorbent for purifying acid gases. Used as emulsifier in various cosmetics and pharmaceuticals. In the textile industry, it can be used as a lubricant, wetting agent, softener and other organic synthetic raw materials.
4. Used as acid absorbent, plasticizer, softener, emulsifier, etc. in adhesives. It is also used as an absorbent for acidic gases (such as hydrogen sulfide, carbon dioxide, etc.) in petroleum gas, natural gas and other gases. It is a raw material for the synthesis of medicines, pesticides, dye intermediates and surfactants. Used as an emulsifier for oils and waxes, and a softener for leather and synthetic fibers under acidic conditions. Used as a thickener and foam improver in shampoos and light detergents. It is also used as detergent, lubricant, brightener and engine piston dust remover.
5. Used as complexing agent for silver plating, cadmium plating, lead plating, zinc plating, etc.
6. Used as analytical reagents, acid gas absorbers, softeners and lubricants, and in organic synthesis. [25]
Raw materials for producing medicines, pesticides, dye intermediates and surfactants. Used as an emulsifier for oils and waxes, and a softener for leather and synthetic fibers under acidic conditions. Used as a thickener and foam improver in shampoos and light detergents. It is also used as detergent, lubricant, brightener and engine piston dust remover.
5. Used as complexing agent for silver plating, cadmium plating, lead plating, zinc plating, etc.
6. Used as analytical reagents, acid gas absorbers, softeners and lubricants, and in organic synthesis. [25]
