p-Cresol p-Cresol
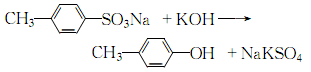
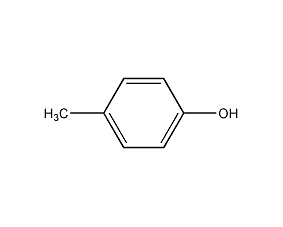
Structural formula
| Business number | 02TG |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C7H8O |
| Molecular weight | 108.14 |
| label |
p-cresol, p-methylphenol, To Kreisseur, 2-methylphenol, 4-Cresol, 1-hydroxy-4-methylbenzene, 1-Methyl-4-hydroxybenzene, 4-Cresol, 4-Methyl-phenol, 4-Methylphenol |
Numbering system
CAS number:106-44-5
MDL number:MFCD00002376
EINECS number:203-398-6
RTECS number:GO6475000
BRN number:1305151
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Characteristics: colorless crystals with aromatic odor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): 35.5[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 201.8 [3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 1.039[4]
5. Relative vapor density (Air=1): 3.72[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 0.13 (53℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -3695.1[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 431.6[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 5.51[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.94[ 10]
11. Flash point (℃): 86 (CC) [11]
12. Ignition temperature (℃) :559[12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 1.1 (150℃)[13]
14 .Lower explosion limit (%): 7.6[14]
15. Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, soluble in ethanol, ether, chloroform, alkali, etc. [15]
16. Viscosity (mPa·s, 20ºC): 18.95
17. Heat of evaporation (KJ/kg, b.p.): 438.9
18. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol): 12.27
19. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 9~28ºC, constant pressure): 2.04
20. Conductivity (S/m, 25ºC): 1.378×10-8
21. Solubility (%, 25ºC, water): 2.1
22. Refractive index at room temperature (n25): 1.531640
23. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 1.017941
24. Eccentricity factor: 0.513
25. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -3772.55
26. Gas phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -125.35
27. Gas phase standard entropy (J· mol-1·K-1): 350.86
28. Gas phase standard free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1): -31.5
29. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 124.97
30. Crystal phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -3698.61
31. Crystal phase standard claim heat (enthalpy) (kJ· mol-1): -199.28
32. Crystal phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 167.2
33. Crystal phase standard formation free energy (kJ·mol-1): -50.96
34. Crystal phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·KAfter the toluene and water are evaporated, the 93-104°C fraction is cut at a vacuum of 0.094 MPa to obtain p-cresol with a purity of 95%.
(2) Toluidine diazo hydrolysis method
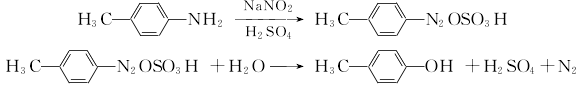 P-toluidine and sulfuric acid produce p-toluidine sulfate, which is diazotized with sodium nitrite at 0 to 5°C. The diazonium salt is then heated and hydrolyzed in dilute sulfuric acid, and the oil is separated with steam. Separate the oil layer and add it to 1% sodium hydroxide, then decolorize and filter, add concentrated sulfuric acid to pH=1, then separate the water layer, add zinc powder and sulfuric acid, neutralize with sodium carbonate until neutral, and separate. The oily substance is washed with water and then distilled under reduced pressure to obtain the finished product.
P-toluidine and sulfuric acid produce p-toluidine sulfate, which is diazotized with sodium nitrite at 0 to 5°C. The diazonium salt is then heated and hydrolyzed in dilute sulfuric acid, and the oil is separated with steam. Separate the oil layer and add it to 1% sodium hydroxide, then decolorize and filter, add concentrated sulfuric acid to pH=1, then separate the water layer, add zinc powder and sulfuric acid, neutralize with sodium carbonate until neutral, and separate. The oily substance is washed with water and then distilled under reduced pressure to obtain the finished product.
(3) It can be obtained by alkali melting sodium p-toluenesulfonate and then acidification.
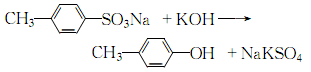
Purpose
1.GB 2760–1996 stipulates that edible spices are allowed to be used. It is used in organic synthesis and is also a raw material for the manufacture of antioxidant 2,6-di-tert-butyl-p-cresol and rubber antioxidant. At the same time, it is an important basic raw material for the production of pharmaceutical TMP and dye colicidine sulfonic acid.
2. Used as analytical reagent. Used in organic synthesis. Also used as a fungicide and antifungal agent.
3. Mainly used in adhesives to make phenolic resin. It is also used as a raw material for the antioxidant 2,6-di-tert-butyl-p-cresol. It is used as a disinfectant in medicine, and trimethoxybenzaldehyde is used as a synergist in the synthesis of sulfa drugs. In addition, it can also be used to make paints, plasticizers, flotation agents, cresolic acid dyes and pesticides, etc.
4. Used in organic synthesis and as fungicides and fungicides. [28]
