Methyl benzoate Methyl benzoate
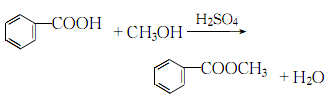
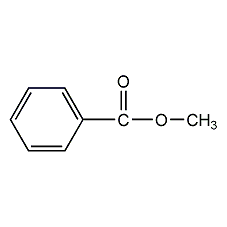
Structural formula
| Business number | 026J |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C8H8O2 |
| Molecular weight | 136.15 |
| label |
Methyl benzoate, Benzoic acid methyl ester, Oil of Niobe, Methyl benzenecarboxylate, essence |
Numbering system
CAS number:93-58-3
MDL number:MFCD00008421
EINECS number:202-259-7
RTECS number:DH3850000
BRN number:1072099
PubChem number:24851053
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless and transparent oily liquid with aromatic smell. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -12.3[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 198[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 1.09[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 4.68[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 0.13 (39℃)[6]
7. Critical pressure (MPa): 3.59[7]
8. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 2.12[8]
9. Flash point (℃): 82.8 (CC) [9]
10. Ignition temperature (℃): 505[10]
11. Explosion upper limit (%): 6.7[11]
12. Explosion lower limit (%): 1.2 [12]
13. Solubility: Insoluble in water, miscible in methanol, ethanol, and ether. [13]
14. Refractive index (16ºC): 1.5164
15. Viscosity (mPa·s, 15ºC): 2.298
16. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, 25ºC): 57.0
17. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol): 9.7
18. Heat of generation (KJ/mol): 3949
19. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): 3952.2
20. Thermal conductivity (W/(m·K)): 0.01468
21 .Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 20ºC, constant pressure): 1.60
22. Conductivity (S/m, 22ºC): 1.37×10-5
23. Volume expansion coefficient (K-1): 0.000876
24. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 1.0885
25. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 1.0838
26. Refractive index at normal temperature (n20): 1.5168
27. Normal temperature Refractive index (n25): 1.5146
28. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 20.476
29.van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 9.530×109
30.van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 73.910
31. Gas phase standard heat of combustion (enthalpy )(kJ·mol-1): -4003.46
32. Gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): – 287.98
33. Liquid phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -3947.90
34. Liquid phase standard claimed heat ( Enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -343.55
35. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 214.2
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[14]
LD50: 1117mg/kg (rat oral); 3330mg/kg (mouse oral Oral); 2170mg/kg (rabbit oral)
2. Irritation No data available
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[15]
EC50: 4.6mg/L (30min) (Microtox toxicity test).
2. Biodegradability No data yet
3. Non-biodegradability[16 ] When the pH value is 7 and 9, the hydrolysis half-life is 2.8a and 10d respectively.
In the air, when the concentration of hydroxyl radicals is 5.00×105/cm3, the degradation half-life is 18.5d (theoretical).
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 38.02
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 127.3
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 312.1
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 36.1
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 15.07
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 26.3
7. Number of heavy atoms: 10
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 114
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Chemical properties: Methyl benzoate is relatively stable, but it hydrolyzes to produce benzoic acid and methanol when heated in the presence of caustic alkali. There is no change when heated at 380~400℃ for 8 hours in a sealed tube. When pyrolyzed on a hot metal mesh, benzene, biphenyl, phenyl methyl benzoate, etc. are produced. Hydrogenation at 10MPa and 350℃ produces toluene. Methyl benzoate undergoes a transesterification reaction with primary alcohols in the presence of alkali metal ethanolates. For example, when reacting with ethanol at room temperature, 94% becomes ethyl benzoate; when reacting with propanol, 84% becomes propyl benzoate. Does not transesterify with isopropyl alcohol. Benzyl alcohol ester and ethylene glycol use chloroform as the solvent, and when a small amount of potassium carbonate is added and refluxed, ethylene glycol benzoate and a small amount of ethylene glycol diphenyl alcohol ester are obtained. When methyl benzoate and glycerin are heated in the presence of sodium methoxide using pyridine as the solvent, they can also undergo a transesterification reaction to obtain the benzoate ester of glycerol.
2. Benzyl alcohol methyl ester is nitrated with nitric acid (relative density 1.517) at room temperature to obtain 3-nitrobenzoic acid methyl ester and 4-nitrobenzoic acid methyl ester in a ratio of 2:1 . Using thorium oxide as a catalyst, it reacts with ammonia at 450-480°C to form benzonitrile. Heated with phosphorus pentachloride to 160~180℃ to obtain benzoyl chloride.
3. Methyl benzoate forms crystalline molecular compounds with aluminum trichloride and tin chloride, and forms flaky crystalline compounds with phosphoric acid.
4. Stability[17] Stable
5. Incompatible substances[18] Strong oxidizing agent, strong alkali
6. Polymerization hazard[19] No polymerization
Storage method
Storage Precautions[20] Stored in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature does not exceed 35°C and the relative humidity does not exceed 85%. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, alkalis, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. Methyl benzoate is found in natural clove oil, ylang-ylang oil and moonseed oil, and can be distilled and extracted from essential oils. Industrial production is produced by the esterification reaction of benzoic acid and methanol in the presence of sulfuric acid. Mix benzoic acid and methanol, slowly add concentrated sulfuric acid, heat to about 70°C and reflux for 4 hours, and evaporate excess methanol. Cool, separate the acid liquid, wash, dry, and distill under reduced pressure. Collect the 104-105°C (5.2kPa) fraction as the finished product. The yield is above 90%.
Refining method: often contains impurities such as free benzoic acid and methanol. During refining, wash with sodium bicarbonate or potassium carbonate solution, dry with anhydrous potassium carbonate or sodium sulfate and then distill. 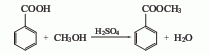
2. Put benzoic acid and methanol into the container , slowly add sulfuric acid while stirring, heat for 12 hours, and react:
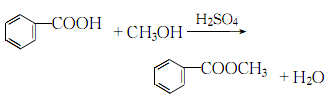
After the reaction, methanol is recovered, washed, dried, and distilled under reduced pressure to obtain the finished product.
Purpose
1. Used as a spice, with a strong aroma of wintergreen oil and cananga oil, used to prepare artificial ylang-ylang oil and moonseed oil for soaps and cosmetics.
2. Food flavors, used to prepare strawberry, pineapple, cherry, rum and other flavors.
3. Used to prepare rose-type, geranium-type essences, etc., and also used as a solvent for cellulose ester, cellulose ether, resin, rubber, etc.
4. Used in baked goods, frozen dairy products, and puddings.
5. Used in perfume industry and as solvent. [21]
