p-Aminophenylarsonic acid p-Arsanilic acid
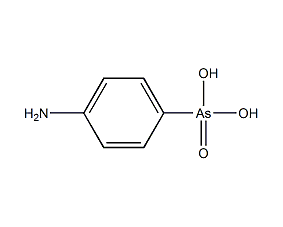
Structural formula
| Business number | 02DY |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H8AsNO3 |
| Molecular weight | 217.06 |
| label |
4-Aminophenylarsonic acid, Arsonic acid aniline, For asan acid, aminoarsinic acid, 4-Aminobenzenearsonic acid, 4-Aminophenylarsonic acid, Aminobenzenearsonic acid, antibacterial growth promoter |
Numbering system
CAS number:98-50-0
MDL number:MFCD00007819
EINECS number:202-674-3
RTECS number:CF7875000
BRN number:1102334
PubChem number:24891428
Physical property data
1. Properties: White, odorless crystalline powder.
2. Density (g/mL, 25℃): Undetermined
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 232
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): Undetermined
6. Boiling point (ºC, kPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive index: Undetermined
8. Flash point (ºC): Undetermined
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Not determined
11. Vapor pressure (mmHg, 40ºC): Not determined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa , 20ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15 . Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) distribution coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V ): Undetermined
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: soluble in hot water, slightly soluble in cold water, ethanol, acetic acid , insoluble in acetone, ether, benzene and chloroform.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: Rat oral LD50: 220mg/kg
Ecological data
This substance is slightly hazardous to water.
Molecular structure data
None
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP):
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 3
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 4
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers:
6. Topological molecular polar surface area (TPSA): 83.6
7. Number of heavy atoms: 11
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 171
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11 , Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Avoid contact with strong oxidizing agents.
Storage method
Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The packaging is sealed. should be kept away from oxidizer, do not store together. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
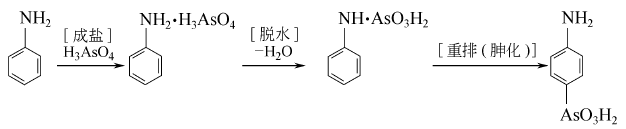
1. Obtained from the reduction of p-nitrophenylarsonic acid. Use sulfuric acid to adjust the pH value of p-nitrophenylarsonic acid solution to 2.8-3.2. First, add 1/3 volume of p-nitrophenylarsonic acid solution to the reaction pot, add iron powder and salt while stirring, heat to 100°C, and keep for 10-15 minutes. The pH will be above 9 when reaching the end point. At 95-100℃, add the remaining 2/3 volume of p-nitrophenylarsonic acid solution within 0.5h, and continue to incubate at 100℃ for 40-50min. The pH at the end point is above 9. Add liquid caustic soda and leave it for more than 3 hours. Filter, and adjust the pH value of the filtrate to 4.5 with sulfuric acid. Add activated carbon, decolorize and filter at 50-90°C, adjust the filtrate with sulfuric acid to pH 2.8-3.2, and cool to 10°C. Filter and wash to obtain p-aminophenylarsonic acid. Industrial production uses aniline and potassium pentoxide as raw materials, and the product purity is over 98.5%.
2. (1) Synthesis using aniline and arsine pentoxide as raw materials.
(2) React aniline and arsinic acid to first generate aniline arsinate, and then dehydrate and rearrange to obtain p-aminophenylarsinic acid.
Put 74.5g of aniline and 6.0g of tetrachlorethylene, heat it up to 125°C, add 0.5g of EDTA, and then add dropwise 36g of arsenic acid aqueous solution. With the addition of arsenic acid, the water solvent produced azeotropically evaporates, and the reaction temperature gradually When the temperature rises to 175°C, the reaction tends to end. Continue to reflux for 1 hour to stop the reaction. After the reaction solution is cooled, adjust the pH to 9 with 10%-15% alkali solution, then stir at 90°C for 1 hour. After layering, the aqueous layer is decolorized with activated carbon, and the solvent is removed by steam distillation. Use hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH of the filtrate to 2, and then reflux at 104°C for 8 hours. After the hydrolysis is completed, adjust the pH to 2-2.5 and let it stand for filtration to obtain a crude product. The mother liquor can be recycled. Dissolve the crude product with 4 times the amount of water, add activated carbon, adjust PH=8, decolorize at 100°C for 30 minutes and filter while hot. Adjust the pH of the filtrate to 3 and let it stand to precipitate the product.
The process route of this method is simple and the raw materials are easily available. However, due to the low activity of the arsine reaction, many by-products, many post-reaction treatment steps, and the single-pass yield is low.
(3) It is obtained from p-nitroaniline through diazotization, arsylation (displacement) and reduction.
Add 281.8g of p-nitroaniline and 352.8g of industrial hydrochloric acid into the reactor and stir at room temperature to fully form salt. After cooling to 0°C, add 30% sodium nitrite aqueous solution dropwise, control the temperature not to exceed 10°C, and check the end point of the diazotization reaction with starch-KI test paper.
Place 323g AsO3 and 30% sodium nitrate solution in the reactor, heat and stir until they are completely dissolved, and boil for 0.5h. Cool to 10°C, add a few drops of CuSO4 solution, and then slowly add the diazonium salt solution under stirring to react to form a nitrobenzene arsenic acid solution, and control the temperature not to exceed 30°C.
Use sulfuric acid to adjust the pH of the p-nitrophenylarsonic acid solution to 2.8-3.2, add 328.1g reduced iron powder and 140g salt, and heat to micro reflux (110°C) for 2 hours. After cooling down slightly, add 164g of iron powder and react under reflux until pH=9. After the reaction is completed (slightly cooled), add 200g of 30% NaOH solution, let it sit for 5 hours and then filter. Adjust the pH of the filtrate to 4.5 with industrial dilute sulfuric acid, add activated carbon, decolorize at 80-90°C (20 min), and filter. Adjust the pH of the filtrate to 2.8-3.2 with sulfuric acid, cool to 10°C, filter and wash to obtain crude product.
Heat and dissolve the crude product, a small amount of antioxidants and 8 times the amount of deionized water, add a small amount of medical activated carbon to reflux and decolorize, filter while hot, cool the filtrate to 5°C to precipitate crystals, filter and dry to obtain the finished product. The total yield is 52% (relative to p-nitroaniline).
4.Add arsinic acid to chlorobenzene and stir at 140°C. Pour nitrogen into the reaction liquid layer. Add aniline dropwise and raise the temperature to 155°C. Maintain React at this temperature, and the mixed vapor of water, chlorobenzene and aniline evaporated during the reaction, react for 12 hours. Pour the above reaction solution into sodium hydroxide, vacuum evaporate the chlorobenzene and unreacted aniline, cool it after evaporation, add water and mix well, let it stand for cooling and filter, and use the filtrate Adjust pH=4.5 with hydrochloric acid, stir and cool to room temperature, and filter to obtain the product. 
Purpose
1. Used in pharmaceutical manufacturing and as reagents for the determination of ammonium, cerium and zirconium.
2.Feed antibiotics. It can promote the growth of livestock and poultry and improve feed efficiency. It has the effect of killing bacteria, protozoa and spirochetes. It is mainly used to treat bacterial infections in poultry and promotes the growth of pigs and chickens.
3.is a fully synthetic antibacterial agent. It is a legal feed additive approved by the US FDA.
