Isobutylamine Isobutylamine
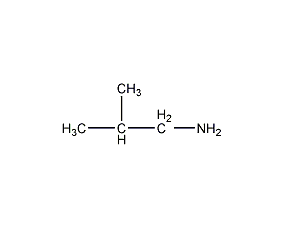
Structural formula
| Business number | 01NM |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H11N |
| Molecular weight | 73 |
| label |
1-amino-2-methylpropane, 1-Amino-2-methylpropane |
Numbering system
CAS number:78-81-9
MDL number:MFCD00008146
EINECS number:201-145-4
RTECS number:NP9900000
BRN number:385626
PubChem number:24881092
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid with ammonia odor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -85.5[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 64~71[3]
4. Relative density (water=1): 0.724 (25℃)[4]
5. Relative vapor density (air=1): 2.5[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 13.33 (18.8℃)[6 ]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -2982.8[7]
8. Critical pressure (MPa): 4.2 [8]
9. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.73[9]
10. Flash point (℃ ): -9 (CC) [10]
11. Ignition temperature (℃): 378[11]
12. Explosion upper limit (%): 12[12]
13. Explosion lower limit (%): 2[13]
14. Solubility: miscible in water, soluble in ethanol, ether, acetone, benzene, hydrocarbons, etc. [14]
15. Viscosity (mPa·s, 25ºC): 0.553
16. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, 25ºC): 33.52
17. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, b.p.): 30.80
18. Heat of generation (KJ/mol): -178.78
19. Specific heat capacity (KJ /(kg·K), 25ºC, constant pressure): 2.66
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: rat caliber LD50: 224mg/kg;
2. Strong toxicity, irritating skin and mucous membranes, causing dermatitis and blistering on contact with skin. Its vapor can cause headaches, thirst, and dry nasal mucosa.
3. Acute toxicity [15] LD50: 224mg/kg (rat oral)
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data yet
2. Biodegradability[16] MITI-I test , the initial concentration is 100ppm, the sludge concentration is 30ppm, and the degradation is 68%~87% after 2 weeks.
3. Non-biodegradability[17] In the air, when the hydroxyl radical concentration is 5.00×105 pcs/cm3, the degradation half-life is 11h (theoretical).
4. Other harmful effects [18] This substance may be harmful to the environment, so special attention should be paid to water bodies.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 24.07
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 98.6
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 217.7
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 23.7
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 9.54
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5.Number of tautomers: None
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 26
7. Number of heavy atoms: 5
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 17.6
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determined number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Uncertain number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Chemical properties: It has the chemical properties of primary amines, and its aqueous solution is alkaline. When a mixture of isobutylamine, benzene, and ammonia passes through a nickel-silica gel catalyst at 250°C under pressure, isobutyronitrile and cyclohexane are generated. Isobutylamine reacts with formaldehyde aqueous solution to generate 1,3,5-tributylcyclohexan-1,3,5-triazine.
2. Stability[19] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[20] Strong oxidants, acids
4. Polymerization hazard[21] No polymerization
Storage method
Storage Precautions[22] Stored in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 37℃. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants and acids, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. The alcohol produced by catalytic dehydration of isobutanol and ammonia can be mixed with primary, secondary and tertiary amines after ammonolysis reaction. The ratio of the three amines is related to the raw materials, catalyst and reaction conditions. By adjusting the ratio of alcohol and ammonia and the reaction conditions, the desired product ratio can be obtained.
![]()
2. From isobutyraldehyde and Ammonia is produced by catalytic hydrogenation.
![]()
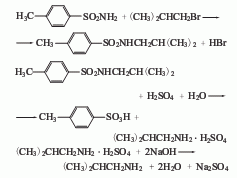
3. Substitute isobutyl bromide Alkane and p-toluenesulfonamide are used as raw materials and are obtained through condensation and hydrolysis. First, reflux p-toluenesulfonamide, isobutane bromide and ethanol alkali solution together for 4 hours, recover ethanol until crystallization appears, and then neutralize with hydrochloric acid, a large amount of light yellow crystals will precipitate, filter and wash with water to obtain a condensate. After mixing the condensate, sulfuric acid and water and heating to reflux for 10 hours, change to a distillation device, add 40% liquid caustic soda to adjust to alkalinity, then evaporate the crude amine under reduced pressure, and then collect the 66.8-68.8°C fraction through crude distillation to become the finished product.

Refining method: Isobutylamine is It is prepared by reacting chloroisobutane with ammonia, or by reducing the nitro compound of isobutane with iron and hydrochloric acid or by catalytic reduction. Therefore, it often contains impurities such as chloroisobutane, ammonia, and diisobutylamine. It is usually refined by distillation. The isobutylamine salt or its adduct may also be recrystallized and purified.
Purpose
Used in organic synthesis and the manufacture of pesticides. [23]
