n-Butyllithium n-Butyllithium
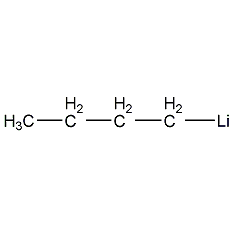
Structural formula
| Business number | 02ZL |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H9Li |
| Molecular weight | 64.05 |
| label |
n-Butyllithium, Solar cell chemicals |
Numbering system
CAS number:109-72-8
MDL number:MFCD00009414
EINECS number:203-698-7
RTECS number:None
BRN number:1209227
PubChem number:24858234
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless to yellow transparent liquid, ignites when exposed to air. [15]
2. Melting point (℃): -76[16]
3. Boiling point (℃): 80~90 (0.0133Pa)[17]
4. Flash point (℃): -12[18]
5. Solubility: Insoluble in water, soluble in pentane, hexane, cyclohexane, benzene, ethers and hydrocarbons. [19]
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity No data available
2. Irritation No data available
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data available
2. Biodegradability No data available
3 .Non-biodegradability No information available
Molecular structure data
None yet
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 0
7. Number of heavy atoms: 5
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 7.6
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 2
Properties and stability
1. n-Butyllithium solution is prone to fire when exposed to air or moisture. The operation of n-butyllithium should be carried out after being isolated from water vapor and O2, and safety equipment such as goggles and anti-corrosion gloves should be worn. Once a fire breaks out, use a dry powder fire extinguisher to extinguish it. Never use fire extinguishers containing water or chlorinated alkanes. Reactions involving n-butyllithium should be protected by nitrogen or argon gas that is isolated from air and moisture. Care must be taken when using it.
2. Stability[20] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[21] Acids, alcohols, water, air, halogens and amines
4. Conditions to avoid contact [22] Humid air
5. Polymerization hazard[23] No polymerization
6. Decomposition products[24] Lithium oxide
Storage method
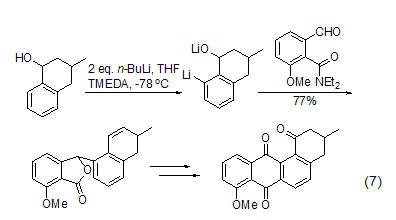
Storage Precautions[25] Store in a cool, dry and well-ventilated dedicated warehouse, away from fire.�OMe, C=NR, SO2NR2 and other groups can promote the ortho-position lithiation reaction on the aromatic ring. This ortho-position lithiation reaction is used in the synthesis of It has very important uses (Formula 7)[8].
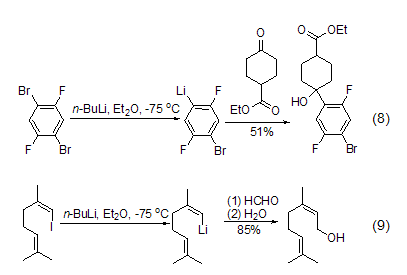
Another version of n-butyllithium An important reaction is the lithium-halogen exchange reaction with halogenated organic substrates. This is a very important method for obtaining organolithium compounds in organic synthesis, especially aryllithium, vinyllithium and cyclopropyllithium. The synthesis is very useful. The activity of the exchange reaction with halogen substituents decreases according to I > Br > Cl > F. Aromatic hydrocarbons containing fluorine substituents basically do not react with n-butyllithium (Formula 8)[9]. For iodide, it is easy to interact with n-butyllithium to undergo lithium halide exchange, and then react with electrophiles such as aldehydes or ketones to obtain addition products (Equation 9).
In addition to the lithium halide exchange reaction, n-Butyllithium can also easily interact with other organometallic reagents containing tin, selenium, tellurium or mercury to cause transfer metallization reactions. The reaction is usually carried out at low temperature and in ether solvents. Among them, the tin-lithium exchange reaction is the most important in synthesis and can be used to synthesize aryl and vinyl lithium compounds (Formula 10, Formula 11)[10,11].
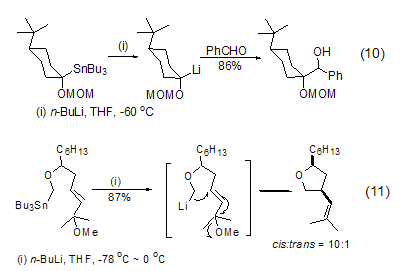
Including benzyl, vinyl, Many organolithium reagents, including alkynyl and lithium alkoxides, can also be obtained through Li-Te exchange reaction (Formula 12)[12]. 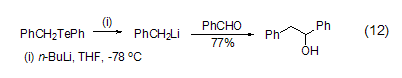
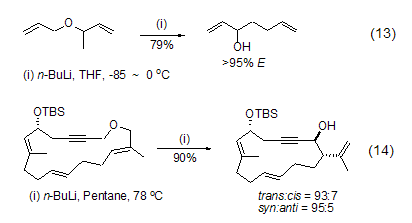
N-butyllithium is also often used in anion rearrangement reactions. For example, allyl ether or propargyl ether undergoes 2,3-Wittig rearrangement under the action of n-butyllithium. The reaction usually first obtains anions through α-deprotonation reaction or Li-Sn exchange reaction at low temperature, and then the temperature is raised to cause intramolecular rearrangement (Formula 13, Formula 14)[13,14 ].

4. Used as polymerization catalyst, Alkylating agent, rocket fuel, etc. [26]
