m-Xylene m-Xylene
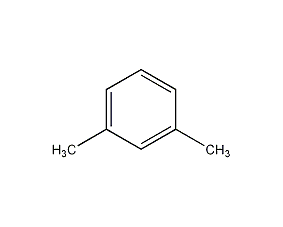

Structural formula
| Business number | 02X0 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C8H10 |
| Molecular weight | 106 |
| label |
1,3-dimethylbenzene, 1,3-xylene, 1,3-Dimethylbenzene, 1,3-xylene, m-Dimethylbenzene, aromatic compounds |
Numbering system
CAS number:108-38-3
MDL number:MFCD00008536
EINECS number:203-576-3
RTECS number:ZE2275000
BRN number:605441
PubChem number:24890183
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless transparent liquid with an odor similar to toluene. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -47.9[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 139[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.86[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 3.66[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 1.33 (28.3℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -4830.7[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 346[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 3.54[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 3.2 [10]
11. Flash point (℃): 25 (CC) [11]
12. Ignition temperature (℃) ): 527[12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 7[13]
14. Explosion lower limit (%): 1.1[14]
15. Solubility: Insoluble in water, miscible in most organic solvents such as ethanol, ether, and chloroform. [15]
16. Viscosity (mPa·s, 25ºC): 0.579
17. Flash point (ºC): 528
18. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, 101.3kPa): 36.38
19. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, 1.1kPa): 42.68
20. Heat of fusion (KJ/ mol, 101.3kPa): 11.58
21. Heat of formation (KJ/mol, 25ºC, gas): 17.250
22. Heat of formation (KJ/mol, 25ºC, liquid): -25.43
23. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol, 25ºC, gas): 4597.60
24. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol, 25ºC, liquid): 4554.90
25. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 25ºC, constant pressure): 1.20
26. Thermal conductivity (W/(m·K), 20≤t<55ºC): (0.1368~2.3957)×10-4 t
27. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 0.8642
28. Refractive index at room temperature ( n20): 1.4972
29. Critical density (g·cm-3): 0.283
30. Critical volume (cm3·mol-1): 375
31. Critical compression factor: 0.259
32. Eccentricity factor: 0.326
33. Lennard-Jones parameter (A): 15.94
34. Lennard-Jones parameter (K): 162.6
35. Solubility parameter ( J·cm-3)0.5:18.090
36. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 8.840×109
37. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1 ): 70.660
38. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -4594.53
39. Gas phase Standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): 17.32
40. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·KStorage method
Storage Precautions[30] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 37°C. Keep container tightly sealed. should be kept away from oxidizer, do not store together. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Its preparation method is to use petroleum xylene or coal tar xylene to separate. The separation method can be low-temperature crystallization, compounding, adsorption, sulfonation hydrolysis, etc. In China, m-xylene was produced by sulfonation hydrolysis in the past, but now adsorption method is used to separate m-xylene. The adsorption method uses molecular sieve as the adsorbent, which can be used for gas phase adsorption or liquid phase adsorption. The process is described below.
(1) Sulfonation hydrolysis method: Distillate the mixed xylene to cut the 130-140°C fraction, then add sulfonation with sulfuric acid, the reaction temperature is 80-90°C, the reaction time is 3.5h, and then the sulfonate is separated The xylene is converted into xylene, then hydrolyzed and distilled, and the 140-150°C fraction is cut to obtain the finished product. This method severely corrodes the equipment and produces a lot of three wastes. It can only be produced on a small scale, so it was replaced by the adsorption method.
(2) Adsorption method: Use molecular sieves for liquid phase adsorption or gas phase adsorption. Liquid phase adsorption uses K-Ba-Y type as the adsorbent and toluene as the desorbent. Continuous adsorption separation is performed on a moving bed. Operation The temperature is 65~85℃, the ratio of adsorbent to raw material is not greater than 10, and the ratio of desorbent to raw material is greater than 5. Gas phase adsorption also uses K-Ba-Y molecular sieve as the adsorbent, the adsorption temperature is 170~180°C, and the operating pressure is normal pressure. Adsorption separation method is a new method for separating xylene in modern times.
2. Industrial preparation: It is made by fractionating the light oil part of coal tar, catalytic reforming light oil, or disproportionation of toluene.
Purpose
1. Used in the production of isophthalic acid, m-toluic acid, isophthalonitrile, etc., and can also be used as raw materials for medicines, dyes, spices, and color film couplers.
2. In addition to being used as solvents and organic synthesis, it is also used as raw materials for pharmaceuticals, spices and dye intermediates and as oil-soluble couplers for color movies. Also used as a raw material for the manufacture of isophthalic acid. However, compared with the ortho- and para-position isomers, the required amount is smaller, so it is often converted into other isomers through isomerization.
3. Used as solvents, medicines, dye intermediates, spices, etc. [31]
