Linalool Linalool

Structural formula
| Business number | 01ND |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C10H18O |
| Molecular weight | 154.25 |
| label |
Linalool; corianol; linalol; linalol; galoxylinol; 3,7-dimethyl-1,6-octadien-3-ol, Linalool, Coriander alcohol, Incense oil terpene alcohol, (R,S)-Linalool, 3,7-Dimethyl-1,6-octadien-3-ol, Phantol, Petitgrainol, artificial flavors, alcohol solvent |
Numbering system
CAS number:78-70-6
MDL number:MFCD00008906
EINECS number:201-134-4
RTECS number:RG5775000
BRN number:1721488
PubChem number:24882195
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid 2. Density (g/mL, 25/4℃): dl 0.865, d 0.8733, l 0.8622
3. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 0.8733
4. Refractive index at room temperature (n20D) : 1.4673
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 199
6. Boiling point (ºC, 5.2kPa): dl 194 ~197℃ (95.99kPa), d 198~200℃, l 198℃
7. Refractive index: d 1.4673, l 1.4604
8. Flash point (ºC): 80
9. Specific rotation (º): [α]D20 d+19.3°, l -20.1°
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11 . Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturation vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Oil and water (octanol/water) Log value of distribution coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Miscible with ethanol and ether, insoluble in water and glycerin.
Toxicological data
This product has low toxicity, rat oral LD50: 2790mg/kg
Ecological data
None yet
Molecular structure data
None yet
Calculate chemical numbers�
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 2.7
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 4
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 20.2
7. Number of heavy atoms: 11
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 154
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 1
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Found in flue-cured tobacco leaves and burley tobacco leaves.
2. The L-body is found in essential oils such as linoleum oil, sassafras oil, bergamot oil, lavender oil, and rosewood oil. The dextrorotary body exists in coriandercoriander seed oil and neroli oil. Orange leaf oil, sweet orange oil. The racemate exists in aromatic perilla oil and jasmine oil.
3. The mixture of left- and right-handed isomers in Brazilian rosewood oil is as high as 85%.
Storage method
Packed in plastic buckets to prevent evaporation and stored in a cool and ventilated place.
Synthesis method
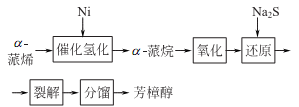
1. Alcohol exists in a variety of essential oils. There are currently two main methods for preparing linalool. One is to separate it from plant essential oils such as linalool, and the main product obtained is the left-handed isomer; the other method is to prepare it from pinene.

2. Tobacco: BU, 56; BU, 14; FC, BU, OR, 18; FC, 40. Synthesis: isolated from natural essential oils; myrcene reacts with hydrogen chloride to generate chloromyrcene, which is hydrolyzed to generate linalool; isoprene reacts with hydrogen chloride to generate chloroisopentene, and then reacts with acetone to generate methylheptene Ketone reacts with acetylene to form dehydrogenated linalool, which is finally hydrogenated to form linalool.
Purpose
It is an important spice and a raw material for blending various artificial essential oils. It is also widely used in the manufacture of various esters of linalool. Linalool and its esters play an important role in the formulation of perfumes and other cosmetics, and are used to prepare floral flavors such as lily, orange blossom, and lilac. Also used as soap flavoring agent.
