n-Butene 1-Butene

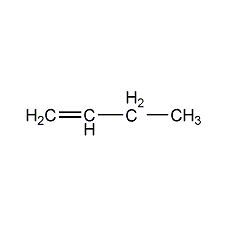
Structural formula
| Business number | 02UC |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H8 |
| Molecular weight | 56.11 |
| label |
1-butene, Ethylethylene, α-Butene, Ethylethylene, Aliphatic hydrocarbons |
Numbering system
CAS number:106-98-9
MDL number:MFCD00009383
EINECS number:203-449-2
RTECS number:None
BRN number:1098262
PubChem number:24851449
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless and odorless compressed or liquefied gas. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -185.3[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): -6.47[3]
4. Relative density (water=1): 0.577 (25℃)[4]
5. Relative vapor density (air=1): 1.93[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 299.3 (25℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -2719.1[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 146.6[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 4.023[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient :2.40[10]
11. Flash point (℃): -80 (CC)[11]
12 .Ignition temperature (℃): 385[12]
13. Explosion limit (%): 10.0[13]
14. Lower explosion limit (%): 1.6[14]
15. Solubility: insoluble in water, slightly soluble in benzene, easily soluble in ethanol and ether. [15]
16. Lennard-Jones parameter (A): 7.142
17. Lennard-Jones parameter (K): 209.6
18. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5: 13.748
19. van der Waals area (cm 2·mol-1): 6.410×109
20. van der Waals volume (cm3 sup>·mol-1): 44.310
21. Critical density (g·cm-3): 0.233
22. Critical volume (cm3·mol-1): 240.8
23. Critical compression factor: 0.2775
24 .Eccentricity factor: 0.187
25. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -2716.8
26. Gas phase standard claim Heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -0.5
27. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 307.86
28. Gas phase standard free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1): 70.4
29. Gas phase Standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 85.56
30. Liquid phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ· mol-1): -2737.4
31. Liquid phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -21.1
32. Liquid phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 229.06
33. Liquid phase standard Free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1): 73.2
34. Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 128.9
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[16]
LC50: 420000mg/m3 (mouse inhalation, 2h )
2. Irritation No data available
3. Subacute and chronicSex [17] Mice inhaled 6% of this product 20 times. After execution, autopsy showed irritating lesions in the bronchus and bone marrow. When rats inhale 100 mg/m3 for 140 days (continuously), blood cholinesterase activity decreases and the total number of white blood cells decreases.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data available
2. Biodegradability No data available
3 .Non-biodegradability[18] In the air, when the concentration of hydroxyl radicals is 5.00×105/cm3 When, the degradation half-life is 12h (theoretical).
4. Other harmful effects [19] This substance may be harmful to the environment, so special attention should be paid to fish. Special attention should also be paid to contamination of surface water, soil, atmosphere and drinking water.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 20.30
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 89.6
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 180.2
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 16.3
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 8.04
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 0
7. Number of heavy atoms: 4
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 14
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. It is not listed as toxic substances, but it has certain suffocation and anesthesia effects. The maximum allowable concentration in the workplace is 100mg/m3. Pay attention to ventilation and prevent air leakage. The explosion limit in air is 1.6~1.7 (volume). Acts as an anesthetic in high concentrations. Its toxicity is about 4.5 times that of ethylene. Skin contact with liquid 1-butene will cause frostbite. Symptoms such as shortness of breath, slowness, muscle imbalance, errors in judgment, fatigue, nausea, and vomiting may occur after inhalation.
2. Stability[20] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[21] Strong oxidants, strong acids, peroxyacids, halogens
4. Conditions to avoid contact[22] Heat
5. Aggregation hazards[23] Aggregation
Storage method
Storage Precautions[24] Stored in a cool, ventilated warehouse dedicated to flammable gases. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 30℃. They should be stored separately from oxidants and acids, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with leakage emergency response equipment.
Synthesis method
1. C4 fractions obtained from catalytic cracking of natural gas, refinery gas and petroleum fractions, and cracking of petroleum hydrocarbons all contain various isomers of butene. After separation, they can be Obtain 1-butene, cis-2-butene, trans-2-butene, isobutene, etc. Use 50% sulfuric acid to extract the isobutene
ene in the C4 fraction. First, the C4 fraction is mixed with sulfuric acid, esterified into tert-butyl hydrogen sulfate, and heated and hydrolyzed to obtain isobutylene and tert-butyl alcohol. Isobutylene is then washed with alkali, water, compressed and distilled to obtain isobutylene with a purity of more than 98%. Tert-butyl alcohol is dehydrated under heating to obtain isobutyleneIn addition, n-butyl alcohol is used Dehydration of alcohol and isobutanol or dehydrogenation of n-butane and isobutane, dehydration of tert-butanol, etc. can produce the corresponding 1-butene, cis and trans 2-butene, isobutene, etc.
2. Methyl tert-butyl ether decomposition method is currently the main method for producing isobutylene. 
The isobutylene in the mixed C4 is selectively etherified with methanol under the action of a catalyst to generate methyl tert-butyl ether. After further decomposition, high-purity isobutylene can be obtained.
3.Using industrial 1-butene (97% content) as raw material, it is dried on silica gel and then sent to the low-temperature distillation tower . The raw material gas is condensed and liquefied by liquid nitrogen refrigerant in the distillation kettle and then fractionated. It can be purified by batch distillation.
Purpose
1. Butene is one of the important basic chemical raw materials. 1-Butene is the raw material for the synthesis of sec-butanol and dehydrogenation to produce butadiene; cis and trans-2-butene are used to synthesize C4 and C5 derivatives and prepare cross-linking agents, superimposed gasoline, etc.; isoene is used in the manufacture of The raw material of butyl rubber and polyisobutylene rubber reacts with formaldehyde to produce isoprene, which can be made into polyisobutylene polymers of different molecular weights for use as lubricant additives, resins, etc. It can be hydrated to produce tert-butyl alcohol and oxidized to produce organic glass. Monomer methyl methacrylate. In addition, isobutylene is also a raw material for antioxidant tert-butyl-p-cresol, epoxy resin and organic synthesis.
2. Used as standard gas and preparation of special standard mixed gas.
3. Used to make butadiene, isoprene, synthetic rubber, etc. [25]
Butanol, methyl methacrylate, a monomer used to oxidize organic glass. In addition, isobutylene is also a raw material for antioxidant tert-butyl-p-cresol, epoxy resin and organic synthesis.
2. Used as standard gas and preparation of special standard mixed gas.
3. Used to make butadiene, isoprene, synthetic rubber, etc. [25]
