Glucose, monohydrate Glucose, monohydrate
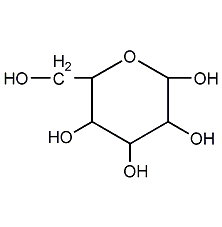

Structural formula
| Business number | 014C |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H12O6.H2O |
| Molecular weight | 198.17 |
| label |
D-glucose, glucose dextrose, dextrose, D-(+)-glucose, α-D-glucose, anhydrous glucose, D-Glucose,anhydrous, D-(+)-Dextrose, Dextrose, Japanese Pharmacopoeia |
Numbering system
CAS number:50-99-7
MDL number:MFCD00063774
EINECS number:200-075-1
RTECS number:LZ6600000
BRN number:1281608
PubChem number:24895314
Physical property data
1. Properties: White granular powder. Odorless and sweet. 2. Density (g/mL, 25/4℃): Undetermined 3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): 1.56 4. Melting point (ºC): The melting point of α-type (anhydrous) is146, and the melting point of β-type is 148~150℃. 5. Melting point (ºC): 146 d6. Crystalline phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -2802.87. Crystalline Phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -1273.38. Flash point (ºC): Undetermined
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure ( kPa, 60ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/ V): Undetermined
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Easily soluble in water, slightly soluble in alcohol and acetone, insoluble In ether.
Toxicological data
None
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 37.25
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 104.0
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 312.7
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 81.7
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 14.76
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): -2.6
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 5
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 6
p>
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers:
6. Topological molecular polar surface area (TPSA): 110
p>
7. Number of heavy atoms: 12
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 151
10. Number of isotope atoms : 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 4
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 1
13. Determine the chemical bond configuration Number of centers: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Stable under normal temperature and pressure.
Storage method
Plastic bag coated with woven bag or kraft paper bag. Store in a cool and dry place.
Synthesis method
1. Glucose is one of the most abundant compounds in nature and is a product of photosynthesis. It exists in free form in plant juices, especially in fruits, honey, plasma, and lymph. The glucose content in normal human blood is 0.08%-0.1%, and a larger amount of it exists in the form of combined sucrose, starch, glycogen, cellulose and glycosides. Initially glucose was separated and crystallized from grape juice, hence its name. Industrially produced glucose is produced by hydrolysis of starch. In the past, dilute hydrochloric acid was used to hydrolyze starch. Now, dilute hydrochloric acid is almost completely replaced by enzymatic hydrolysis.
2.Starch can be hydrolyzed to obtain glucose.
Purpose
1. Can be used as nutritional sweeteners, water retaining agents, texture improvers, molding and processing aids.
2. Can be used as reducing agent, biological culture medium and biochemical reagents.
